代码、内容参考来自于包括《操作系统真象还原》、《一个64位操作系统的设计与实现》以及《ORANGE’S:一个操作系统的实现》。
1.获取当前目录
linux可以通过pwd获取当前目录
在任何目录中都有目录项”..”,它表示父目录。 先通过”..”获取当前目录的父目录,在父目录中搜索当前目录的目录项,从目录项中获取当前目录名称,然后再向上找父目录的父目录,沿着目录树层层而上,就能构建出当前目录的绝对路径。
修改fs/fs.c
/* 获得父目录的inode编号 */
static uint32_t get_parent_dir_inode_nr(uint32_t child_inode_nr, void* io_buf) {
struct inode* child_dir_inode = inode_open(cur_part, child_inode_nr);
/* 目录中的目录项".."中包括父目录inode编号,".."位于目录的第0块 */
uint32_t block_lba = child_dir_inode->i_sectors[0];
ASSERT(block_lba >= cur_part->sb->data_start_lba);
inode_close(child_dir_inode);
ide_read(cur_part->my_disk, block_lba, io_buf, 1);
struct dir_entry* dir_e = (struct dir_entry*)io_buf;
/* 第0个目录项是".",第1个目录项是".." */
ASSERT(dir_e[1].i_no < 4096 && dir_e[1].f_type == FT_DIRECTORY);
return dir_e[1].i_no; // 返回..即父目录的inode编号
}
/* 在inode编号为p_inode_nr的目录中查找inode编号为c_inode_nr的子目录的名字,
* 将名字存入缓冲区path.成功返回0,失败返-1 */
static int get_child_dir_name(uint32_t p_inode_nr, uint32_t c_inode_nr, char* path, void* io_buf) {
struct inode* parent_dir_inode = inode_open(cur_part, p_inode_nr);
/* 填充all_blocks,将该目录的所占扇区地址全部写入all_blocks */
uint8_t block_idx = 0;
uint32_t all_blocks[140] = {0}, block_cnt = 12;
while (block_idx < 12) {
all_blocks[block_idx] = parent_dir_inode->i_sectors[block_idx];
block_idx++;
}
if (parent_dir_inode->i_sectors[12]) { // 若包含了一级间接块表,将共读入all_blocks.
ide_read(cur_part->my_disk, parent_dir_inode->i_sectors[12], all_blocks + 12, 1);
block_cnt = 140;
}
inode_close(parent_dir_inode);
struct dir_entry* dir_e = (struct dir_entry*)io_buf;
uint32_t dir_entry_size = cur_part->sb->dir_entry_size;
uint32_t dir_entrys_per_sec = (512 / dir_entry_size);
block_idx = 0;
/* 遍历所有块 */
while(block_idx < block_cnt) {
if(all_blocks[block_idx]) { // 如果相应块不为空则读入相应块
ide_read(cur_part->my_disk, all_blocks[block_idx], io_buf, 1);
uint8_t dir_e_idx = 0;
/* 遍历每个目录项 */
while(dir_e_idx < dir_entrys_per_sec) {
if ((dir_e + dir_e_idx)->i_no == c_inode_nr) {
strcat(path, "/");
strcat(path, (dir_e + dir_e_idx)->filename);
return 0;
}
dir_e_idx++;
}
}
block_idx++;
}
return -1;
}get_parent_dir_inode_nr函数接受2个参数,子目录inode编号child_inode_nr、缓冲区io_buf,功能是获得父目录的 inode 编号。
此函数是利用子目录中目录项”.”来实现的,在函数开头先通过inode_open获得子目录的inode,用指针child_dir_inode保存其地址。目录项”.”和”..”是在执行sys_mkdir创建空目录的时候生成的,它们位于目录第0个直接块中,即i_sectors[0]中,因此先将该块中的数据读入到io_buf中。块中第0个目录项是”.”,第1个目录项是”..”,return dir_e[1].i_no返回第1个目录项的inode编号,函数结束。
函数get_child_dir_name接受4个参数,父目录inode编号p_inode_nr、子目录inode编号c_inode_nr、存储路径的缓冲区path、硬盘读写缓冲区io_buf,功能是在inode编号为p_inode_nr的目录中查找inode编号为c_inode_nr的子目录,将子目录的名字存入缓冲区path,成功返回0,失败返-1。名称是在目录项中存储,故获取名称必然免不了读取目录项所在的块,因此先打开父目录的inode,接着很老套地把目录的所有块地址收集到all_blocks,while(block_idx < block_cnt)遍历所有块,然后在每一个块中遍历所有目录项。在if ((dir_e + dir_e_idx)->i_no == c_inode_nr) 如果发现目录项的i_no等于c_inode_nr,就在strcat(path, “/”)用函数strcat将路径分隔符追加到path中,然后在下一行将目录项的名称追加到”/”之后,最后通过 return 返回 0,函数结束。
Linux 中用 getewd 函数来获取当前工作路径。
对应的,我们实现内核sys_getcwd函数
先修改下pcb,我们要在pcb中加个记录当前工作目录的成员cwd_inode_nr,用它来记录工作目录的 inode 编号。
修改thread/thread.h
/* 进程或线程的pcb,程序控制块 */
struct task_struct {
uint32_t* self_kstack; // 各内核线程都用自己的内核栈
pid_t pid;
enum task_status status;
char name[16];
uint8_t priority;
uint8_t ticks; // 每次在处理器上执行的时间嘀嗒数
/* 此任务自上cpu运行后至今占用了多少cpu嘀嗒数,
* 也就是此任务执行了多久*/
uint32_t elapsed_ticks;
/* general_tag的作用是用于线程在一般的队列中的结点 */
struct list_elem general_tag;
/* all_list_tag的作用是用于线程队列thread_all_list中的结点 */
struct list_elem all_list_tag;
uint32_t* pgdir; // 进程自己页表的虚拟地址
struct virtual_addr userprog_vaddr; // 用户进程的虚拟地址
struct mem_block_desc u_block_desc[DESC_CNT]; // 用户进程内存块描述符
int32_t fd_table[MAX_FILES_OPEN_PER_PROC]; // 已打开文件数组
uint32_t cwd_inode_nr; // 进程所在的工作目录的inode编号
uint32_t stack_magic; // 用这串数字做栈的边界标记,用于检测栈的溢出
};接着还要修改初始化线程函数 init_thread,为 cwd_inode_nr 初始化
修改thread/thread.c
/* 初始化线程基本信息 */
void init_thread(struct task_struct* pthread, char* name, int prio) {
memset(pthread, 0, sizeof(*pthread));
pthread->pid = allocate_pid();
strcpy(pthread->name, name);
if (pthread == main_thread) {
/* 由于把main函数也封装成一个线程,并且它一直是运行的,故将其直接设为TASK_RUNNING */
pthread->status = TASK_RUNNING;
} else {
pthread->status = TASK_READY;
}
/* self_kstack是线程自己在内核态下使用的栈顶地址 */
pthread->self_kstack = (uint32_t*)((uint32_t)pthread + PG_SIZE);
pthread->priority = prio;
pthread->ticks = prio;
pthread->elapsed_ticks = 0;
pthread->pgdir = NULL;
/* 标准输入输出先空出来 */
pthread->fd_table[0] = 0;
pthread->fd_table[1] = 1;
pthread->fd_table[2] = 2;
/* 其余的全置为-1 */
uint8_t fd_idx = 3;
while (fd_idx < MAX_FILES_OPEN_PER_PROC) {
pthread->fd_table[fd_idx] = -1;
fd_idx++;
}
pthread->cwd_inode_nr = 0; // 以根目录做为默认工作路径
pthread->stack_magic = 0x19870916; // 自定义的魔数
}
修改fs/fs.c
/* 把当前工作目录绝对路径写入buf, size是buf的大小.
当buf为NULL时,由操作系统分配存储工作路径的空间并返回地址
失败则返回NULL */
char* sys_getcwd(char* buf, uint32_t size) {
/* 确保buf不为空,若用户进程提供的buf为NULL,
系统调用getcwd中要为用户进程通过malloc分配内存 */
ASSERT(buf != NULL);
void* io_buf = sys_malloc(SECTOR_SIZE);
if (io_buf == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
struct task_struct* cur_thread = running_thread();
int32_t parent_inode_nr = 0;
int32_t child_inode_nr = cur_thread->cwd_inode_nr;
ASSERT(child_inode_nr >= 0 && child_inode_nr < 4096); // 最大支持4096个inode
/* 若当前目录是根目录,直接返回'/' */
if (child_inode_nr == 0) {
buf[0] = '/';
buf[1] = 0;
sys_free(io_buf);
return buf;
}
memset(buf, 0, size);
char full_path_reverse[MAX_PATH_LEN] = {0}; // 用来做全路径缓冲区
/* 从下往上逐层找父目录,直到找到根目录为止.
* 当child_inode_nr为根目录的inode编号(0)时停止,
* 即已经查看完根目录中的目录项 */
while ((child_inode_nr)) {
parent_inode_nr = get_parent_dir_inode_nr(child_inode_nr, io_buf);
if (get_child_dir_name(parent_inode_nr, child_inode_nr, full_path_reverse, io_buf) == -1) { // 或未找到名字,失败退出
sys_free(io_buf);
return NULL;
}
child_inode_nr = parent_inode_nr;
}
ASSERT(strlen(full_path_reverse) <= size);
/* 至此full_path_reverse中的路径是反着的,
* 即子目录在前(左),父目录在后(右) ,
* 现将full_path_reverse中的路径反置 */
char* last_slash; // 用于记录字符串中最后一个斜杠地址
while ((last_slash = strrchr(full_path_reverse, '/'))) {
uint16_t len = strlen(buf);
strcpy(buf + len, last_slash);
/* 在full_path_reverse中添加结束字符,做为下一次执行strcpy中last_slash的边界 */
*last_slash = 0;
}
sys_free(io_buf);
return buf;
}sys_getewd函数接受两个参数,存储绝对路径的缓冲区buf、缓冲区大小size,功能是把当前工作目录的绝对路径写入buf,成功返回buf地址,失败返回NULL。
函数开头用”ASSERT(buf != NULL)”限制了buf不为空,buf可以由用户进程提供,也可以由操作系统提供,若用户进程传给buf的实参是NULL,也就是未提供缓冲区,我们会在系统调用getcwd中为buf通过malloc分配内存。 接着是为缓冲区io_buf申请1扇区大小的内存。
先获得当前任务工作目录的inode编号,即存储在pcb中的cwd_inode_nr,将其赋值给child_inode_nr。
if (child_inode_nr == 0)判断如果child_inode_nr是0,这说明是根目录的inode编号,因此把buf直接置为”/”后返回。 接着定义了数组full_path_reverse[MAX_PATH_LEN],它用于存储工作目录所在的全路径,即绝对路径,不过从名字上看,它是反转的绝对路径,因此它只是临时数据,一会还要将其反转回来。 注意,这里只是反转目录顺序,目录名本身不反转。 如若原路径为”/ab/c”,在full_path_reverse的将是”/c/ab”,并不是”/c/ba”。
从当前目录向上回溯,逐层找父目录,一直找到根目录为止。 parent_inode_nr = get_parent_dir_inode_nr(child_inode_nr, io_buf)调用 get_parentdir_inode_nr获得父目录的inode编号存入parent_inode_nr,接着调用get_child_dir_name把当前工作目录的名字写入full_path_reverse中。 然后将child_inode_nr更新为parent_inode_nr开始下一轮循环。 循环过后,在full_path_reverse中得到了绝对路径的反转形式,下面将其转换为正常的顺序。 代码while ((last_slash = strrchr(full_path_reverse, ‘/’)))通过while循环逐层解析目录名,将最终的路径写入buf中。
2.切换当前目录
linux还会通过cd命令来切换目录,用函数chdir来实现
同样修改fs/fs.c
/* 更改当前工作目录为绝对路径path,成功则返回0,失败返回-1 */
int32_t sys_chdir(const char* path) {
int32_t ret = -1;
struct path_search_record searched_record;
memset(&searched_record, 0, sizeof(struct path_search_record));
int inode_no = search_file(path, &searched_record);
if (inode_no != -1) {
if (searched_record.file_type == FT_DIRECTORY) {
running_thread()->cwd_inode_nr = inode_no;
ret = 0;
} else {
printk("sys_chdir: %s is regular file or other!\n", path);
}
}
dir_close(searched_record.parent_dir);
return ret;
}sys_chdir函数接受1个参数,新工作目录的绝对路径path,功能是更改当前工作目录为绝对路径path,成功则返回0,失败返回-1。任务的工作目录记录在pcb中的cwd_inode_nr,因此更改工作目录的核心原理就是修改cwd_inode_nr,工作目录必须是在硬盘上存在的,因此在更改工作目录之前,先要保证新路径path 是存在的。
搜索path,如果未找到,也就是返回值inode_no为-1,直接返回默认的返回值ret,即-1,如果找到了 path,要确认 path 是否为目录,万一要是普通文件也会失败。 if (searched_record.file_type == FT_DIRECTORY)判断如果是目录,就用目录path的inode号inode_no给任务的cwd_inode_nr赋值,从而完成了工作目录的更改,然后将返回值ret置为0。 最后关闭目录,返回ret。
对应fs/fs.h加入函数声明
char* sys_getcwd(char* buf, uint32_t size); int32_t sys_chdir(const char* path);
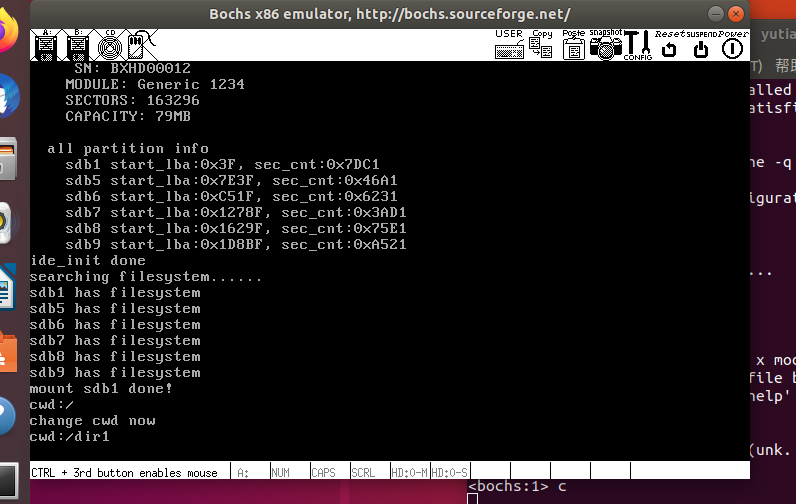
修改main.c测试
int main(void) {
put_str("I am kernel\n");
init_all();
/******** 测试代码 ********/
char cwd_buf[32] = {0};
sys_getcwd(cwd_buf, 32);
printf("cwd:%s\n", cwd_buf);
sys_chdir("/dir1");
printf("change cwd now\n");
sys_getcwd(cwd_buf, 32);
printf("cwd:%s\n", cwd_buf);
/******** 测试代码 ********/
while(1);
return 0;
}执行结果如下:
3.显示文件属性
同样的linux执行ls命令时会输出文件的属性
修改fs/fs.h,添加上文件属性结构
/* 文件属性结构体 */
struct stat {
uint32_t st_ino; // inode编号
uint32_t st_size; // 尺寸
enum file_types st_filetype; // 文件类型
};
修改fs/fs.c
/* 在buf中填充文件结构相关信息,成功时返回0,失败返回-1 */
int32_t sys_stat(const char* path, struct stat* buf) {
/* 若直接查看根目录'/' */
if (!strcmp(path, "/") || !strcmp(path, "/.") || !strcmp(path, "/..")) {
buf->st_filetype = FT_DIRECTORY;
buf->st_ino = 0;
buf->st_size = root_dir.inode->i_size;
return 0;
}
int32_t ret = -1; // 默认返回值
struct path_search_record searched_record;
memset(&searched_record, 0, sizeof(struct path_search_record)); // 记得初始化或清0,否则栈中信息不知道是什么
int inode_no = search_file(path, &searched_record);
if (inode_no != -1) {
struct inode* obj_inode = inode_open(cur_part, inode_no); // 只为获得文件大小
buf->st_size = obj_inode->i_size;
inode_close(obj_inode);
buf->st_filetype = searched_record.file_type;
buf->st_ino = inode_no;
ret = 0;
} else {
printk("sys_stat: %s not found\n", path);
}
dir_close(searched_record.parent_dir);
return ret;
}sys_stat函数接受2个参数,待获取属性的文件路径path、存储属性的缓冲区buf,功能是在buf中填充文件结构相关信息,成功时返回 0,失败返回-1。函数开头判断path是否为根目录,如果是就直接在buf中写入根目录的信息并成功返回。int32_t ret = -1定义了返回值ret,默认为-1。然后在文件系统上查找文件path,如果文件存在,struct inode* obj_inode = inode_open(cur_part, inode_no)打开文件的inode,这是为了获取文件大小。下面分别填充buf中的st_size,st_filetype和st_ino,并将ret置为0。如果文件不存在,输出文件不存在的提示。最后关闭目录,返回 ret。
对应fs/fs.h也加入声明
int32_t sys_stat(const char* path, struct stat* buf);
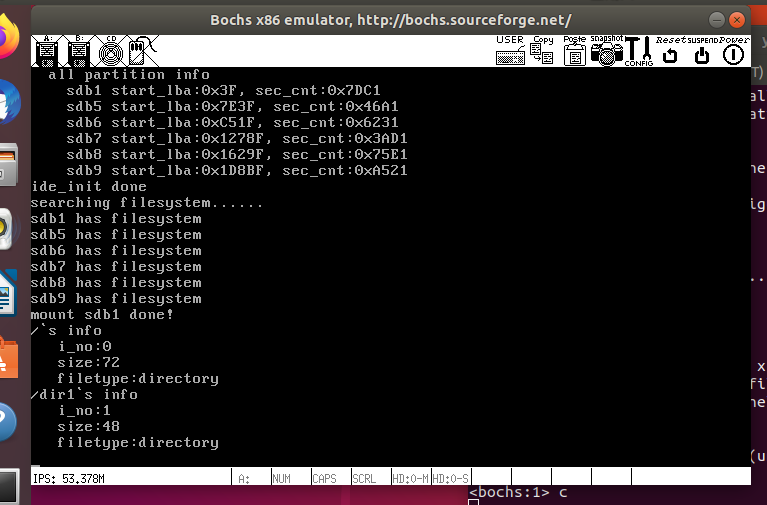
修改main.c测试
int main(void) {
put_str("I am kernel\n");
init_all();
/******** 测试代码 ********/
struct stat obj_stat;
sys_stat("/", &obj_stat);
printf("/`s info\n i_no:%d\n size:%d\n filetype:%s\n", \
obj_stat.st_ino, obj_stat.st_size, \
obj_stat.st_filetype == 2 ? "directory" : "regular");
sys_stat("/dir1", &obj_stat);
printf("/dir1`s info\n i_no:%d\n size:%d\n filetype:%s\n", \
obj_stat.st_ino, obj_stat.st_size, \
obj_stat.st_filetype == 2 ? "directory" : "regular");
/******** 测试代码 ********/
while (1);
return 0;
}
执行结果如下:
可以看到成功输出了属性了
4.参考
郑钢著操作系统真象还原
田宇著一个64位操作系统的设计与实现
丁渊著ORANGE’S:一个操作系统的实现