1.环境及准备工作
项目环境
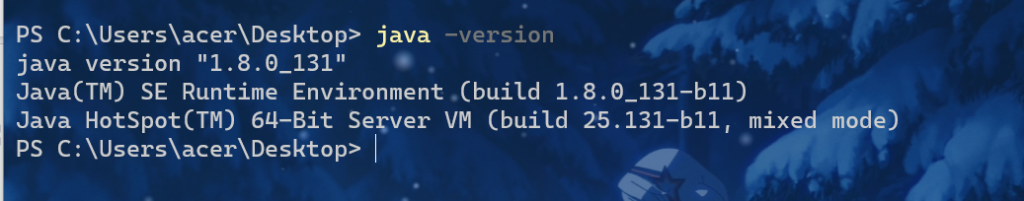
java1.8
maven3.6.3
准备工作
新建项目
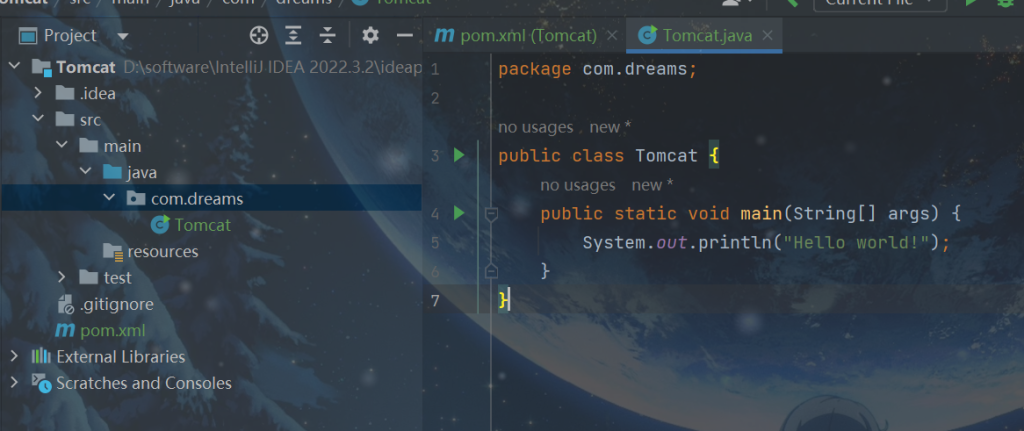
在pom.xml文件加入依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.基本请求
全部代码都在文章里了,大多数代码,我都加了注释。
tomcat启动从main方法进入
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
tomcat.start();
System.out.println("Hello world!");
}
调用start完成真正的使用:
代码还没写全,但是,我们先解决一个问题,如下:
服务器一次只能连接一个客户端
public void start(){
try {
//一个服务端的端口8080,socket连接TCP
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);
//得到socket连接
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
//其他代码......
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
tomcat在解决这个问题时使用了BIO模型,参考后,我们对其改一下:
public void start(){
try {
//使用线程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(30);
//一个服务端的端口8080,socket连接TCP
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);
while (true){
//得到socket连接
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
//交给线程池中的线程处理
executorService.execute(new SocketProcessor(socket));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
在当前目录下,新建socket目录下新建SocketProcessor类代码如下:
package com.dreams.socket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class SocketProcessor implements Runnable{
private Socket socket;
public SocketProcessor(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//具体处理
process(socket);
}
private void process(Socket socket) {
// 具体处理的逻辑
}
}
具体处理的逻辑
private void process(Socket socket) {
//处理逻辑
try {
//比如浏览器发送数据,在这里获取发送的数据
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
//构造一个字节数组,1KB
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
//每次读取1KB,暂时先如此,今后优化
inputStream.read(bytes);
//暂时输出测试,解析字节流
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
先测试一下:
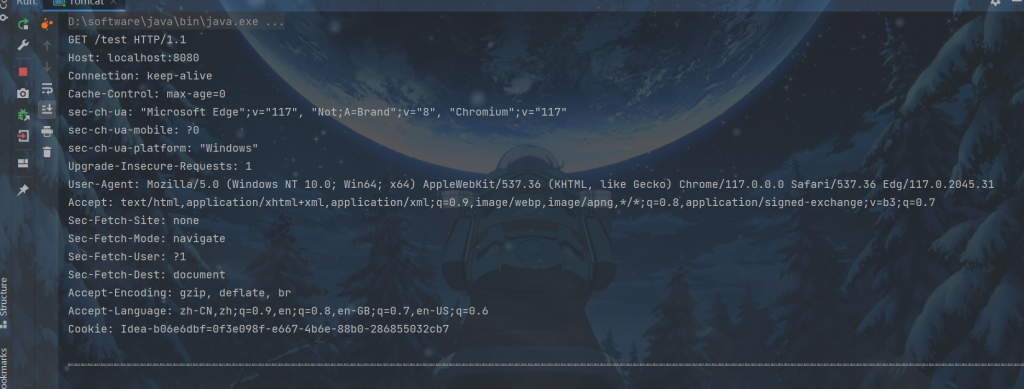
我们截取一下上述的请求头,其余也可以截取,但是一个小型的tomcat就不处理了
再改一下代码:
private void process(Socket socket) {
//处理逻辑
try {
//比如浏览器发送数据,在这里获取发送的数据
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
//构造一个字节数组,1KB
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
//每次读取1KB,暂时先如此,今后优化
inputStream.read(bytes);
String request = new String(bytes);
int index1,index2,index3;
index1 = request.indexOf(' ');
index2 = request.indexOf(' ',index1+1);
index3 = request.indexOf('\r');
String method = request.substring(0,index1);
String url = request.substring(index1 + 1,index2);
String protocl = request.substring(index2,index3);
//System.out.println(" " + method + " " + url + " " + protocl);
//获取request和response
Request request = new Request(method, url, protocl,socket);
Response response = new Response(request);
Servlet servlet = new Servlet();
servlet.service(request,response);
//发送响应
response.send();
} catch (IOException e | ServletException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
知道请求方法后,对其进行处理
新建一个Servlet类,承担Servlet功能,继承HttpServlet
package com.dreams;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Servlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//Get请求逻辑
}
}
新建一个http目录,存放Request对象和Response对象
Request对象如下:
package com.dreams.http;
public class Request {
private String method;
private String url;
private String protocol;
//其余也可以截取,但是一个小型的tomcat就不处理了,就暂时处理3个参数
//绑定socket
private Socket socket;
public Request(String method, String url, String protocol, Socket socket) {
this.method = method;
this.url = url;
this.protocol = protocol;
this.socket = socket;
}
public Socket getSocket() {
return socket;
}
public Request(String method, String url, String protocol) {
this.method = method;
this.url = url;
this.protocol = protocol;
}
public String getMethod() {
return method;
}
public StringBuffer getUrl() {
return new StringBuffer(url);
}
public String getProtocol() {
return protocol;
}
}
当然,Request对象应该实现HttpServletRequest,需要我们重写很多方法
在idea,我们按Alt+Enter,直接自动重写,代码都是自动生成的,就不再展出。
Response对象
package com.dreams.http;
import javax.servlet.ServletOutputStream;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Response implements HttpServletResponse {
private int status = 200;
private String message = "OK";
private Map<String,String> headers = new HashMap<>();
//常量,空格
private byte SP = ' ';
//常量,回车
private byte CR = '\r';
//常量,换行
private byte LF = '\n';
//每个response对应一个request
private Request request;
private OutputStream socketOutputStream;
//对于一个响应体只要一个响应体
private ResponseServletOutputStream responseServletOutputStream = new ResponseServletOutputStream();
public Response(Request request) {
this.request = request;
try {
this.socketOutputStream = request.getSocket().getOutputStream();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void setStatus(int status,String message) {
status = status;
message = message;
}
public void addHeader(String s1, String s2) {
headers.put(s1,s2);
}
//响应
public ResponseServletOutputStream getOutputStream() {
return responseServletOutputStream;;
}
public void send(){
//发送响应
//响应行
sendResponseLine();
//响应头
sendResponseHeader();
//响应体
sendResponseBody();
}
private void sendResponseBody() {
}
private void sendResponseHeader() {
}
private void sendResponseLine() {
}
}当然,Response对象应该实现HttpServletResponse,需要我们重写很多方法
在idea,我们按Alt+Enter,直接自动重写,代码都是自动生成的,就不再展出。
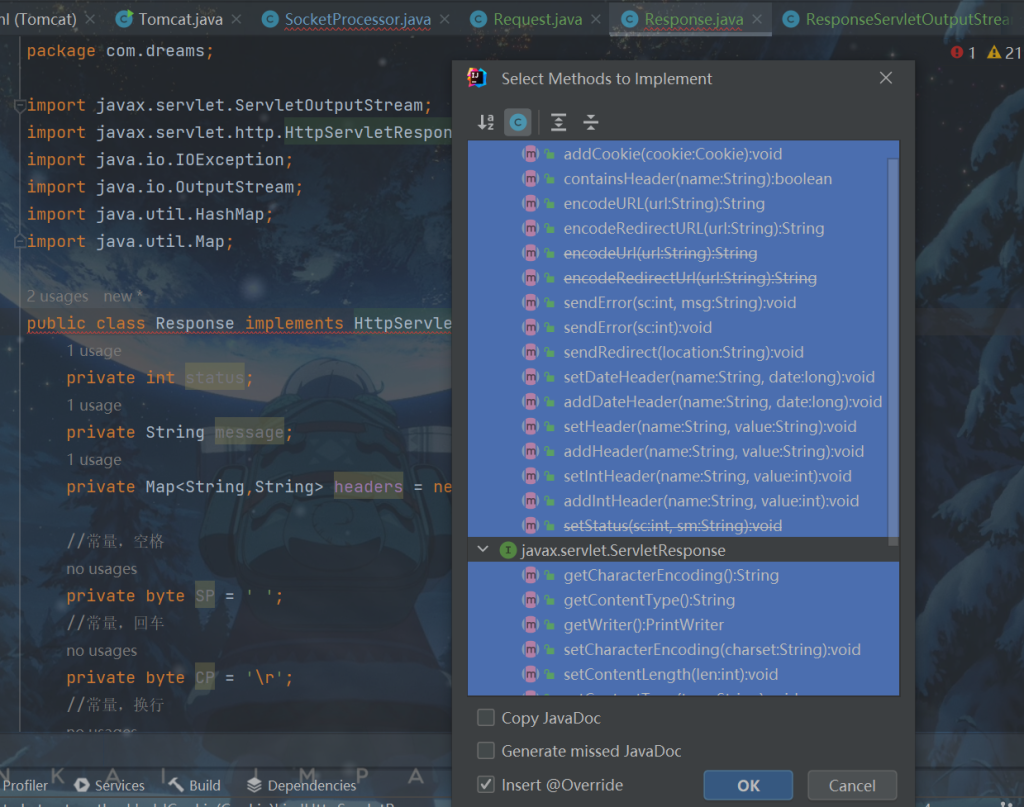
ResponseServletOutputStream类
package com.dreams.http;
import javax.servlet.ServletOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ResponseServletOutputStream extends ServletOutputStream {
private byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
private int index = 0;
@Override
public void write(int b) throws IOException {
bytes[index] = (byte) b;
index++;
}
public byte[] getBytes() {
return bytes;
}
public int getIndex() {
return index;
}
public void send(){
//响应完成
}
}
随便打开一个网页,查看响应:
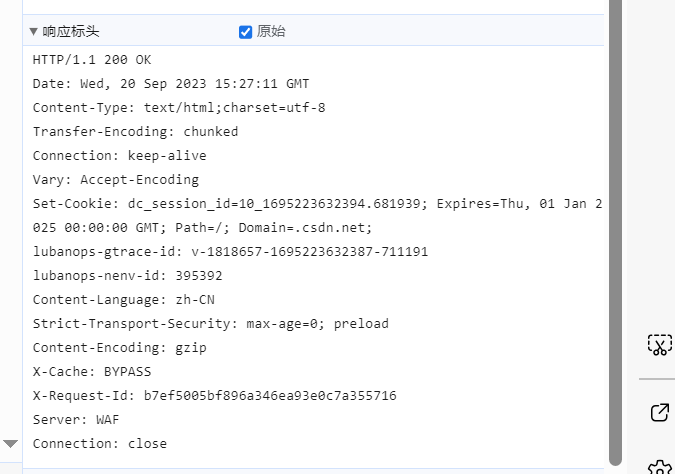
sendResponseBody方法逻辑如下:
private void sendResponseBody() throws IOException {
socketOutputStream.write(getOutputStream().getBytes());
}sendResponseHeader方法逻辑如下:
private void sendResponseHeader() throws IOException {
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : headers.entrySet()) {
String key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
socketOutputStream.write(key.getBytes());
socketOutputStream.write(":".getBytes());
socketOutputStream.write(value.getBytes());
socketOutputStream.write(CR);
socketOutputStream.write(LF);
}
socketOutputStream.write(CR);
socketOutputStream.write(LF);
}sendResponseLine方法逻辑如下:
private void sendResponseLine() throws IOException {
socketOutputStream.write(request.getProtocol().getBytes());
socketOutputStream.write(SP);
socketOutputStream.write(status);
socketOutputStream.write(SP);
socketOutputStream.write(message.getBytes());
socketOutputStream.write(CR);
socketOutputStream.write(LF);
}
因为我们抛出了异常,所以记得捕获
public void send(){
//发送响应
try {
//响应行
sendResponseLine();
//响应头
sendResponseHeader();
//响应体
sendResponseBody();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
回到我们重写的doGet请求
手动写一些响应,测试一下
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//Get请求逻辑
//数据长度
resp.addHeader("Content-Length","12");
//以纯文本方式展示
resp.addHeader("Content-Type","text/plain;charset=utf-8");
resp.getOutputStream().write("Hello World!".getBytes());
}
访问
http://localhost:8080/test
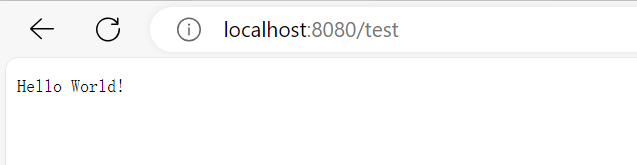
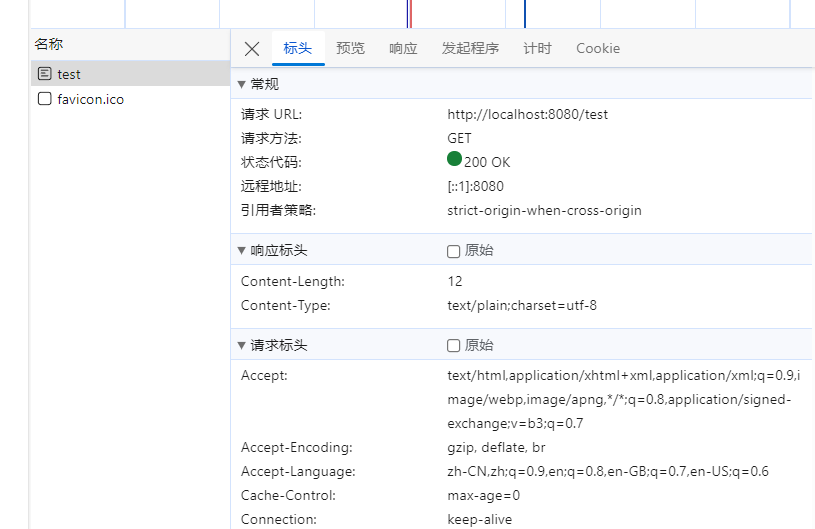
3.查找应用
实际应用会放在webapps下
新建如图目录
在servlet加入注解
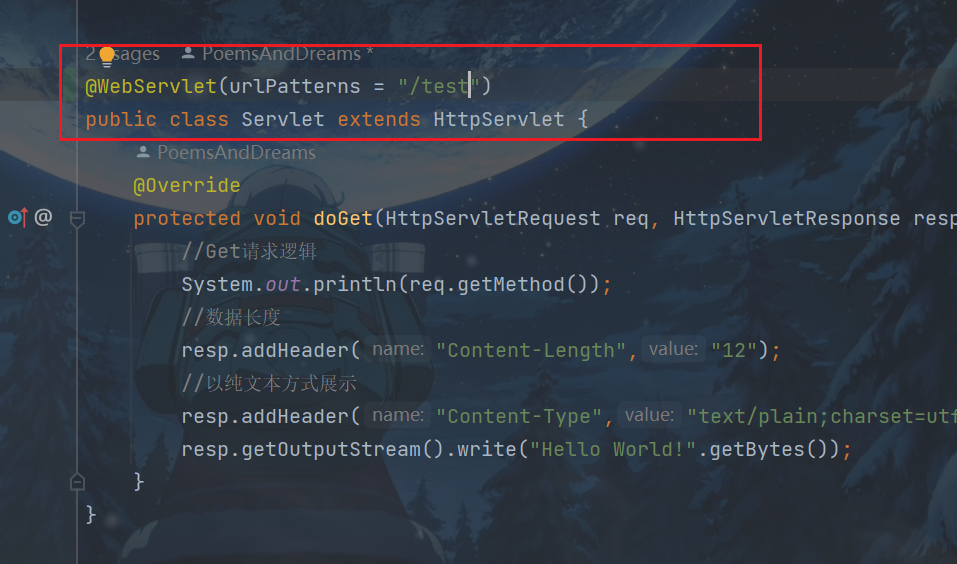
再将Servlet文件编译成class文件,放到如图目录下,删除原Servlet文件。
上述操作只是暂时拿来代替一个应用。
修改一下main方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
//先初始化
tomcat.init();
tomcat.start();
System.out.println("Hello world!");
}
初始化逻辑,目前暂时只是先部署
private void init() {
//先部署
deploys();
}
deploys()方法实现
private void deploys() {
//拿到当前目录下的webapps目录
File webapps = new File(System.getProperty("user.dir"), "webapps");
//webapps目录下每一个app
for (String app : webapps.list()) {
//每一个app的部署
deploy(webapps,app);
}
}
真正逻辑在deploy方法
获取文件,加载为class对象,然后通过反射,判断是否继承了HttpServlet
private void deploy(File webapps, String appName) {
//查看有哪些servlet
//获得appName文件夹
File appDirectory = new File(webapps, appName);
//获得classes文件夹
File classesDirectory = new File(appDirectory, "classes");
////获得classes文件夹下所有文件
List<File> files = getAllFilePath(classesDirectory);
for (File file : files) {
//获取全限定类名
String path = file.getPath();
path = path.replace(classesDirectory.getPath() + "\\", "");
path = path.replace(".class","");
path = path.replace("\\",".");
//System.out.println(path);
//加载一个类
try {
//自定义类加载器自定义加载目录
WebaddsClassLoader webaddsClassLoader = new WebaddsClassLoader(new URL[]{classesDirectory.toURL()});
Class<?> servletClass = webaddsClassLoader.loadClass(path);
//......代码在下面
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
新建ClassLoader目录,存放自定义类加载器,自定义类加载器自定义加载目录否则无法加载webapps目录下的文件
package com.dreams.ClassLoader;
import java.net.URL;
import java.net.URLClassLoader;
public class WebaddsClassLoader extends URLClassLoader {
//自定义类加载器自定义加载目录
public WebaddsClassLoader(URL[] urls) {
super(urls);
}
}getAllFilePath方法获取所有目录
//递归调用获取所有目录
public List<File> getAllFilePath(File srcFile){
ArrayList<File> fileList = new ArrayList<>();
File[] files = srcFile.listFiles();
if (files != null){
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isDirectory()){
fileList.addAll(getAllFilePath(file));
}
else {
fileList.add(file);
}
}
}
return fileList;
}
判断是否是HttpServlet的子类,将参数urlPatterns内容保存在common下的context,一个应用保存在一个Map
private void deploy(File webapps, String appName) {
//查看有哪些servlet
//每个应用对应一个context对象
Context context = new Context(appName);
//获得appName文件夹
File appDirectory = new File(webapps, appName);
//获得classes文件夹
File classesDirectory = new File(appDirectory, "classes");
////获得classes文件夹下所有文件
List<File> files = getAllFilePath(classesDirectory);
for (File file : files) {
//获取全限定类名
String path = file.getPath();
path = path.replace(classesDirectory.getPath() + "\\", "");
path = path.replace(".class","");
path = path.replace("\\",".");
//System.out.println(path);
//加载一个类
try {
//自定义类加载器自定义加载目录
WebaddsClassLoader webaddsClassLoader = new WebaddsClassLoader(new URL[]{classesDirectory.toURL()});
Class<?> servletClass = webaddsClassLoader.loadClass(path);
//判断是否是HttpServlet的子类
if (HttpServlet.class.isAssignableFrom(servletClass)){
//判断是否存在WebServlet注解
if (servletClass.isAnnotationPresent(WebServlet.class)){
//获取WebServlet注解内容
WebServlet annotation = servletClass.getAnnotation(WebServlet.class);
//获取WebServlet参数urlPatterns内容
String[] urlPatterns = annotation.urlPatterns();
//这里保存在common下的context,一个应用保存在一个Map
for (String urlPattern : urlPatterns) {
context.addUrlurlPatternMap(urlPattern, (Servlet) servletClass.newInstance());
}
}
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//tomcat也会保存有哪些应用
contextMap.put(appName,context);
}
新建common下的context
package com.dreams.common;
import javax.servlet.Servlet;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Context {
private String appName;
private Map<String,Servlet> urlPatternMap = new HashMap<>();
public Context(String appName) {
this.appName = appName;
}
//保存
public void addUrlurlPatternMap(String urlPattern, Servlet servlet) {
urlPatternMap.put(urlPattern,servlet);
}
//获取
public Servlet getUrlurlPattern(String urlPattern){
return urlPatternMap.get("/" + urlPattern);
}
}
当然tomcat也会保存有哪些应用
在tomcat提供一个成员变量,在上面的deployf方法那里添加,代码已给出。
private Map<String,Context> contextMap = new HashMap<>();
获取tomcat也会保存有哪些应用
//获取tomcat也会保存有哪些应用
public Map<String, Context> getContextMap() {
return contextMap;
}
真正对路径处理的逻辑来了
因为会用到Tomcat类,就在SocketProcessor加入成员变量
private Tomcat tomcat;
修改一下构造方法
public SocketProcessor(Socket socket,Tomcat tomcat) {
this.socket = socket;
this.tomcat = tomcat;
}
在创建对象是多传一个参数
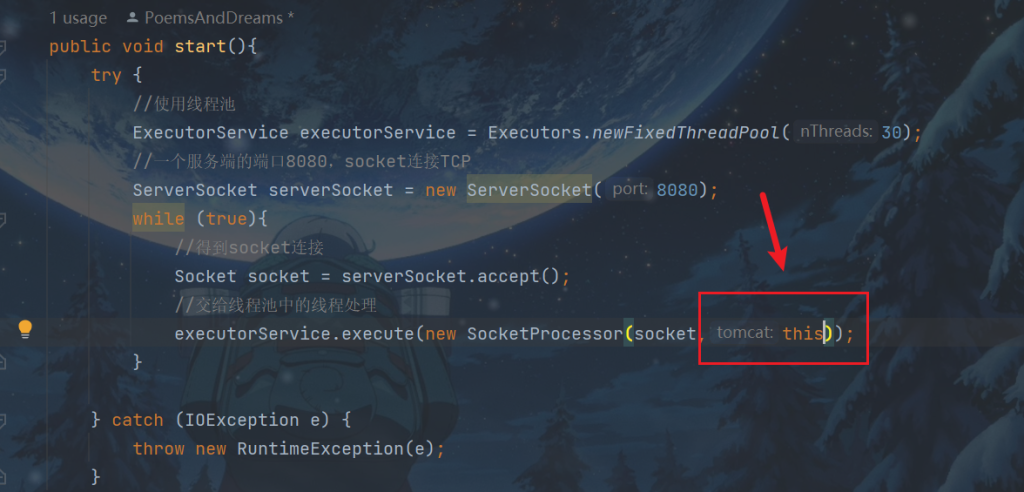
SocketProcessor类的process方法更改如下:
private void process(Socket socket) {
//处理逻辑
try {
//比如浏览器发送数据,在这里获取发送的数据
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
//构造一个字节数组,1KB
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
//每次读取1KB,暂时先如此,今后优化
inputStream.read(bytes);
String re = new String(bytes);
int index1,index2,index3;
index1 = re.indexOf(' ');
index2 = re.indexOf(' ',index1+1);
index3 = re.indexOf('\r');
String method = re.substring(0,index1);
String url = re.substring(index1 + 1,index2);
String protocl = re.substring(index2,index3);
System.out.println(" " + method + " " + url + " " + protocl);
Request request = new Request(method, url, protocl,socket);
Response response = new Response(request);
//拆分/Text/text......如/应用名/servlet路径名
String requestURI = request.getUrl().toString();
requestURI = requestURI.substring(1);
String[] paths = requestURI.split("/");
//应用名
String appName = paths[0];
//获取到tomcat保存的servlet
Context context = tomcat.getContextMap().get(appName);
if (context != null){
//servlet路径名
String servletName = paths[1];
//根据名字获取到servlet
Servlet servlet = context.getUrlurlPattern(servletName);
//得到servlet对象,
servlet.service(request,response);
}
//发送响应
response.send();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (ServletException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
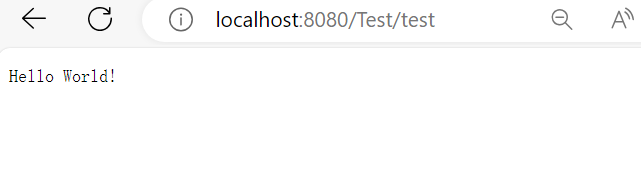
访问
http://localhost:8080/Test/test
但是,还是可能会有访问不存在的路径
if (context != null){
//servlet路径名
String servletName = paths[1];
//根据名字获取到servlet
Servlet servlet = context.getUrlurlPattern(servletName);
if (servlet != null){
//得到servlet对象,
servlet.service(request,response);
//发送响应
response.send();
}
else {
System.out.println("Not Find Path!");
//自定义一个servlet,找不到路径跳转
NotFindServlet notFindServlet = new NotFindServlet();
notFindServlet.service(request,response);
//发送响应
response.send();
}
}
新建servlet目录下NotFindServlet类
package com.dreams.servlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
public class NotFindServlet extends HttpServlet {
//处理业务
}
3.静态页面
因为只是一个超级超级超级超级简单的tomcat,就取巧一下
在SocketProcessor下的process方法的如下图位置
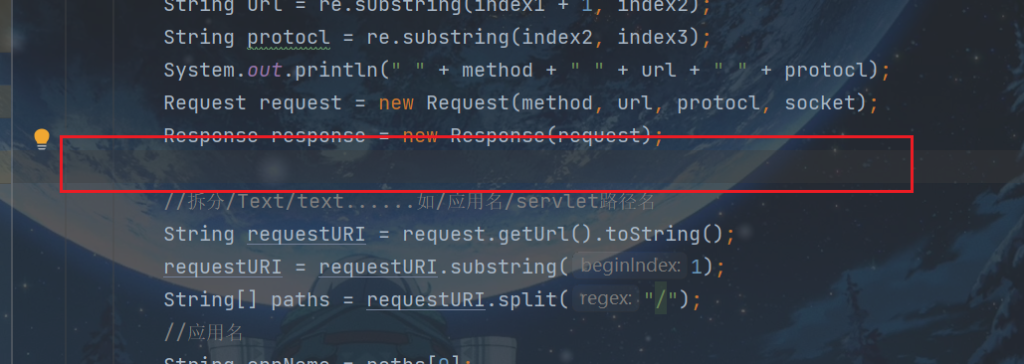
加入处理静态资源的逻辑,因为只是一个超级超级超级超级简单的tomcat,所以,就不考虑性能及优化了。
//直接处理静态资源,取巧只处理html文件
if (url.contains(".html")) {
//拿到当前目录下的webapps目录
File file = new File(System.getProperty("user.dir") + "\\webapps" + url);
//返回目标资源
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
//就直接使用等大的大小了,不再优化了
byte[] disposeBytes = new byte[(int) file.length()];
fileInputStream.read(disposeBytes);
response.addHeader("Content-Length", disposeBytes.length + "");
response.getOutputStream().write(disposeBytes);
response.send();
return;
}
在ResponseServletOutputStream类加入以下方法,来给其赋值。
@Override
public void write(byte[] b) throws IOException {
bytes = new byte[b.length];
bytes = b;
}
比如,在webapps下新建一个index.html页面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>tomcat</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>tomcat</h1>
</body>
</html>
访问
http://localhost:8080/index.html
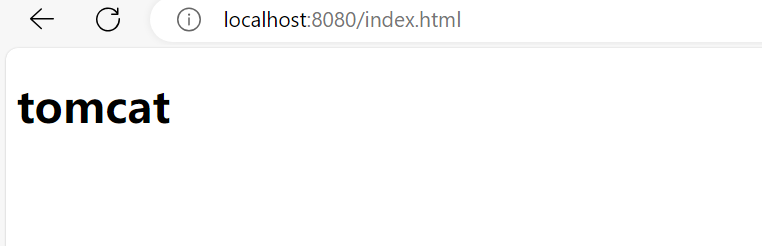
目前就这样了,慢慢优化吧
参考
图灵学院的教程