1.概述
Gin 是一个用于构建 Web 应用程序的轻量级 Go 语言框架。它提供了一种快速、高效的方式来创建具有路由、中间件、参数绑定等功能的 Web 服务器。
2.简单例子
新建一个Go项目
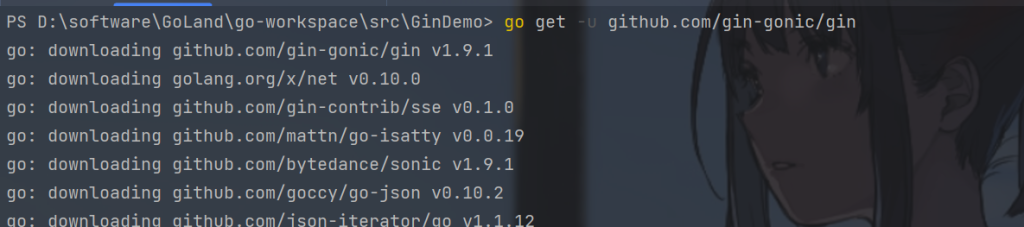
导入Gin
go get -u github.com/gin-gonic/gin
main.go代码
创建一个简单的服务
package main
import "github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
func main() {
//创建一个服务
ginServer := gin.Default()
//访问地址,处理请求
ginServer.GET("/test", func(context *gin.Context) {
context.JSON(200, gin.H{"msg": "hello world"})
})
//服务器端口
ginServer.Run(":8082")
}ginServer 是一个 *gin.Engine 类型的变量,表示一个 Gin 引擎实例。如果需要传递使用 *gin.Engine 类型。
gin.H是Gin框架中的一个默认HTTP头信息映射。类似java我们经常会定义一个Result对象返回给前端,context.JSON方法是Gin框架中的一个HTTP响应辅助函数,用于将数据以JSON格式返回给客户端。类似java的注解
ginServer.Run(“:8082”) 是使用 Gin 框架启动一个 HTTP 服务器,监听来自端口 8082 的请求。
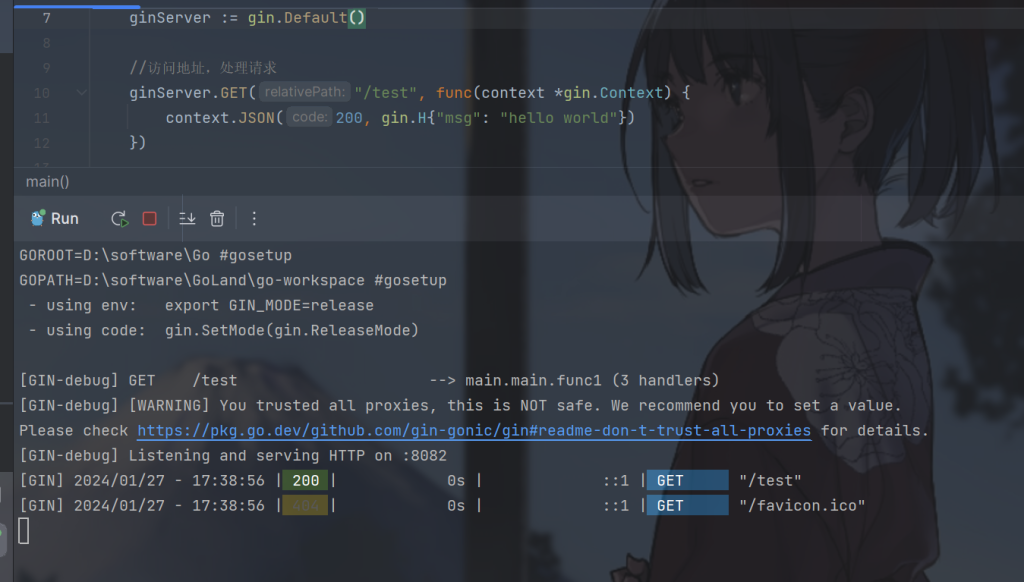
3.请求响应
Get请求
ginServer.GET("/test", func(context *gin.Context) {
context.JSON(200, gin.H{"msg": "hello world"})
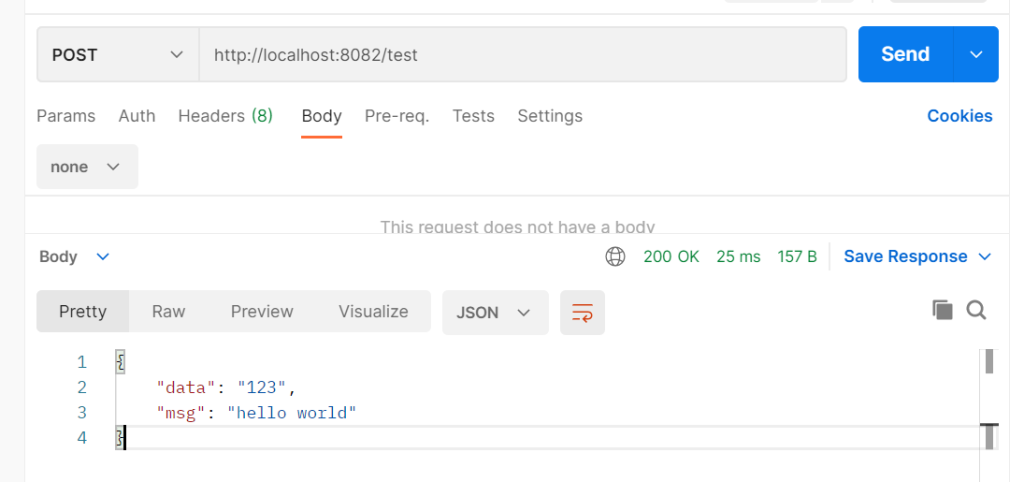
})ginServer.POST("/test", func(context *gin.Context) {
context.JSON(200, gin.H{"msg": "hello world", "data": "123"})
})
ginServer.PUT("/put", func(context *gin.Context) {
// 业务
})
ginServer.DELETE("/delete", func(context *gin.Context) {
// 业务
})func get(context *gin.Context) {
context.JSON(200, gin.H{"msg": "hello world", "data": "123"})
}//访问地址,处理请求
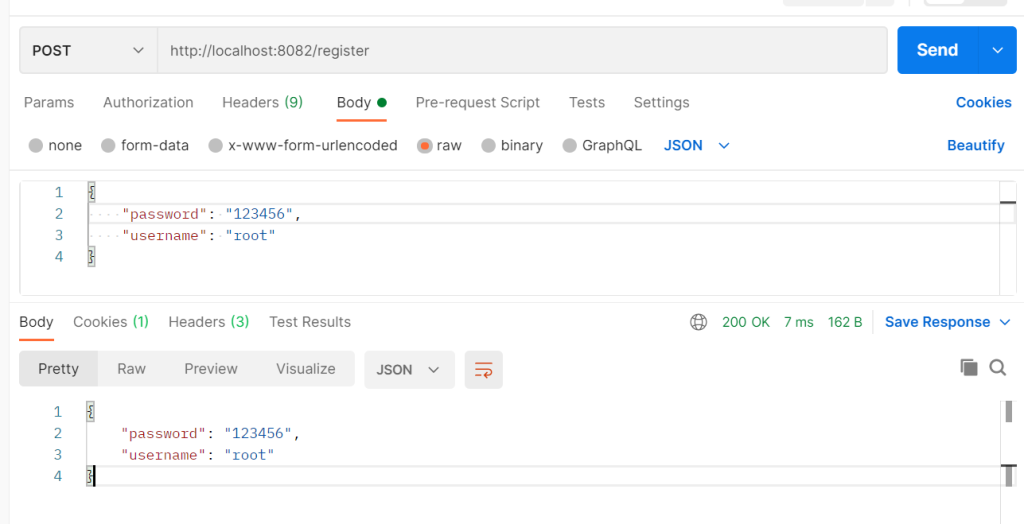
ginServer.GET("/test", get)ginServer.POST("/register", func(context *gin.Context) {
data, err := context.GetRawData()
if err != nil {
context.JSON(400, gin.H{"msg": "发生未知错误"})
}
var dataByQ map[string]any
error := json.Unmarshal(data, &dataByQ)
if error != nil {
context.JSON(400, gin.H{"msg": "发生未知错误"})
}
context.JSON(200, dataByQ)
})
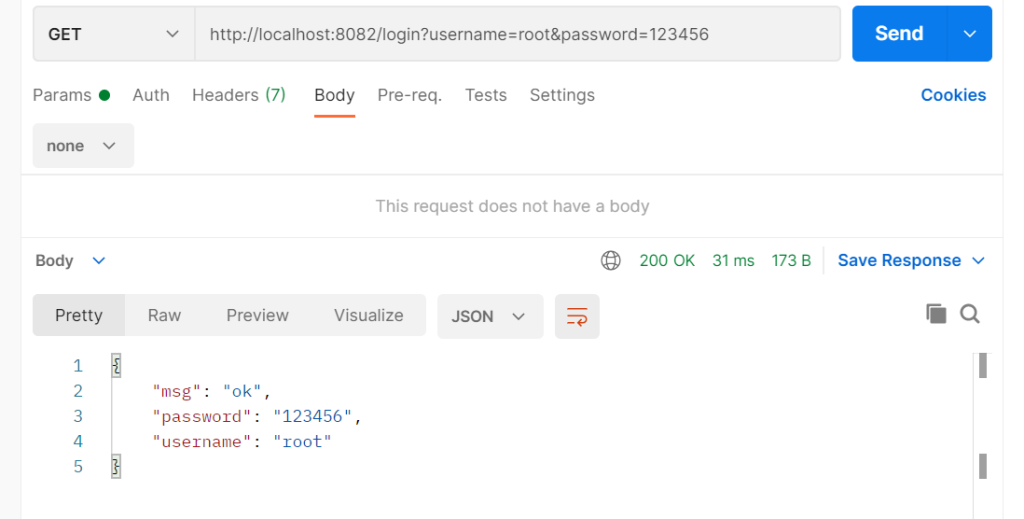
//http://localhost:8082/login?username=root&password=123456
ginServer.GET("/login", func(context *gin.Context) {
username := context.Query("username")
password := context.Query("password")
context.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"username": username,
"password": password,
"msg": "ok",
})
})
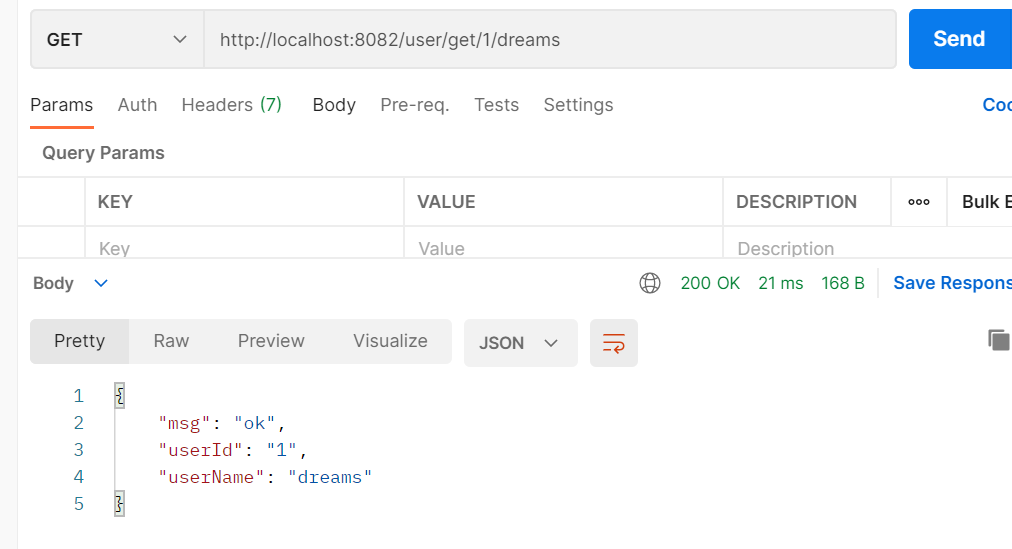
//http://localhost:8082/user/get/1/dreams
ginServer.GET("/user/get/:userId/:userName", func(context *gin.Context) {
userId := context.Param("userId")
userName := context.Param("userName")
context.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"userId": userId,
"userName": userName,
"msg": "ok",
})
})
3.页面响应
新建一个目录templates存放前端
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Go</title> </head> <body> <h1>Hello Go And Gin!</h1> </body> </html>
新建一个目录存放资源目录
index.css
body{
background: cadetblue;
}index.js
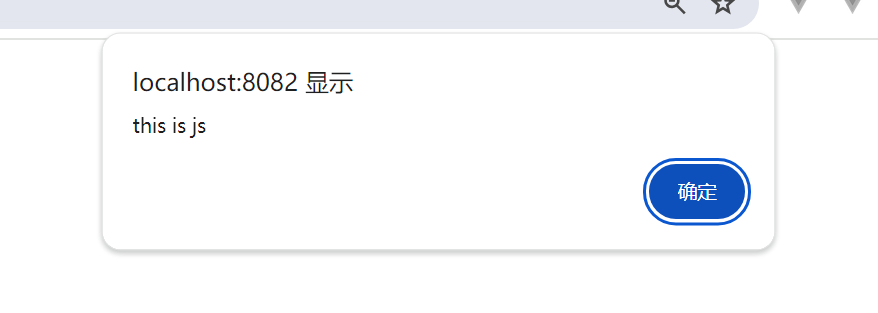
alert("this is js")
页面响应
//加载静态页面
//全局加载该目录下文件
ginServer.LoadHTMLGlob("templates/*")
//加载指定前端页面
//ginServer.LoadHTMLFiles("templates/index.html")
//加载资源目录
ginServer.Static("/static", "./static")
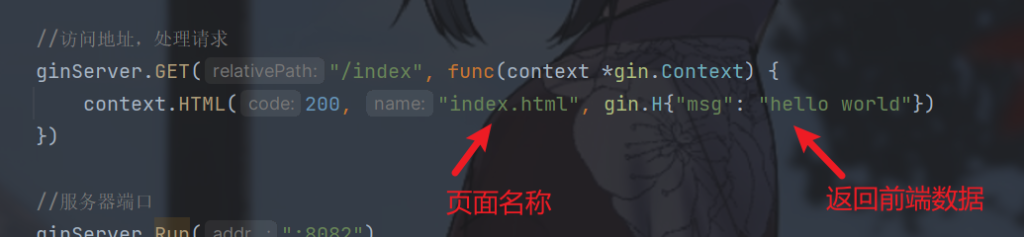
//访问地址,处理请求
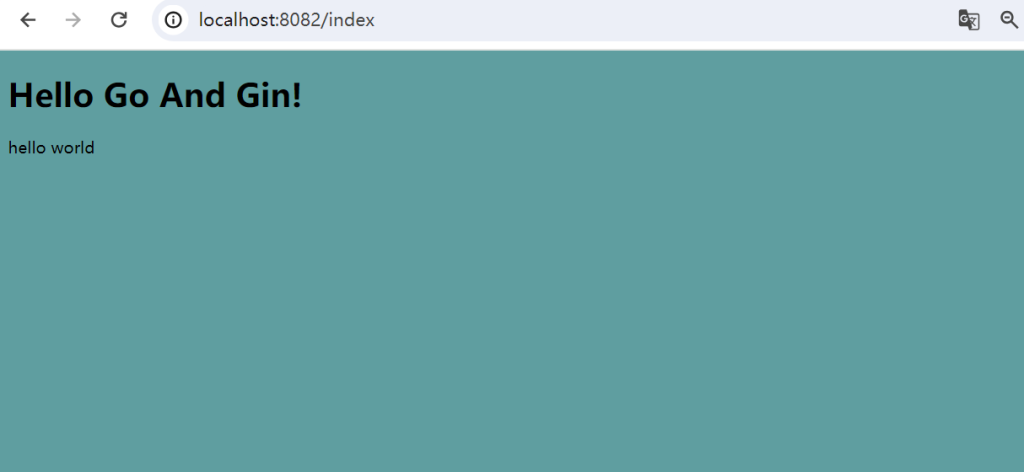
ginServer.GET("/index", func(context *gin.Context) {
context.HTML(200, "index.html", gin.H{"msg": "hello world"})
})
前端想要获取后端传的数据只要
{{.msg}}如:
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Go</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello Go And Gin!</h1>
{{.msg}}
</body>
</html>
导入资源语法没变
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/css/index.css">
<script src="/static/js/index.js"></script>
<title>Go</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello Go And Gin!</h1>
{{.msg}}
</body>
</html>
访问http://localhost:8082/index
4.处理表单
前端
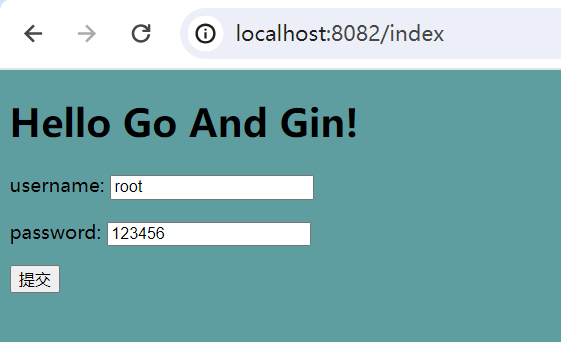
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/css/index.css"> <script src="/static/js/index.js"></script> <title>Go</title> </head> <body> <h1>Hello Go And Gin!</h1> <form action="/user/login" method="post"> <P>username: <input type="text" name="username"></P> <P>password: <input type="text" name="passwoed"></P> <button type="submit">提交</button> </form> </body> </html>
使用post请求
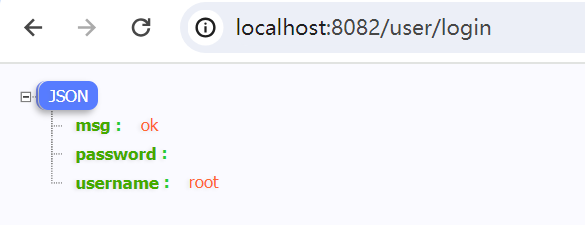
ginServer.POST("/user/login", func(context *gin.Context) {
username := context.PostForm("username")
password := context.PostForm("password")
context.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"username": username,
"password": password,
"msg": "ok",
})
})context.PostForm 是 Gin 框架中的方法,用于从 POST 请求中获取表单参数的取值。
访问http://localhost:8082/index
跳转之后
5.绑定对象与校验
还有一种方式就是绑定,绑定一个form表单
type loginRequest struct {
Username string `form:"username"`
Password string `form:"password"`
}
func login(c *gin.Context) {
req := loginRequest{}
c.Bind(&req)
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, req)
}c.Bind(&req)是绑定post请求,c.BindQuery(&req)是绑定get请求
注意:
这里绑定使用反引号
同时要求结构体的属性要大写,才能绑定成功
Go 开发规范认为:只有开头是大写字母的对象,方法才被认为是公开的,可以在包外访问,否则就是私有的,外部对象无法访问。
一样传入
ginServer.POST("/login/band", login)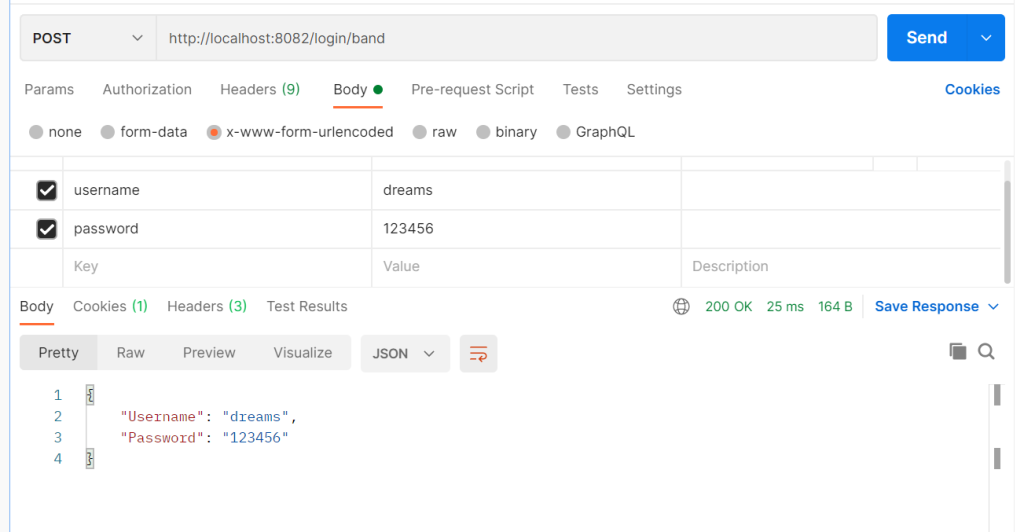
我们加上gin框架自带的校验
type registerRequest struct {
Username string `form:"username" binding:"required"`
Password string `form:"password" binding:"required"`
Phone string `form:"phone" binding:"required,e164"`
Email string `form:"email" binding:"omitempty,email"`
}
func register(c *gin.Context) {
req := registerRequest{}
err := c.ShouldBind(&req)
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{
"msg": err.Error(),
})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, req)
}与 c.Bind() 方法不同的是,c.ShouldBind() 方法会返回一个err来处理
required就是必须传入,omitempty,是可以为空,e164是Gin框架对手机号的校验,email是Gin框架对email的校验。
同样传入
ginServer.POST("/register/band", register)这是错误示例
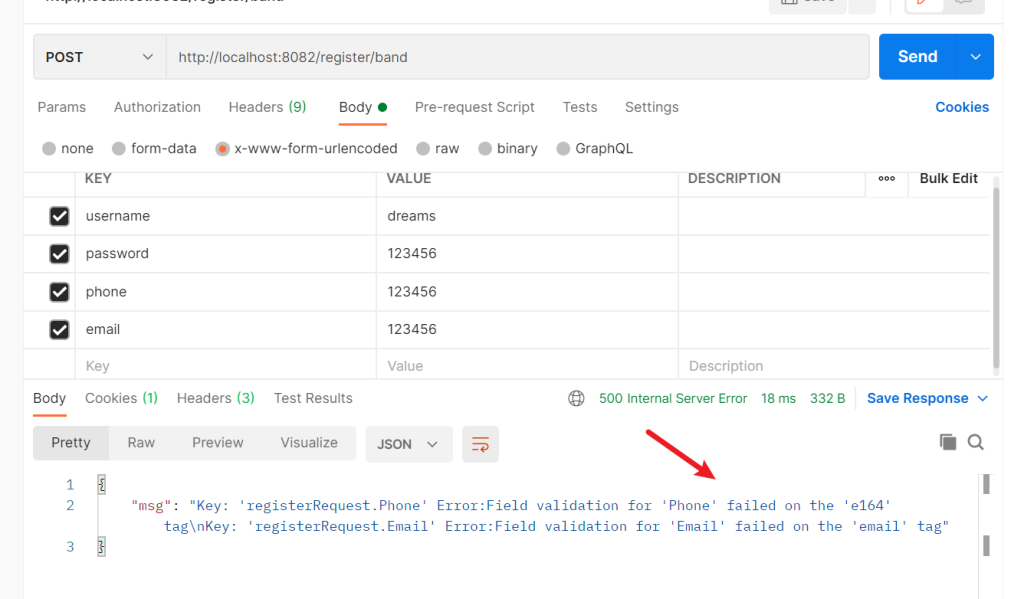
email可以为空
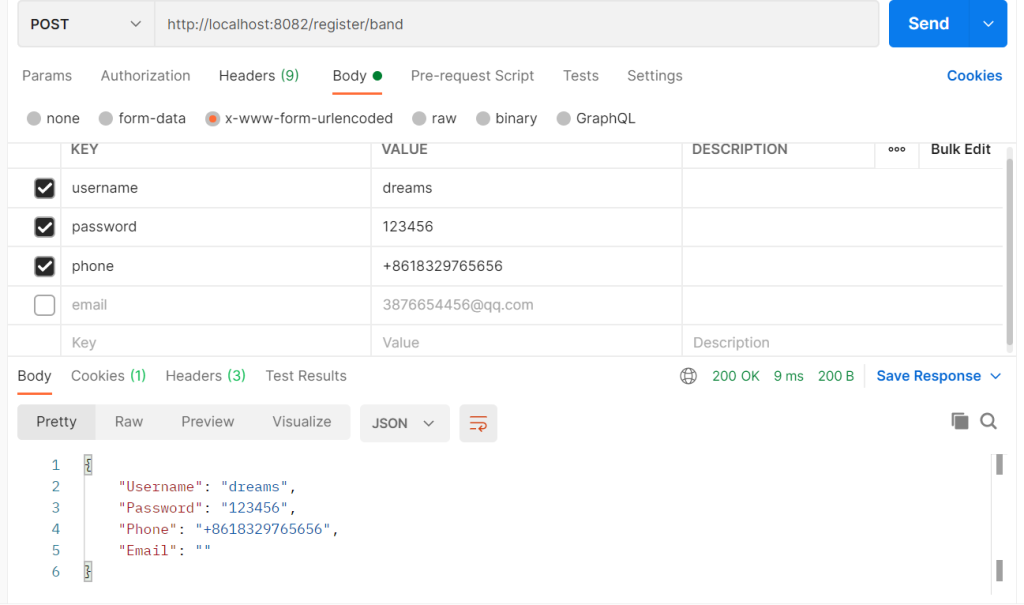
成功案例
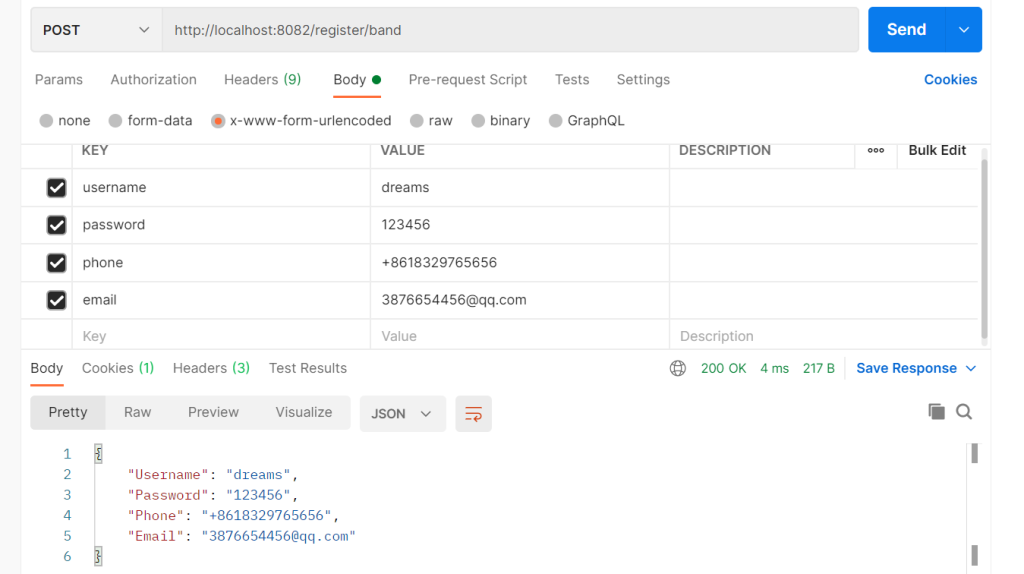
c.BindJSON(&req)是绑定json请求。
type loginRequest struct {
U string `json:"username"`
P string `json:"password"`
}
func login(c *gin.Context) {
req := loginRequest{}
c.Bind(&req)
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, req)
}一样传入
ginServer.POST("/login/band", login)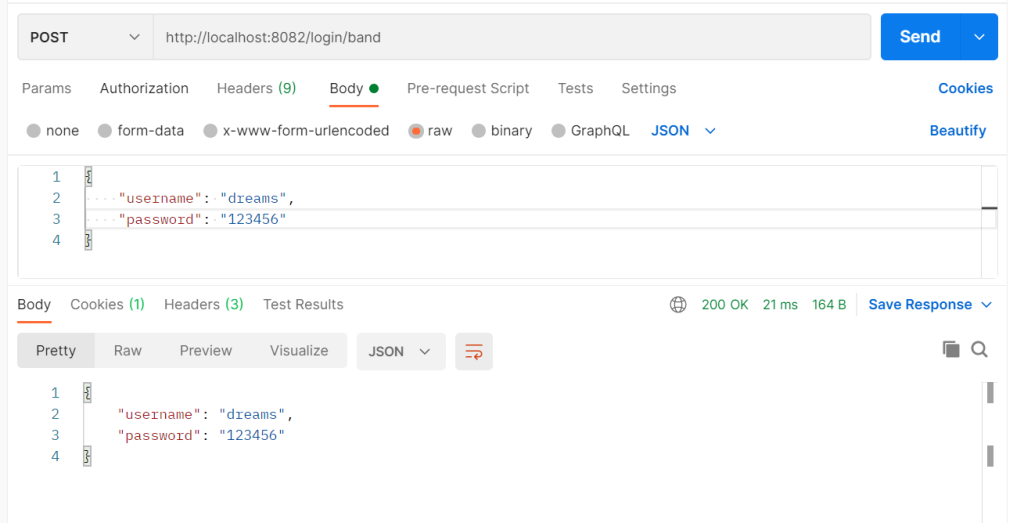
校验与form一样,只是把form换成json
我们加上gin框架自带的校验。
type registerRequest struct {
Username string `json:"username" binding:"required"`
Password string `json:"password" binding:"required"`
Phone string `json:"phone" binding:"required,e164"`
Email string `json:"email" binding:"omitempty,email"`
}
func register(c *gin.Context) {
req := registerRequest{}
err := c.ShouldBind(&req)
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{
"msg": err.Error(),
})
return
}
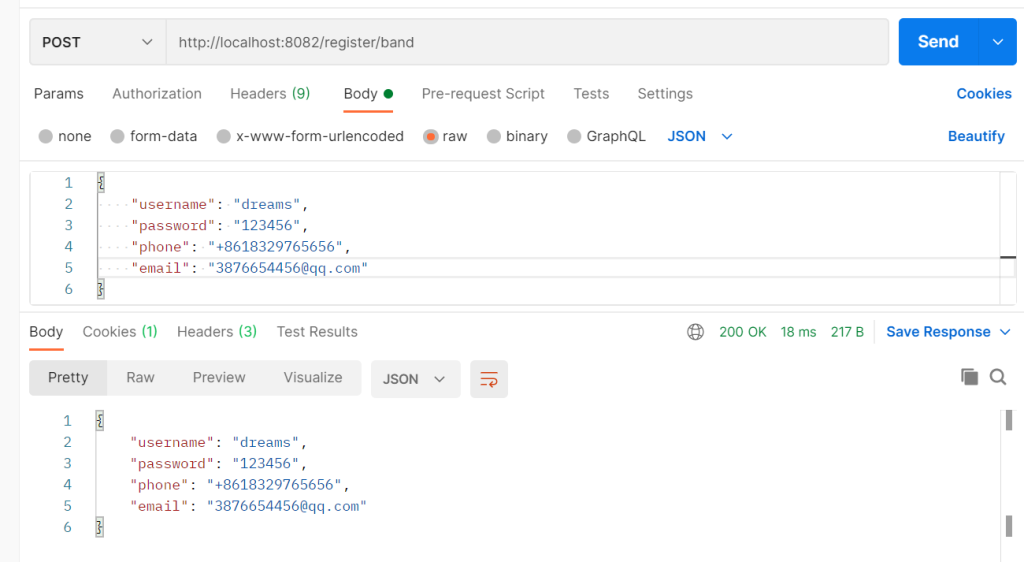
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, req)
}
6.路由
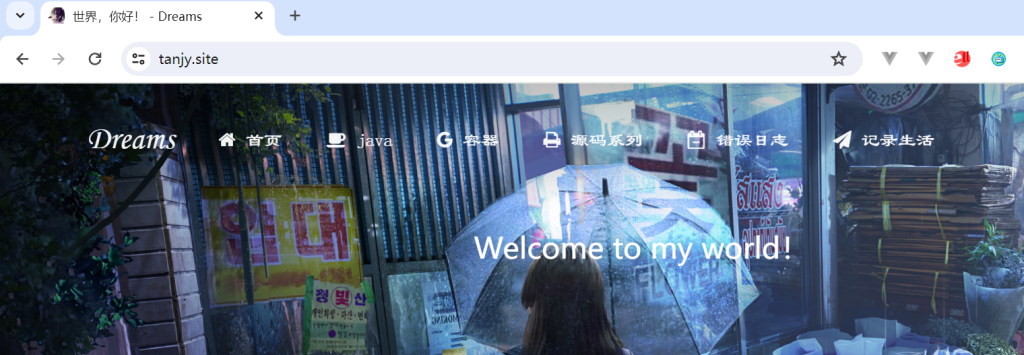
比如重定向
ginServer.GET("/dreams", func(context *gin.Context) {
// 重定向
context.Redirect(http.StatusMovedPermanently, "https://www.tandream.site")
})
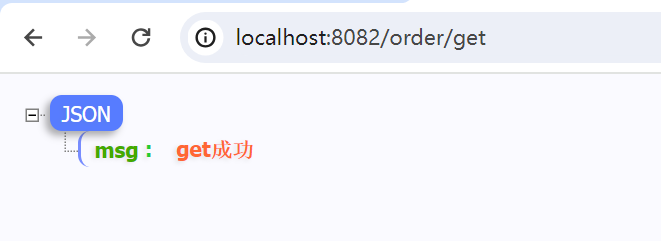
定义一个路由组
orderGroup := ginServer.Group("/order")
{
orderGroup.GET("/get", func(context *gin.Context) {
// 业务
context.JSON(200, gin.H{"msg": "get成功"})
})
orderGroup.POST("/add", func(context *gin.Context) {
// 业务
context.JSON(200, gin.H{"msg": "add成功"})
})
}这样就类似springboot里一个controlller文件,访问由路由组成
自定义404页面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>404</title>
</head>
<body>
{{.msg}}
</body>
</html>跳转
//加载静态页面
// 全局加载该目录下文件
ginServer.LoadHTMLGlob("templates/*")
// 加载资源目录
ginServer.Static("/static", "./static")
// 404
ginServer.NoRoute(func(context *gin.Context) {
context.HTML(http.StatusNotFound, "404.html", gin.H{"msg": "发生未知错误"})
})随便访问
7.中间件(拦截器)
类似java里的拦截器,在go里称呼为中间件
首先定义一个函数
func webHandler() gin.HandlerFunc {
return func(context *gin.Context) {
fmt.Println("中间件开始操作----")
// 存储键值,所有调用了中间件的都可以拿到
context.Set("key-1", "value-1")
// 判断
if true {
// 放行
context.Next()
} else {
// 阻止
context.Abort()
}
}
}我们就可以在这里做处理
每一个请求想要拦截就多传入我们定义的中间件函数就行
context.MustGet() 是 Gin 框架中的一个方法,它用于从上下文中获取指定的值。可以获取拦截器中定义的键值对。比如可以用来登录验证。
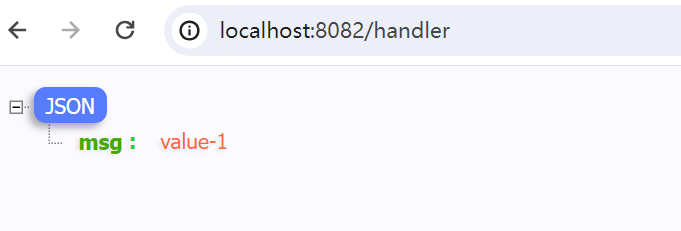
ginServer.GET("/handler", webHandler(), func(context *gin.Context) {
get := context.MustGet("key-1")
context.JSON(200, gin.H{"msg": get})
})
如果想要所有请求都使用中间件,只要注册就行,就不用多传入我们定义的中间件函数。
//注册中间件 ginServer.Use(webHandler())
比如我们可以获取token,该方法用于获取 HTTP 请求头部中指定键名的值。
context.Request.Header.Get("token")
我们还可以使用context.AbortWithError(code int, err error) *Error 是一个 Gin 框架中的方法,用于将请求处理过程中发生的错误返回给客户端,并停止后续的处理逻辑。
func handleRequest(c *gin.Context) {
// ...
if err != nil {
c.AbortWithError(http.StatusInternalServerError, err)
}
// ...
}
注意这里的传入了c *gin.Context的参数,这是另一中写法,这样传入就不用加()了。
ginServer.DELETE("/delete", handleRequest,func(context *gin.Context) {
//业务
})
当然,能够在delete这些请求使用,也可以在Group使用
orderGroup := ginServer.Group("/order",handleRequest)
像这些中间件,可以传入多个
orderGroup := ginServer.Group("/order", handleRequest,webHandler())