手写spring主要是为了熟悉源码,所以参考源码实现了一个简单的spring。
源码:spring-projects/spring-framework: Spring Framework (github.com)
1.自定义注解
要使用@Controller就要导入spring-context依赖,所以源码也在spring-context下
官方源码:
参考官方源码:
新建com.dreams.springframework.stereotype包,在其下新建四个注解
@Controller,@Service,@Repository都有带@Component父注解
源码有个@Documented注解,生成帮助文档的,没什么用,就不加。
首先实现Component
package com.dreams.springframework.stereotype;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) //TYPE:用于描述类、接口(包括注解类型) 或enum声明
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //注解不仅被保存到class文件中,jvm加载class文件之后,仍然存在;
public @interface Component {
String value() default ""; //注解参数
}
如下代码,
@AliasFor(annotation = Component.class) 该注解是为了属性起别名,但是我暂时只是想实现一个简单的spring,就不写它了
实现@Controller
package com.dreams.springframework.stereotype;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) //TYPE:用于描述类、接口(包括注解类型) 或enum声明
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //注解不仅被保存到class文件中,jvm加载class文件之后,仍然存在;
@Component
public @interface Controller {
//@AliasFor(annotation = Component.class)
String value() default ""; //注解参数
}
实现@Service
package com.dreams.springframework.stereotype;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) //TYPE:用于描述类、接口(包括注解类型) 或enum声明
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //注解不仅被保存到class文件中,jvm加载class文件之后,仍然存在;
@Component
public @interface Service {
//@AliasFor(annotation = Component.class)
String value() default ""; //注解参数
}
实现@Repository
package com.dreams.springframework.stereotype;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) //TYPE:用于描述类、接口(包括注解类型) 或enum声明
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //注解不仅被保存到class文件中,jvm加载class文件之后,仍然存在;
@Component
public @interface Repository {
//@AliasFor(annotation = Component.class)
String value() default ""; //注解参数
}
实现@Autowired
package com.dreams.springframework.stereotype;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* ElementType:
* CONSTRUCTOR:用于描述构造器
* METHOD:用于描述方法
* FIELD:用于描述域
* LOCAL_VARIABLE:用于描述局部变量
* PACKAGE:用于描述包
* PARAMETER:用于描述参数
* TYPE:用于描述类、接口(包括注解类型) 或enum声明
*/
@Target({ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Autowired {
//参数默认值为true
boolean required() default true;
}
2.BeanDefinition 类
BeanDefinition 主要是用来描述 Bean,其存储了 Bean 的相关信息,Spring 实例化 Bean 时需读取该 Bean 对应的 BeanDefinition。BeanDefinition 整体可以分为两类,一类是描述通用的 Bean,还有一类是描述注解形式的 Bean。
官方源码:
所以我们新建一个BeanDefinition 类
package com.dreams.springframework.beans.factory.config;
/**
* @author PoemsAndDreams
* Bean的定义类
*/
public class BeanDefinition {
private String BeanName;
private Class clazz;
//其他信息,如单例等,这里实现一个简单的spring,就不实现了
//Getter and Setter
public Class getClazz() {
return clazz;
}
public void setClazz(Class clazz) {
this.clazz = clazz;
}
public String getBeanName() {
return BeanName;
}
public void setBeanName(String beanName) {
BeanName = beanName;
}
}
3.Bean工厂类
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory为父接口
package com.dreams.springframework.beans.factory.config;
import com.dreams.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
/**
* @author PoemsAndDreams
* @description //TODO
*/
public interface ConfigurableListableBeanFactory {
ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> getInstanceMap();
ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition> getBeanDefinitionMap();
Object getBean(String beanName);
Object getBean(Class<?> clazz);
void createBeanInstance() ;
}默认实现为DefaultListableBeanFactory
将上面的beanDefinition存储在beanDefinitionMap属性中,
InstanceMap存储实例化后的对象
package com.dreams.springframework.beans.factory.config;
import com.dreams.springframework.stereotype.Autowired;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
/**
* @author PoemsAndDreams
* @description //默认工厂实现类
*/
public class DefaultListableBeanFactory implements ConfigurableListableBeanFactory {
//存储bean定义信息,所以扫描到的
ConcurrentHashMap<String,BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//实例化存储
ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> InstanceMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
public ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition> getBeanDefinitionMap() {
return beanDefinitionMap;
}
@Override
public ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> getInstanceMap() {
return InstanceMap;
}
@Override
public void createBeanInstance() {
//......
}
@Override
public Object getBean(String beanName){
//......
}
@Override
public Object getBean(Class<?> clazz) {
//......
}
//@Autowired注入逻辑
public void postProcessProperties() {
//......
}
}
主要方法的逻辑是
createBeanInstance()方法负责根据存储在 beanDefinitionMap 中的定义来创建 bean 的实例
@Override
public void createBeanInstance() {
for (String beanName : beanDefinitionMap.keySet()) {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
Class clazz = beanDefinition.getClazz();
try {
//实例化
Object instance = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
//保存至InstanceMap,方便使用
InstanceMap.put(beanName, instance);
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//自动注入逻辑
this.postProcessProperties();
}在上面已经获取到bean的实例后,就是实现@Autowired注解的逻辑了,即将bean实例注入到@Autowired标注的属性中,于是就调用postProcessProperties()
方法代码如下:
//@Autowired注入逻辑
public void postProcessProperties() {
for (String beanName : beanDefinitionMap.keySet()) {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
//获取到实际的class
Class clazz = beanDefinition.getClazz();
//获取到所有字段
Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field declaredField : declaredFields) {
//是否有Autowired注解
if (declaredField.isAnnotationPresent(Autowired.class)) {
Class<?> aClass = declaredField.getType();
Object instance = null;
try {
String name = declaredField.getName();
//获取实现该接口的类
instance = InstanceMap.get(name);
Object o = InstanceMap.get(beanName);
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
declaredField.set(o, instance);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的getBean方法需要获取到bean实例,所以我们在Bean工厂提供这两个方法。根据给定的 beanName,从 InstanceMap 中获取对应的 bean 实例方法以及根据给定的 clazz(类类型),从 beanDefinitionMap 中寻找对应的 bean 实例方法。
@Override
public Object getBean(String beanName){
Object o = InstanceMap.get(beanName);
//获取不到即抛出异常
if (o == null){
throw new RuntimeException("No bean named" + beanName +" available");
}
return o;
}
@Override
public Object getBean(Class<?> clazz) {
Object bean = new Object();
for (BeanDefinition value : beanDefinitionMap.values()) {
Class aClass = value.getClazz();
if (aClass == clazz){
String beanName = value.getBeanName();
bean = InstanceMap.get(beanName);
return bean;
}
}
//获取不到即抛出异常
throw new RuntimeException("No qualifying bean of type" + clazz + " available");
}
4.xml解析类
接下来就是xml解析类了
package com.dreams.springframework.beans.factory.xml;
import com.dreams.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import com.dreams.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import com.dreams.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.dreams.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.dom4j.Attribute;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
import com.dreams.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import com.dreams.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
/**
* @author PoemsAndDreams
* @description xml解析类
*/
public class XmlBeanDefinitionReader {
//加载xml配置文件
public void loadBeanDefinitions(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, String configResources){
//......
}
private void findScanPackagePath(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, String scanPackage) {
//......
}
//加载
private void loadAllClass(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, File path) {
//......
}
//获取扫描包
private String getComponentScanPackage(String configResources) {
//。。。。。。
}
}逻辑如下:
加载xml配置文件主要调用loadBeanDefinitions方法
//加载xml配置文件
public void loadBeanDefinitions(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, String configResources){
//获取扫描包
String scanPackage = getComponentScanPackage(configResources);
//获取扫描包路径
findScanPackagePath(beanFactory,scanPackage);
}
获取扫描包getComponentScanPackage方法,使用了 DOM4J 库来解析 XML 文件,并提取属性值作为扫描包的路径。也就是要获取com.dreams
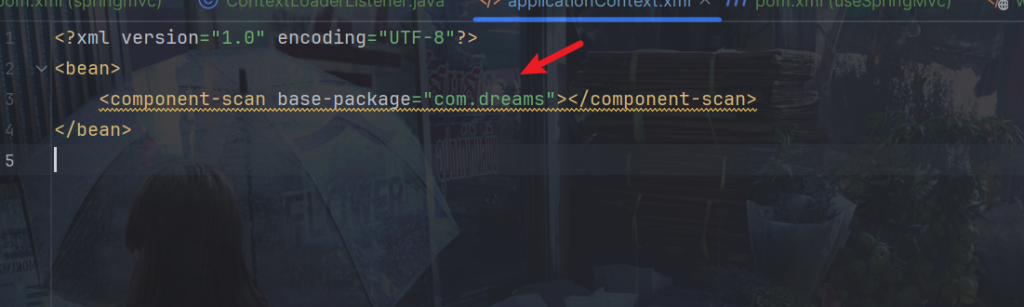
代码如下:
//获取扫描包
private String getComponentScanPackage(String configResources) {
//DOM4J 解析 XML
InputStream resourceAsStream = null;
try {
//创建 SAXReader 对象
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
//获取class对象加载文件返回流
resourceAsStream = XmlBeanDefinitionReader.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(configResources);
//获取document对象
Document document = saxReader.read(resourceAsStream);
//获取根节点
Element rootElement = document.getRootElement();
//获取扫描包
Element element = rootElement.element("component-scan");
Attribute attribute = element.attribute("base-package");
return attribute.getValue();
} catch (DocumentException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
if (resourceAsStream != null){
try {
resourceAsStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
findScanPackagePath方法通过getComponentScanPackage返回的包名com.dreams获取真正的路径,这里因为获取到的目录可能有空格,所以简单替换一下:
private void findScanPackagePath(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, String scanPackage) {
ClassLoader classLoader = XmlBeanDefinitionReader.class.getClassLoader();
scanPackage = scanPackage.replace(".","/");
URL url = classLoader.getResource(scanPackage);
//因为获取的目录可能含有空格,且会使用%20替代空格,所以我们需要替换回去
String urlFile = url.getFile();
if (urlFile.contains("%20")){
urlFile = urlFile.replace("%20"," ");
}
File file = new File(urlFile);
//加载并实例化
loadAllClass(beanFactory,file);
}
最后findScanPackagePath方法会调用loadAllClass加载全部的class
扫描指定目录下的所有 .class 文件,并加载这些文件中定义的类。如果类上标注了 @Component、@Controller、@Service 或 @Repository 注解,则将这些类作为 Spring Bean 添加到 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory 中的beanDefinitionMap,默认以配置的value为key,否则以开头小写的类名作为key也就是实例名。
//加载
private void loadAllClass(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, File path) {
ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionMap();
File[] files = path.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
//如果是个目录
if (!file.isDirectory()){
//获取文件路劲
String fileName = file.getAbsolutePath();
if (fileName.endsWith(".class")){
String className = fileName.substring(fileName.indexOf("com"), fileName.indexOf(".class"));
className = className.replace("\\",".");
//获取类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = XmlBeanDefinitionReader.class.getClassLoader();
try {
//加载类
Class<?> clazz = classLoader.loadClass(className);
//类是否有Component,Service,Controller,Repository注解
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class) || clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Controller.class) || clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Service.class) || clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Repository.class)){
Component componentAnnotation = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Component.class);
Controller controllerAnnotation = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Controller.class);
Service serviceAnnotation = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Service.class);
Repository repositoryAnnotation = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Repository.class);
String value = "";
//Bean定义类
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();
//判断注解是否有value值
if (componentAnnotation != null || controllerAnnotation != null || serviceAnnotation != null || repositoryAnnotation != null){
if (componentAnnotation != null && !componentAnnotation.value() .equals("")){
value = componentAnnotation.value();
}else if (controllerAnnotation != null && !controllerAnnotation.value().equals("")){
value = controllerAnnotation.value();
}else if (serviceAnnotation != null && !serviceAnnotation.value().equals("")){
value = serviceAnnotation.value();
} else if (repositoryAnnotation != null && !repositoryAnnotation.value().equals("")) {
value = repositoryAnnotation.value();
} else {
String name = clazz.getSimpleName();
//默认以开头小写的类名作为实例名
value = name.valueOf(name.charAt(0)).toLowerCase() + name.substring(1);
}
//不能重名
if (beanDefinitionMap.get(value) != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("spring IOC Container is already exists " + beanDefinitionMap.get(value));
}
beanDefinition.setClazz(clazz);
beanDefinition.setBeanName(value);
//保存到bean定义
beanDefinitionMap.put(value,beanDefinition);
//获取到该类实现的所有接口
Class[] interfaces = clazz.getInterfaces();
//在beanDefinitionMap中存储为一个接口对应一个实现类
for (Class anInterface : interfaces) {
String interfaceSimpleName = anInterface.getSimpleName();
interfaceSimpleName = interfaceSimpleName.valueOf(interfaceSimpleName.charAt(0)).toLowerCase() + interfaceSimpleName.substring(1);
beanDefinitionMap.put(interfaceSimpleName,beanDefinition);
}
}
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
else {
loadAllClass(beanFactory, file);
}
}
}
5.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类
常见的,我们需要读取xml文件
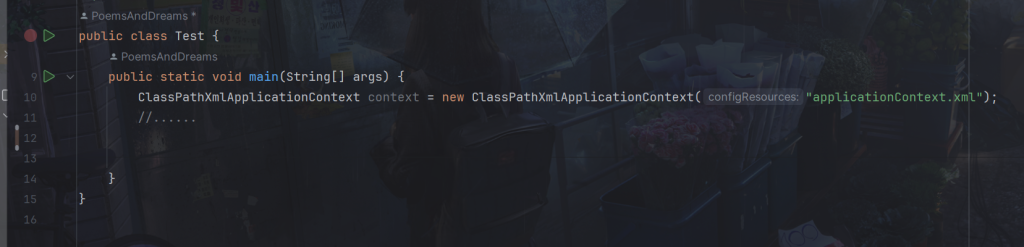
比如component-scan属性
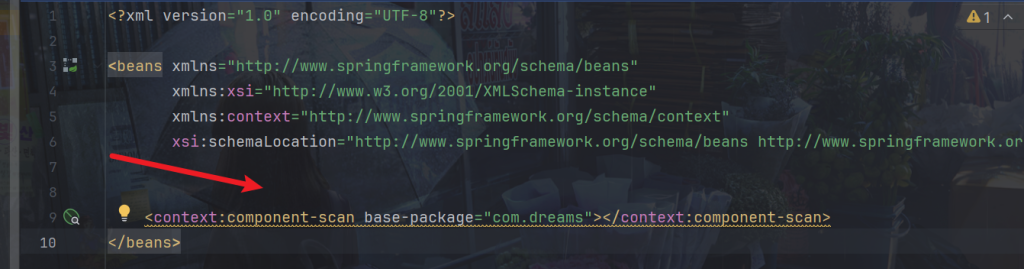
参考官方源码:
在源码中还有考虑到许多,比如获取到spring XML配置文件的地址,配置它的环境,设置成员属性等,这里我们只是实现一个简单的spring,不考虑这么多。
首先创建一个bean工厂BeanFactory(),默认实现是DefaultListableBeanFactory。初始化spring容器中的refresh()方法中,会调用obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法,设置工厂的一些属性,obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法其中调用loadBeanDefinition方法,这里是读取xml配置文件,所以就通过XmlBeanDefinitionReader进行Bean定义信息的读取。
代码如下:
package com.dreams.springframework.context;
import com.dreams.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import com.dreams.springframework.beans.factory.config.DefaultListableBeanFactory;
import com.dreams.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader;
/**
* @author PoemsAndDreams
*/
public class ClassPathXmlApplicationContext {
private ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
private String configResources;
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configResources) {
this.configResources = configResources;
//初始化spring容器
refresh();
}
private void refresh() {
// obtainFreshBeanFactory 加载spring入口
obtainFreshBeanFactory();
//实例化Bean
beanFactory.createBeanInstance();
}
private void obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
//加载xml配置文件
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
}
private void loadBeanDefinitions(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
XmlBeanDefinitionReader xmlBeanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader();
xmlBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory,configResources);
}
public Object getBean(String beanName){
return beanFactory.getBean(beanName);
}
public Object getBean(Class<?> clazz) {
return beanFactory.getBean(clazz);
}
}
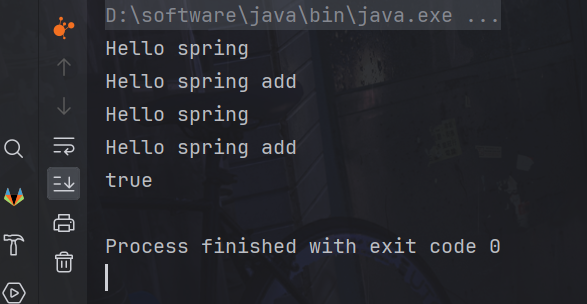
6.测试
新建一个模块UseSpring来测试功能,spring模块是上述我们写的代码的模块
引入我们写的spring项目依赖,这样就可以使用我们自己写的代码了
<dependency>
<groupId>com.dreams</groupId>
<artifactId>spring</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>在resources加入新建applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!--以下为spring格式校验链接,引入可以对xml格式校验-->
<!--<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"-->
<!-- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"-->
<!-- xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"-->
<!-- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">-->
<!--spring的xml格式校验链接结束-->
<!-- 获取扫描包路径,spring的xml需要加入context:,我们自己实现的spring就不需要加-->
<!-- <context:component-scan base-package="com.dreams"></context:component-scan>-->
<component-scan base-package="com.dreams"></component-scan>
<!--</beans>-->
在UserController
package com.dreams.controller;
import com.dreams.service.impl.UserServiceImpl;
import com.dreams.springframework.stereotype.Autowired;
import com.dreams.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
/**
* @author PoemsAndDreams
*/
@Controller(value = "uc")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
UserServiceImpl userService;
public void test(){
userService.test();
}
}
在UserService
package com.dreams.service;
/**
* @author PoemsAndDreams
*/
public interface UserService {
void test();
}
在UserServiceImpl
package com.dreams.service.impl;
import com.dreams.Dao.UserDao;
import com.dreams.service.UserService;
import com.dreams.springframework.stereotype.Autowired;
import com.dreams.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author PoemsAndDreams
*/
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
UserDao userDao;
@Override
public void test() {
userDao.test();
}
}
UserDao
package com.dreams.Dao;
/**
* @author PoemsAndDreams
*/
public interface UserDao {
void test();
}
UserDaoImpl
package com.dreams.Dao.Impl;
import com.dreams.Dao.UserDao;
import com.dreams.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
/**
* @author PoemsAndDreams
*/
@Repository
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
@Override
public void test() {
System.out.println("Hello spring");
}
}
在test
import com.dreams.controller.UserController;
import com.dreams.springframework.context.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @author PoemsAndDreams
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//......
UserController userController = (UserController) context.getBean("uc");
userController.test();
UserController userController1 = (UserController) context.getBean(UserController.class);
userController1.test();
System.out.println(userController1 == userController);
}
}运行如图