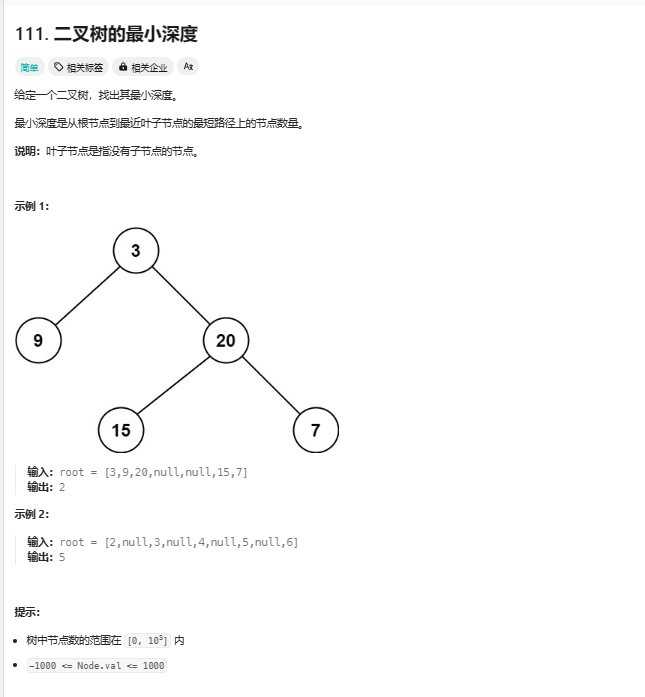
使用递归实现
public int minDepth(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
int d1 = minDepth(node.left); // 1
int d2 = minDepth(node.right); // 0
if (d2 == 0) { // 当右子树为null
return d1 + 1; // 返回左子树深度+1
}
if (d1 == 0) { // 当左子树为null
return d2 + 1; // 返回右子树深度+1
}
return Integer.min(d1, d2) + 1;
}
跟求最大深度不同,层序遍历最小深度效率更高,因为遇到的第一个叶子节点所在层就是最小深度。
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
depth ++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode poll = queue.poll();
if (poll.left == null && poll.right == null) {
return depth;
}
if (poll.left != null) {
queue.offer(poll.left);
}
if (poll.right != null) {
queue.offer(poll.right);
}
}
}
return depth;
}
参考