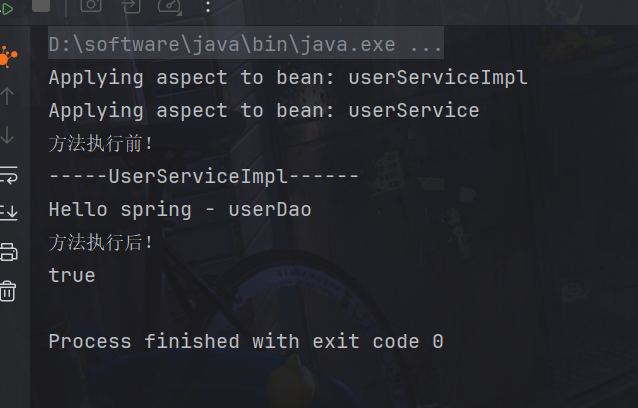
前面已经实现了IOC逻辑
下面实现AOP
1.回顾AOP
AOP(面向切面编程)是一种强大的编程范式,它允许你在不修改源代码的情况下向程序中添加横切关注点(如日志记录、安全检查、事务管理等)。 AOP的用法很简单,只要导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>然后添加配置类
package com.dreams.aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author PoemsAndDreams
* @description //
*/
@Aspect
@Component
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy //开启注解版AOP
public class MyAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.dreams.service.impl.*..*(..))")
public void pointCut(){}
@Before("pointCut()")
public void before(){
System.out.println("方法执行前!");
}
@After("pointCut()")
public void after(){
System.out.println("方法执行后!");
}
}运行个方法,自动在所有方法前或后加上各类操作。
2.AOP注解
在AOP中,@Aspect 注解来标记它为一个切面。
在前面的IOC逻辑代码的基础上接着开发,首先新建上面需要的注解
参考源码新建
注解Aspect
package com.dreams.springframework.aspectj.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
/**
* @author PoemsAndDreams
* //Aspect declaration
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Aspect {
String value() default "";
}
Before注解
package com.dreams.springframework.aspectj.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
/**
* @author PoemsAndDreams
* Before advice
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface Before {
String value();
String argNames() default "";
}
After注解
package com.dreams.springframework.aspectj.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @author PoemsAndDreams
* @description //
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface After {
String value();
String argNames() default "";
}
Pointcut注解
package com.dreams.springframework.aspectj.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
/**
* @author PoemsAndDreams
* Pointcut declaration
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface Pointcut {
String value() default "";
String argNames() default "";
}
3.加载@Aspect注解的类
在工厂类DefaultListableBeanFactory中添加属性来存储切面数据,key为@Pointcut 注解的值,value为切面类的class。
ConcurrentHashMap<String, Class<?>> advisorsCacheMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
public ConcurrentHashMap<String, Class<?>> getAdvisorsCacheMap() {
return advisorsCacheMap;
}
在XmlBeanDefinitionReader中的loadAllClass中加入以下代码,判断是否是加了Aspect注解,如果加了,他就是一个切面类,获取 @Pointcut 注解的值,并使用它作为键,将类存储在 advisorsCacheMap 中。
//判断是否是切面类
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Aspect.class) && clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)){
//获取 @Pointcut 注解的值,并使用它作为键,将类存储在 advisorsCacheMap 中。
for (Method method : clazz.getDeclaredMethods()) {
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(Pointcut.class)) {
Pointcut pointcut = method.getAnnotation(Pointcut.class);
String pointcutExpression = pointcut.value();
if (!advisorsCacheMap.containsKey(pointcutExpression)) {
advisorsCacheMap.put(pointcutExpression, clazz);
}
}
}
continue;
}
改造后的loadAllClass类,代码如下:
//加载
private void loadAllClass(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, File path) {
ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionMap();
ConcurrentHashMap<String, Class<?>> advisorsCacheMap = beanFactory.getAdvisorsCacheMap();
File[] files = path.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
//如果是个目录
if (!file.isDirectory()){
//获取文件路劲
String fileName = file.getAbsolutePath();
if (fileName.endsWith(".class")){
String className = fileName.substring(fileName.indexOf("com"), fileName.indexOf(".class"));
className = className.replace("\\",".");
//获取类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = XmlBeanDefinitionReader.class.getClassLoader();
try {
//加载类
Class<?> clazz = classLoader.loadClass(className);
//判断是否是切面类
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Aspect.class) && clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)){
//获取 @Pointcut 注解的值,并使用它作为键,将类存储在 advisorsCacheMap 中。
for (Method method : clazz.getDeclaredMethods()) {
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(Pointcut.class)) {
Pointcut pointcut = method.getAnnotation(Pointcut.class);
String pointcutExpression = pointcut.value();
if (!advisorsCacheMap.containsKey(pointcutExpression)) {
advisorsCacheMap.put(pointcutExpression, clazz);
}
}
}
continue;
}
//类是否有Component,Service,Controller,Repository注解
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class) || clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Controller.class) || clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Service.class) || clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Repository.class)){
Component componentAnnotation = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Component.class);
Controller controllerAnnotation = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Controller.class);
Service serviceAnnotation = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Service.class);
Repository repositoryAnnotation = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Repository.class);
String value = "";
//Bean定义类
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();
//判断注解是否有value值
if (componentAnnotation != null || controllerAnnotation != null || serviceAnnotation != null || repositoryAnnotation != null){
if (componentAnnotation != null && !componentAnnotation.value() .equals("")){
value = componentAnnotation.value();
}else if (controllerAnnotation != null && !controllerAnnotation.value().equals("")){
value = controllerAnnotation.value();
}else if (serviceAnnotation != null && !serviceAnnotation.value().equals("")){
value = serviceAnnotation.value();
} else if (repositoryAnnotation != null && !repositoryAnnotation.value().equals("")) {
value = repositoryAnnotation.value();
} else {
String name = clazz.getSimpleName();
//默认以开头小写的类名作为实例名
value = name.valueOf(name.charAt(0)).toLowerCase() + name.substring(1);
}
//不能重名
if (beanDefinitionMap.get(value) != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("spring IOC Container is already exists " + beanDefinitionMap.get(value));
}
beanDefinition.setClazz(clazz);
beanDefinition.setBeanName(value);
//保存到bean定义
beanDefinitionMap.put(value,beanDefinition);
//获取到该类实现的所有接口
Class[] interfaces = clazz.getInterfaces();
//在beanDefinitionMap中存储为一个接口对应一个实现类
for (Class anInterface : interfaces) {
String interfaceSimpleName = anInterface.getSimpleName();
interfaceSimpleName = interfaceSimpleName.valueOf(interfaceSimpleName.charAt(0)).toLowerCase() + interfaceSimpleName.substring(1);
beanDefinitionMap.put(interfaceSimpleName,beanDefinition);
}
}
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
else {
loadAllClass(beanFactory, file);
}
}
}
4.处理切面
最后就是处理切面,因为JDK代理要求目标类要实现接口,所以我使用CGLIB代理方便,先加入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>cglib</groupId>
<artifactId>cglib</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2</version>
</dependency>同样在DefaultListableBeanFactory加入处理切面的方法。
我们从advisorsCacheMap中拿到需要AOP的包,然后遍历InstanceMap,将里面的实例类改成代理的类,这个代理的类我们在MethodInterceptor中对其处理,获取切面类加了before注解的方法在目标类前执行,after在目标类后执行,更新InstanceMap,将里面的实例类更新为代理的类。
代码如下:
//处理切面
private void resolveInstantiationAspect() {
for (Map.Entry<String, Class<?>> entry : advisorsCacheMap.entrySet()) {
String packagePattern = entry.getKey();
Class<?> aspectClass = entry.getValue();
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> beanEntry : InstanceMap.entrySet()) {
Object bean = beanEntry.getValue();
String beanName = beanEntry.getKey();
if (bean.getClass().getPackage().getName().matches(packagePattern.replace("*", ".*"))) {
System.out.println("Applying aspect to bean: " + beanName);
// 创建 Enhancer 对象,用于生成代理类
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
// 设置目标类的父类,即被代理的类
enhancer.setSuperclass(bean.getClass());
// 设置回调,即拦截器
enhancer.setCallback(new CustomInterceptor(bean, aspectClass));
// 生成代理对象
Object proxy = enhancer.create();
InstanceMap.put(beanName, proxy);
}
}
}
}
// MethodInterceptor 实现类,用于处理方法调用
class CustomInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
private final Object target;
private final Class<?> aspectClass;
public CustomInterceptor(Object target, Class<?> aspectClass) {
this.target = target;
this.aspectClass = aspectClass;
}
@Override
public Object intercept(Object obj, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy proxy) throws Throwable {
Method beforeMethod = null;
Method afterMethod = null;
Method[] methods = aspectClass.getMethods();
for (Method m : methods) {
if (m.isAnnotationPresent(Before.class)) {
beforeMethod = m;
} else if (m.isAnnotationPresent(After.class)) {
afterMethod = m;
}
}
Object aspectInstance = null;
try {
aspectInstance = aspectClass.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
beforeMethod.invoke(aspectInstance);
// 调用目标对象的方法
Object result = proxy.invokeSuper(obj, args);
afterMethod.invoke(aspectInstance);
return result;
}
}然后调用就行
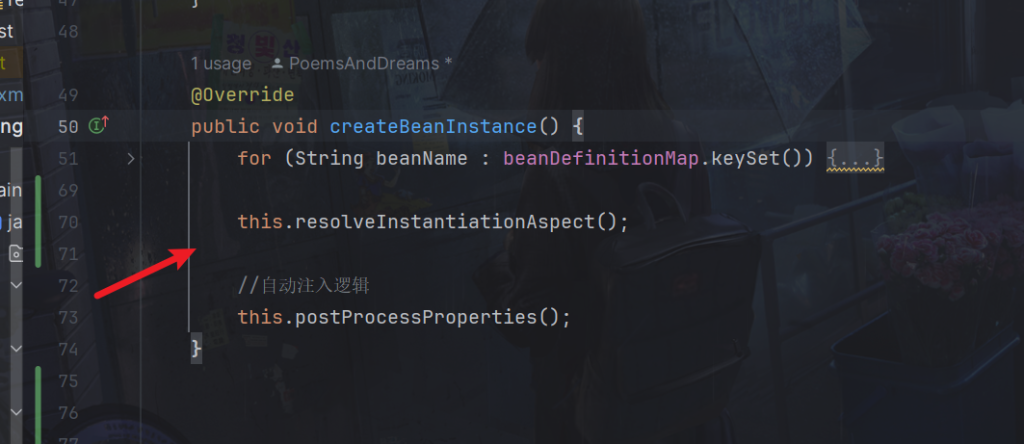
this.resolveInstantiationAspect();
同样在该类下,在实例化保存至InstanceMap后,在自动注入逻辑前
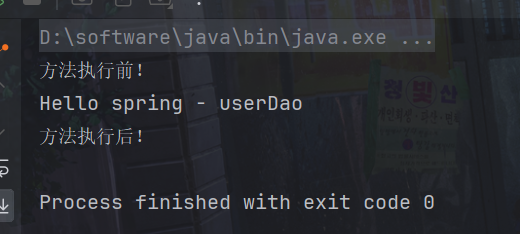
5.测试
在测试模块
添加切面类
package com.dreams.aspect;
import com.dreams.springframework.aspectj.annotation.After;
import com.dreams.springframework.aspectj.annotation.Aspect;
import com.dreams.springframework.aspectj.annotation.Before;
import com.dreams.springframework.aspectj.annotation.Pointcut;
import com.dreams.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author PoemsAndDreams
* @description //日志
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class MyAspect {
@Pointcut("com.dreams.service.impl")
public void pointCut(){}
@Before("pointCut()")
public void before(){
System.out.println("方法执行前!");
}
@After("pointCut()")
public void after(){
System.out.println("方法执行后!");
}
}注意这是我们的方法
运行测试