代码、内容参考来自于张秀宏大佬的自己动手写Java虚拟机 (Java核心技术系列)以及尚硅谷宋红康:JVM全套教程。
我们先编写一个简单的解释器。目前只能执行一个Java方法,在后面再不
断完善它。
1.整体代码
在/目录下创建interpreter.go文件,在其中定义interpret()函数,代码如下:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"jvmgo/ch05/classfile"
"jvmgo/ch05/instructions"
"jvmgo/ch05/instructions/base"
"jvmgo/ch05/rtda"
)
func interpret(methodInfo *classfile.MemberInfo) {
codeAttr := methodInfo.CodeAttribute()
maxLocals := codeAttr.MaxLocals()
maxStack := codeAttr.MaxStack()
bytecode := codeAttr.Code()
thread := rtda.NewThread()
frame := thread.NewFrame(maxLocals, maxStack)
thread.PushFrame(frame)
defer catchErr(frame)
loop(thread, bytecode)
}
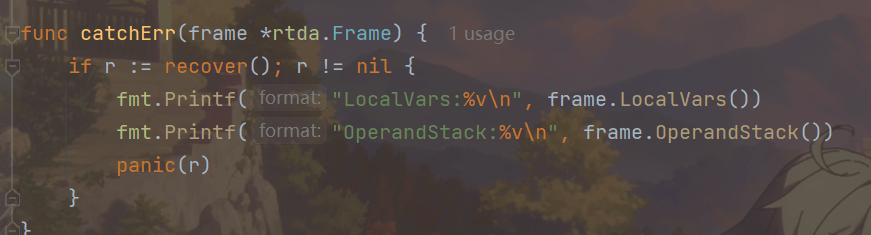
func catchErr(frame *rtda.Frame) {
if r := recover(); r != nil {
fmt.Printf("LocalVars:%v\n", frame.LocalVars())
fmt.Printf("OperandStack:%v\n", frame.OperandStack())
panic(r)
}
}
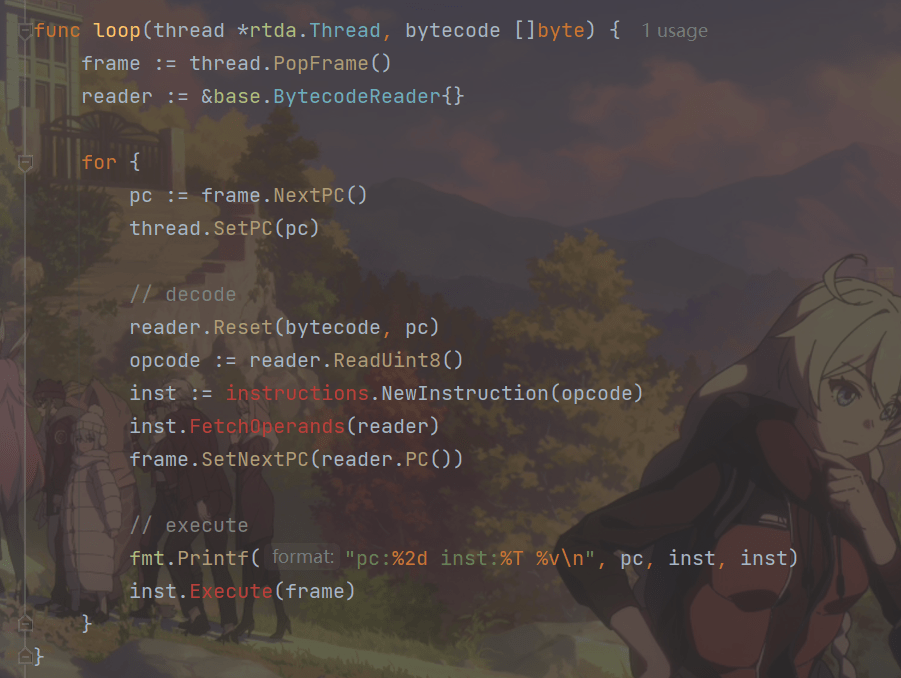
func loop(thread *rtda.Thread, bytecode []byte) {
frame := thread.PopFrame()
reader := &base.BytecodeReader{}
for {
pc := frame.NextPC()
thread.SetPC(pc)
// decode
reader.Reset(bytecode, pc)
opcode := reader.ReadUint8()
inst := instructions.NewInstruction(opcode)
inst.FetchOperands(reader)
frame.SetNextPC(reader.PC())
// execute
fmt.Printf("pc:%2d inst:%T %v\n", pc, inst, inst)
inst.Execute(frame)
}
}
interpret()方法的参数是MemberInfo指针,调用MemberInfo结构体的CodeAttribute()方法可以获取它的Code属性。
CodeAttribute()方法是新增加的,代码在ch05\classfile\member_info.go文件中,代码如下:
func (self *MemberInfo) CodeAttribute() *CodeAttribute {
for _, attrInfo := range self.attributes {
switch attrInfo.(type) {
case *CodeAttribute:
return attrInfo.(*CodeAttribute)
}
}
return nil
}
得到Code属性之后,可以进一步获得执行方法所需的局部变量表和操作数栈空间,以及方法的字节码。interpret()方法的其余代码先创建一个Thread实例,然后创建一个帧并把它推入Java虚拟机栈顶,最后执行方法。完整的代码如下:
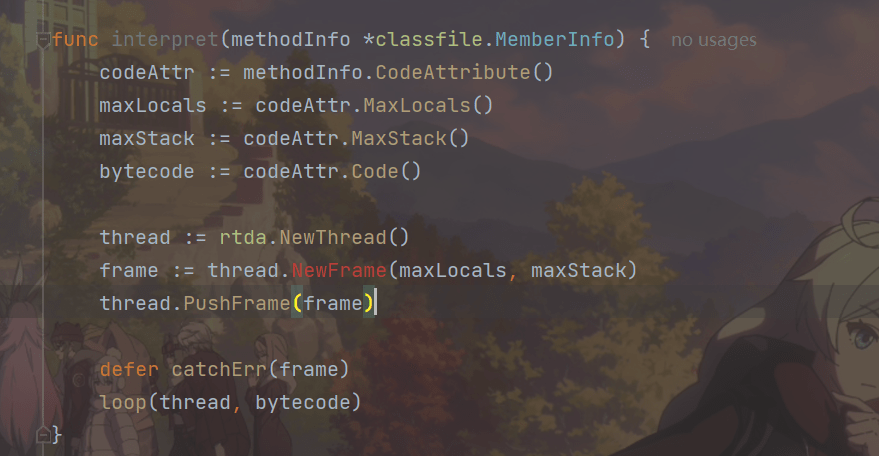
Thread结构体的NewFrame()方法是新增加的,代码在ch05\rtda\thread.go文件中,如下所示:
func (self *Thread) NewFrame(maxLocals, maxStack uint) *Frame {
return newFrame(self, maxLocals, maxStack)
}Frame结构体也有变化,增加了两个字段这两个字段主要是为了实现跳转指令Branch()方法而添加的,以及和Getter方法,Frame结构体的newFrame()方法也相应发生了变化,改动如下(在ch05\rtda\frame.go文件中):
package rtda
// stack frame
type Frame struct {
lower *Frame // stack is implemented as linked list
localVars LocalVars
operandStack *OperandStack
thread *Thread
nextPC int // the next instruction after the call
}
func newFrame(thread *Thread, maxLocals, maxStack uint) *Frame {
return &Frame{
thread: thread,
localVars: newLocalVars(maxLocals),
operandStack: newOperandStack(maxStack),
}
}
// getters & setters
func (self *Frame) LocalVars() LocalVars {
return self.localVars
}
func (self *Frame) OperandStack() *OperandStack {
return self.operandStack
}
func (self *Frame) Thread() *Thread {
return self.thread
}
func (self *Frame) NextPC() int {
return self.nextPC
}
func (self *Frame) SetNextPC(nextPC int) {
self.nextPC = nextPC
}
回到interpret()方法,我们的解释器目前还没有办法优雅地结束运行。因为每个方法的最后一条指令都是某个return指令,而还没有实现return指令,所以方法在执行过程中必定会出现错误,此时解释器逻辑会转到catchErr()函数,把局部变量表和操作数栈的内容打印出来,以此来观察方法的执行结果。
loop()函数循环执行“计算pc、解码指令、执行指令”这三个步骤,直到遇到错误!
NewInstruction()。这个函数是switch-case语句,根据操作码创建具体的指令,代码在instructions\factory.go文件中,如下所示:
package instructions
import "fmt"
import "jvmgo/ch05/instructions/base"
import . "jvmgo/ch05/instructions/comparisons"
import . "jvmgo/ch05/instructions/constants"
import . "jvmgo/ch05/instructions/control"
import . "jvmgo/ch05/instructions/conversions"
import . "jvmgo/ch05/instructions/extended"
import . "jvmgo/ch05/instructions/loads"
import . "jvmgo/ch05/instructions/math"
import . "jvmgo/ch05/instructions/stack"
import . "jvmgo/ch05/instructions/stores"
// NoOperandsInstruction singletons
var (
nop = &NOP{}
aconst_null = &ACONST_NULL{}
iconst_m1 = &ICONST_M1{}
iconst_0 = &ICONST_0{}
iconst_1 = &ICONST_1{}
iconst_2 = &ICONST_2{}
iconst_3 = &ICONST_3{}
iconst_4 = &ICONST_4{}
iconst_5 = &ICONST_5{}
lconst_0 = &LCONST_0{}
lconst_1 = &LCONST_1{}
fconst_0 = &FCONST_0{}
fconst_1 = &FCONST_1{}
fconst_2 = &FCONST_2{}
dconst_0 = &DCONST_0{}
dconst_1 = &DCONST_1{}
iload_0 = &ILOAD_0{}
iload_1 = &ILOAD_1{}
iload_2 = &ILOAD_2{}
iload_3 = &ILOAD_3{}
lload_0 = &LLOAD_0{}
lload_1 = &LLOAD_1{}
lload_2 = &LLOAD_2{}
lload_3 = &LLOAD_3{}
fload_0 = &FLOAD_0{}
fload_1 = &FLOAD_1{}
fload_2 = &FLOAD_2{}
fload_3 = &FLOAD_3{}
dload_0 = &DLOAD_0{}
dload_1 = &DLOAD_1{}
dload_2 = &DLOAD_2{}
dload_3 = &DLOAD_3{}
aload_0 = &ALOAD_0{}
aload_1 = &ALOAD_1{}
aload_2 = &ALOAD_2{}
aload_3 = &ALOAD_3{}
// iaload = &IALOAD{}
// laload = &LALOAD{}
// faload = &FALOAD{}
// daload = &DALOAD{}
// aaload = &AALOAD{}
// baload = &BALOAD{}
// caload = &CALOAD{}
// saload = &SALOAD{}
istore_0 = &ISTORE_0{}
istore_1 = &ISTORE_1{}
istore_2 = &ISTORE_2{}
istore_3 = &ISTORE_3{}
lstore_0 = &LSTORE_0{}
lstore_1 = &LSTORE_1{}
lstore_2 = &LSTORE_2{}
lstore_3 = &LSTORE_3{}
fstore_0 = &FSTORE_0{}
fstore_1 = &FSTORE_1{}
fstore_2 = &FSTORE_2{}
fstore_3 = &FSTORE_3{}
dstore_0 = &DSTORE_0{}
dstore_1 = &DSTORE_1{}
dstore_2 = &DSTORE_2{}
dstore_3 = &DSTORE_3{}
astore_0 = &ASTORE_0{}
astore_1 = &ASTORE_1{}
astore_2 = &ASTORE_2{}
astore_3 = &ASTORE_3{}
// iastore = &IASTORE{}
// lastore = &LASTORE{}
// fastore = &FASTORE{}
// dastore = &DASTORE{}
// aastore = &AASTORE{}
// bastore = &BASTORE{}
// castore = &CASTORE{}
// sastore = &SASTORE{}
pop = &POP{}
pop2 = &POP2{}
dup = &DUP{}
dup_x1 = &DUP_X1{}
dup_x2 = &DUP_X2{}
dup2 = &DUP2{}
dup2_x1 = &DUP2_X1{}
dup2_x2 = &DUP2_X2{}
swap = &SWAP{}
iadd = &IADD{}
ladd = &LADD{}
fadd = &FADD{}
dadd = &DADD{}
isub = &ISUB{}
lsub = &LSUB{}
fsub = &FSUB{}
dsub = &DSUB{}
imul = &IMUL{}
lmul = &LMUL{}
fmul = &FMUL{}
dmul = &DMUL{}
idiv = &IDIV{}
ldiv = &LDIV{}
fdiv = &FDIV{}
ddiv = &DDIV{}
irem = &IREM{}
lrem = &LREM{}
frem = &FREM{}
drem = &DREM{}
ineg = &INEG{}
lneg = &LNEG{}
fneg = &FNEG{}
dneg = &DNEG{}
ishl = &ISHL{}
lshl = &LSHL{}
ishr = &ISHR{}
lshr = &LSHR{}
iushr = &IUSHR{}
lushr = &LUSHR{}
iand = &IAND{}
land = &LAND{}
ior = &IOR{}
lor = &LOR{}
ixor = &IXOR{}
lxor = &LXOR{}
i2l = &I2L{}
i2f = &I2F{}
i2d = &I2D{}
l2i = &L2I{}
l2f = &L2F{}
l2d = &L2D{}
f2i = &F2I{}
f2l = &F2L{}
f2d = &F2D{}
d2i = &D2I{}
d2l = &D2L{}
d2f = &D2F{}
i2b = &I2B{}
i2c = &I2C{}
i2s = &I2S{}
lcmp = &LCMP{}
fcmpl = &FCMPL{}
fcmpg = &FCMPG{}
dcmpl = &DCMPL{}
dcmpg = &DCMPG{}
// ireturn = &IRETURN{}
// lreturn = &LRETURN{}
// freturn = &FRETURN{}
// dreturn = &DRETURN{}
// areturn = &ARETURN{}
// _return = &RETURN{}
// arraylength = &ARRAY_LENGTH{}
// athrow = &ATHROW{}
// monitorenter = &MONITOR_ENTER{}
// monitorexit = &MONITOR_EXIT{}
// invoke_native = &INVOKE_NATIVE{}
)
func NewInstruction(opcode byte) base.Instruction {
switch opcode {
case 0x00:
return nop
case 0x01:
return aconst_null
case 0x02:
return iconst_m1
case 0x03:
return iconst_0
case 0x04:
return iconst_1
case 0x05:
return iconst_2
case 0x06:
return iconst_3
case 0x07:
return iconst_4
case 0x08:
return iconst_5
case 0x09:
return lconst_0
case 0x0a:
return lconst_1
case 0x0b:
return fconst_0
case 0x0c:
return fconst_1
case 0x0d:
return fconst_2
case 0x0e:
return dconst_0
case 0x0f:
return dconst_1
case 0x10:
return &BIPUSH{}
case 0x11:
return &SIPUSH{}
// case 0x12:
// return &LDC{}
// case 0x13:
// return &LDC_W{}
// case 0x14:
// return &LDC2_W{}
case 0x15:
return &ILOAD{}
case 0x16:
return &LLOAD{}
case 0x17:
return &FLOAD{}
case 0x18:
return &DLOAD{}
case 0x19:
return &ALOAD{}
case 0x1a:
return iload_0
case 0x1b:
return iload_1
case 0x1c:
return iload_2
case 0x1d:
return iload_3
case 0x1e:
return lload_0
case 0x1f:
return lload_1
case 0x20:
return lload_2
case 0x21:
return lload_3
case 0x22:
return fload_0
case 0x23:
return fload_1
case 0x24:
return fload_2
case 0x25:
return fload_3
case 0x26:
return dload_0
case 0x27:
return dload_1
case 0x28:
return dload_2
case 0x29:
return dload_3
case 0x2a:
return aload_0
case 0x2b:
return aload_1
case 0x2c:
return aload_2
case 0x2d:
return aload_3
// case 0x2e:
// return iaload
// case 0x2f:
// return laload
// case 0x30:
// return faload
// case 0x31:
// return daload
// case 0x32:
// return aaload
// case 0x33:
// return baload
// case 0x34:
// return caload
// case 0x35:
// return saload
case 0x36:
return &ISTORE{}
case 0x37:
return &LSTORE{}
case 0x38:
return &FSTORE{}
case 0x39:
return &DSTORE{}
case 0x3a:
return &ASTORE{}
case 0x3b:
return istore_0
case 0x3c:
return istore_1
case 0x3d:
return istore_2
case 0x3e:
return istore_3
case 0x3f:
return lstore_0
case 0x40:
return lstore_1
case 0x41:
return lstore_2
case 0x42:
return lstore_3
case 0x43:
return fstore_0
case 0x44:
return fstore_1
case 0x45:
return fstore_2
case 0x46:
return fstore_3
case 0x47:
return dstore_0
case 0x48:
return dstore_1
case 0x49:
return dstore_2
case 0x4a:
return dstore_3
case 0x4b:
return astore_0
case 0x4c:
return astore_1
case 0x4d:
return astore_2
case 0x4e:
return astore_3
// case 0x4f:
// return iastore
// case 0x50:
// return lastore
// case 0x51:
// return fastore
// case 0x52:
// return dastore
// case 0x53:
// return aastore
// case 0x54:
// return bastore
// case 0x55:
// return castore
// case 0x56:
// return sastore
case 0x57:
return pop
case 0x58:
return pop2
case 0x59:
return dup
case 0x5a:
return dup_x1
case 0x5b:
return dup_x2
case 0x5c:
return dup2
case 0x5d:
return dup2_x1
case 0x5e:
return dup2_x2
case 0x5f:
return swap
case 0x60:
return iadd
case 0x61:
return ladd
case 0x62:
return fadd
case 0x63:
return dadd
case 0x64:
return isub
case 0x65:
return lsub
case 0x66:
return fsub
case 0x67:
return dsub
case 0x68:
return imul
case 0x69:
return lmul
case 0x6a:
return fmul
case 0x6b:
return dmul
case 0x6c:
return idiv
case 0x6d:
return ldiv
case 0x6e:
return fdiv
case 0x6f:
return ddiv
case 0x70:
return irem
case 0x71:
return lrem
case 0x72:
return frem
case 0x73:
return drem
case 0x74:
return ineg
case 0x75:
return lneg
case 0x76:
return fneg
case 0x77:
return dneg
case 0x78:
return ishl
case 0x79:
return lshl
case 0x7a:
return ishr
case 0x7b:
return lshr
case 0x7c:
return iushr
case 0x7d:
return lushr
case 0x7e:
return iand
case 0x7f:
return land
case 0x80:
return ior
case 0x81:
return lor
case 0x82:
return ixor
case 0x83:
return lxor
case 0x84:
return &IINC{}
case 0x85:
return i2l
case 0x86:
return i2f
case 0x87:
return i2d
case 0x88:
return l2i
case 0x89:
return l2f
case 0x8a:
return l2d
case 0x8b:
return f2i
case 0x8c:
return f2l
case 0x8d:
return f2d
case 0x8e:
return d2i
case 0x8f:
return d2l
case 0x90:
return d2f
case 0x91:
return i2b
case 0x92:
return i2c
case 0x93:
return i2s
case 0x94:
return lcmp
case 0x95:
return fcmpl
case 0x96:
return fcmpg
case 0x97:
return dcmpl
case 0x98:
return dcmpg
case 0x99:
return &IFEQ{}
case 0x9a:
return &IFNE{}
case 0x9b:
return &IFLT{}
case 0x9c:
return &IFGE{}
case 0x9d:
return &IFGT{}
case 0x9e:
return &IFLE{}
case 0x9f:
return &IF_ICMPEQ{}
case 0xa0:
return &IF_ICMPNE{}
case 0xa1:
return &IF_ICMPLT{}
case 0xa2:
return &IF_ICMPGE{}
case 0xa3:
return &IF_ICMPGT{}
case 0xa4:
return &IF_ICMPLE{}
case 0xa5:
return &IF_ACMPEQ{}
case 0xa6:
return &IF_ACMPNE{}
case 0xa7:
return &GOTO{}
// case 0xa8:
// return &JSR{}
// case 0xa9:
// return &RET{}
case 0xaa:
return &TABLE_SWITCH{}
case 0xab:
return &LOOKUP_SWITCH{}
// case 0xac:
// return ireturn
// case 0xad:
// return lreturn
// case 0xae:
// return freturn
// case 0xaf:
// return dreturn
// case 0xb0:
// return areturn
// case 0xb1:
// return _return
// case 0xb2:
// return &GET_STATIC{}
// case 0xb3:
// return &PUT_STATIC{}
// case 0xb4:
// return &GET_FIELD{}
// case 0xb5:
// return &PUT_FIELD{}
// case 0xb6:
// return &INVOKE_VIRTUAL{}
// case 0xb7:
// return &INVOKE_SPECIAL{}
// case 0xb8:
// return &INVOKE_STATIC{}
// case 0xb9:
// return &INVOKE_INTERFACE{}
// case 0xba:
// return &INVOKE_DYNAMIC{}
// case 0xbb:
// return &NEW{}
// case 0xbc:
// return &NEW_ARRAY{}
// case 0xbd:
// return &ANEW_ARRAY{}
// case 0xbe:
// return arraylength
// case 0xbf:
// return athrow
// case 0xc0:
// return &CHECK_CAST{}
// case 0xc1:
// return &INSTANCE_OF{}
// case 0xc2:
// return monitorenter
// case 0xc3:
// return monitorexit
case 0xc4:
return &WIDE{}
// case 0xc5:
// return &MULTI_ANEW_ARRAY{}
case 0xc6:
return &IFNULL{}
case 0xc7:
return &IFNONNULL{}
case 0xc8:
return &GOTO_W{}
// case 0xc9:
// return &JSR_W{}
// case 0xca: breakpoint
// case 0xfe: impdep1
// case 0xff: impdep2
default:
panic(fmt.Errorf("Unsupported opcode: 0x%x!", opcode))
}
}有很大一部分指令是没有操作数的,所以没有必要每次都创建不同的实例。为了优化,可以给这些指令定义单例变量,
如:
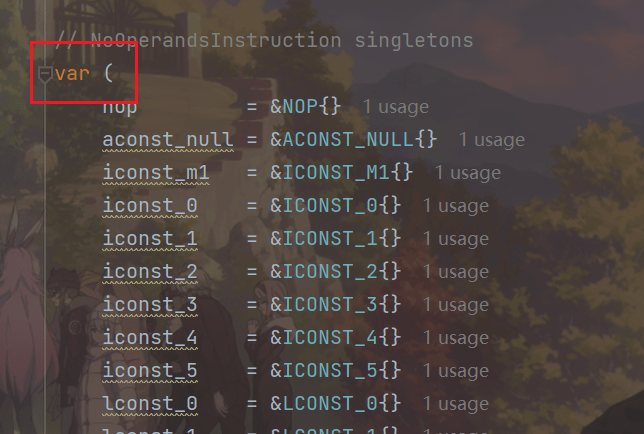
对于这类指令,在NewInstruction()函数中直接返回单例变量即可,代码如下:
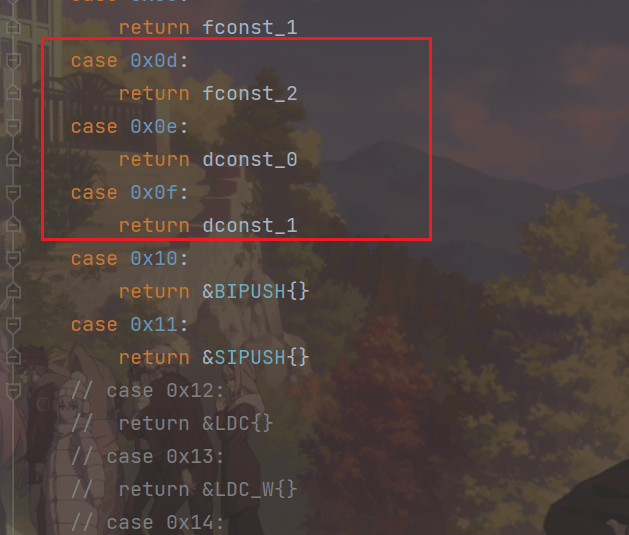
2.测试代码
考验一下虚拟机是否可以工作。代码如下:
java代码:
package jvmgo.book.ch03;
public class GaussShu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
sum += i;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
下面改造main.go文件。首先修改import语句,代码如下:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"jvmgo/ch05/classfile"
"jvmgo/ch05/classpath"
"strings"
)
func main() {
cmd := parseCmd()
if cmd.versionFlag {
fmt.Println("version 0.0.1")
} else if cmd.helpFlag || cmd.class == "" {
printUsage()
} else {
startJVM(cmd)
}
}
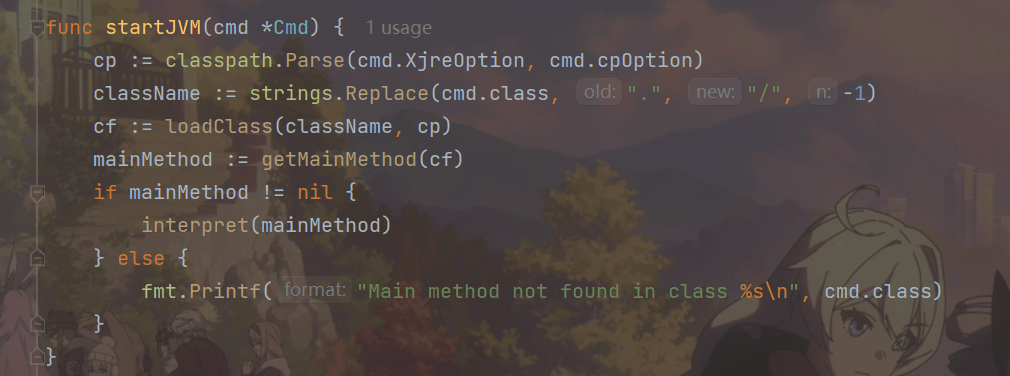
func startJVM(cmd *Cmd) {
cp := classpath.Parse(cmd.XjreOption, cmd.cpOption)
className := strings.Replace(cmd.class, ".", "/", -1)
cf := loadClass(className, cp)
mainMethod := getMainMethod(cf)
if mainMethod != nil {
interpret(mainMethod)
} else {
fmt.Printf("Main method not found in class %s\n", cmd.class)
}
}
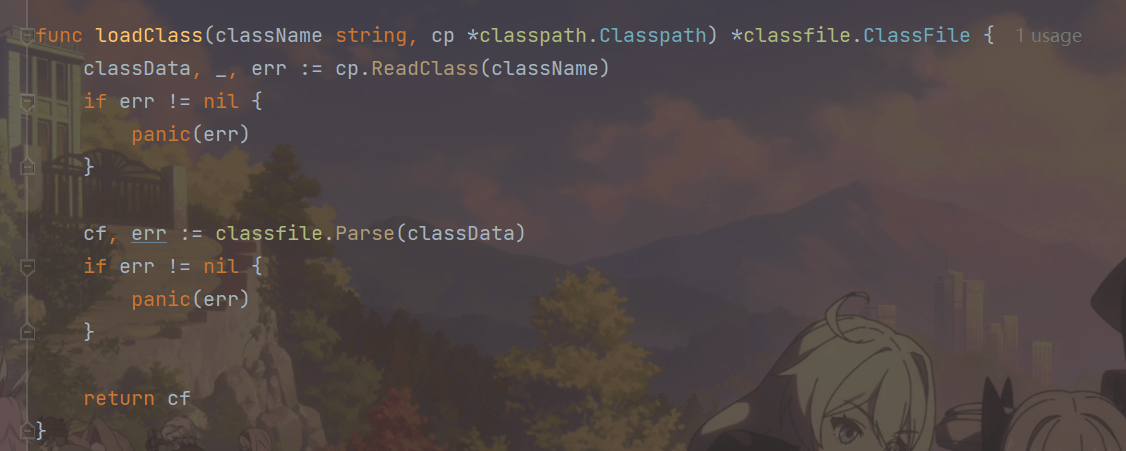
func loadClass(className string, cp *classpath.Classpath) *classfile.ClassFile {
classData, _, err := cp.ReadClass(className)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cf, err := classfile.Parse(classData)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
return cf
}
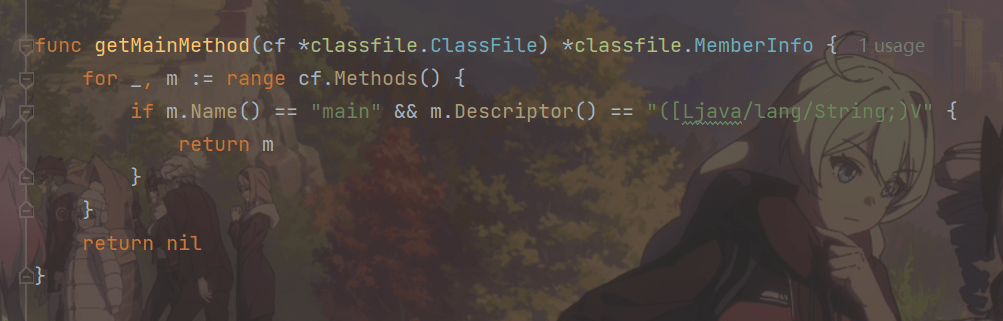
func getMainMethod(cf *classfile.ClassFile) *classfile.MemberInfo {
for _, m := range cf.Methods() {
if m.Name() == "main" && m.Descriptor() == "([Ljava/lang/String;)V" {
return m
}
}
return nil
}
main函数不变,修改startJVM()函数,startJVM()首先调用loadClass()方法读取并解析class文件,然后调用getMainMethod()函数查找类的main()方法,最后调用interpret()函数解释执行main方法。
loadClass()函数的代码如下:
getMainMethod()函数的代码如下:
打开命令行窗口,执行下面的命令编译本章代码。
go install jvmgo\ch05
我将class文件放到这
ch05 -classpath D:\MAT_log -Xjre "D:\software\java\jre" GaussShu
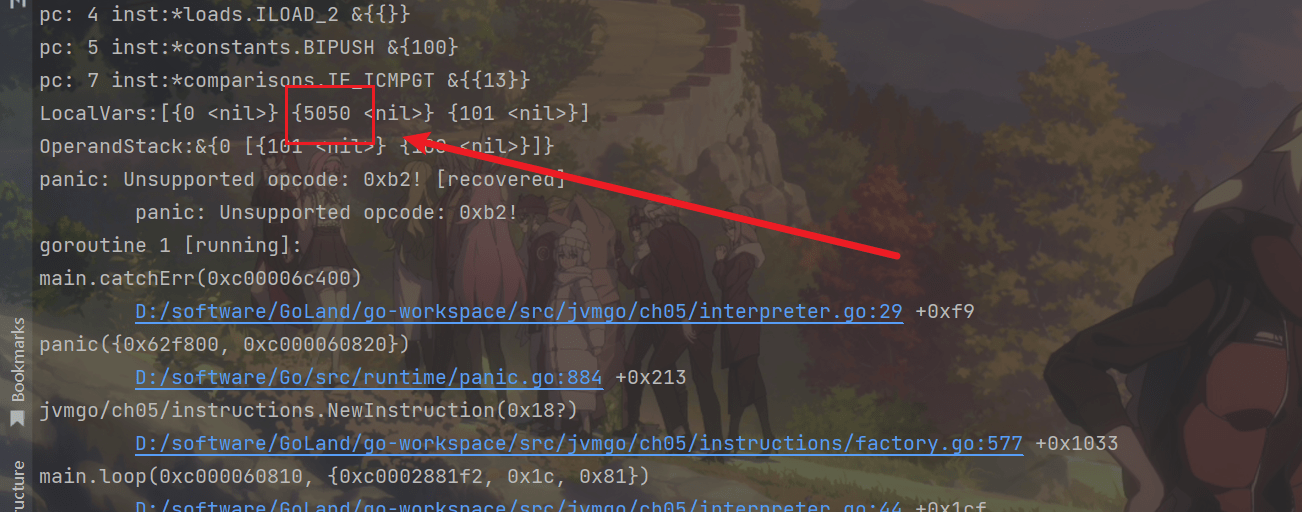
方法执行的最后出现了错误,是正常的,局部变量表和操作数栈的状态也打印了出来,但可以看到5050这个数字。
3.参考
尚硅谷宋红康:JVM全套教程:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PJ411n7xZ
周志明:深入理解java虚拟机
张秀宏:自己动手写Java虚拟机 (Java核心技术系列)