1.粘包和半包
基本概念
粘包和半包问题通常发生在传输层,主要涉及到TCP协议。
粘包
- 如果发送缓冲区中的多个数据包被一次性发送到接收方,并在网络传输中未被分割,那么接收方可能会一次性接收到多个数据包,这就是粘包问题的发生。
滑动窗口:假设发送方 256 bytes 表示一个完整报文,但由于接收方处理不及时且窗口大小足够大,这 256 bytes 字节就会缓冲在接收方的滑动窗口中,当滑动窗口中缓冲了多个报文就会粘包
半包
- 如果发送缓冲区中的多个小数据包在网络传输中被合并成一个大数据包,或者接收方未及时接收到所有小数据包,那么接收方可能会收到部分数据或不完整的数据包,这就是半包问题的发生。
滑动窗口:假设接收方的窗口只剩了 128 bytes,发送方的报文大小是 256 bytes,这时放不下了,只能先发送前 128 bytes,等待 ack 后才能发送剩余部分,这就造成了半包
短链接方式
短链接是一种连接方式,通常用于临时性的通信,与长连接相比,其连接持续时间更短,一般在完成一次通信后即关闭连接。短链接可以一定程度上减轻粘包问题的发生,因为每次通信都是在一个新的连接上进行,不会受到之前通信数据的影响。
package com.dreams.buns;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j
public class Server1 {
void start() {
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
// 调整系统的接收缓冲器(滑动窗口)
// serverBootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, 10);
// 调整 netty 的接收缓冲区(byteBuf)
// serverBootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.RCVBUF_ALLOCATOR, new AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator(16, 16, 16));
serverBootstrap.group(boss, worker);
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8080).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("server error", e);
} finally {
boss.shutdownGracefully();
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Server1().start();
}
}这里的解决方法就是发送完一个消息后断开链接,发送下一条消息再连接
package com.dreams.buns;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class Client1 {
static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Client1.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
send();
}
System.out.println("finish");
}
private static void send() {
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(worker);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
// 会在连接 channel 建立成功后,会触发 active 事件
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ByteBuf buf = ctx.alloc().buffer(16);
buf.writeBytes(new byte[]{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15});
ctx.writeAndFlush(buf);
ctx.channel().close();
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 8080).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("client error", e);
} finally {
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}可以看到并没有粘包
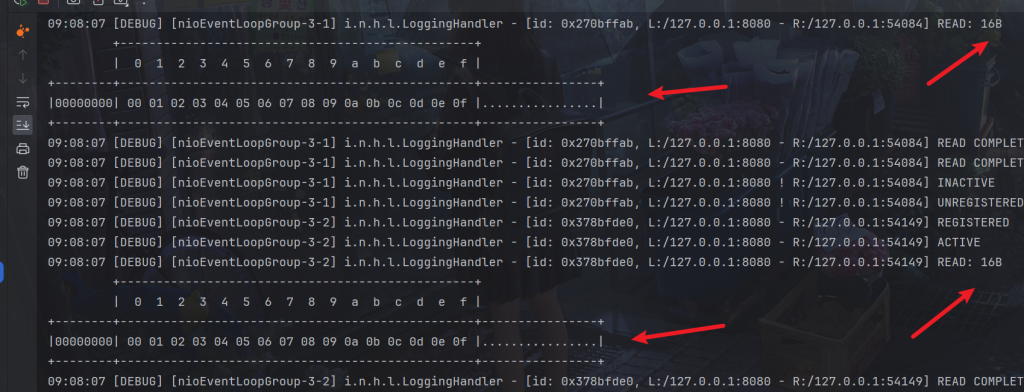
但是无法解决半包问题,而且效率低下。
使用使用了AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator作为接收缓冲区分配器。AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator是Netty提供的一种自适应的接收缓冲区分配器,它可以根据接收到的数据量动态调整接收缓冲区的大小。
参数设置为(16, 16, 16)AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator的初始大小、最小增长量和最大增长量。含义:
- 初始大小(initial):指定了接收缓冲区的初始大小,即在初始阶段,接收缓冲区的大小为16字节。
- 最小增长量(minIncrement):指定了接收缓冲区每次增长的最小值。如果接收到的数据量超过了当前缓冲区的大小,接收缓冲区会按照这个最小增长量进行扩容。
- 最大增长量(maxIncrement):指定了接收缓冲区每次增长的最大值。如果需要扩容的大小超过了最大增长量,接收缓冲区会按照这个最大增长量进行扩容。
serverBootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.RCVBUF_ALLOCATOR, new AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator(16, 16, 16));
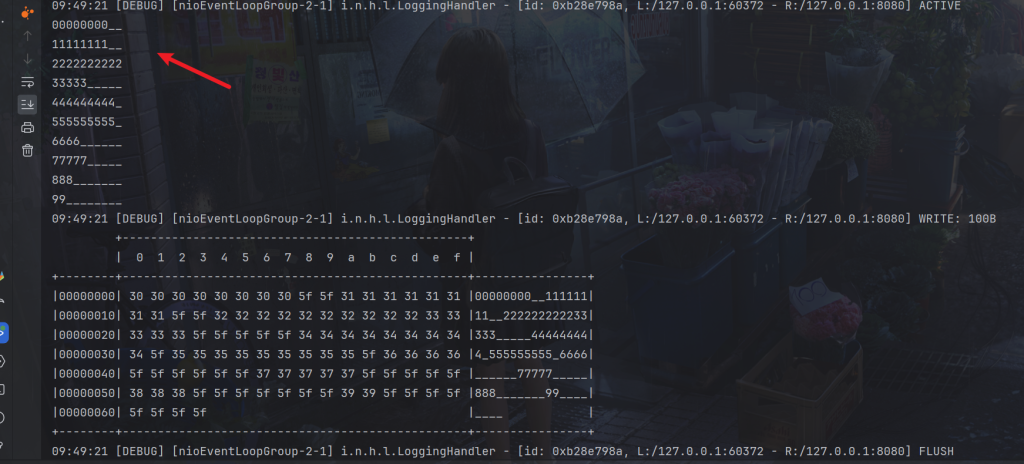
代码注释掉,客户端发送超过16字节大小就会发生半包了
定长解码器
客户端,我们定义指定长度的消息
package com.dreams.buns;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
public class Client2 {
static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Client1.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
send();
System.out.println("finish");
}
public static byte[] fill10Bytes(char c, int len) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[10];
Arrays.fill(bytes, (byte) '_');
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
bytes[i] = (byte) c;
}
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
return bytes;
}
private static void send() {
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(worker);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
// 会在连接 channel 建立成功后,会触发 active 事件
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ByteBuf buf = ctx.alloc().buffer();
char c = '0';
Random r = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
byte[] bytes = fill10Bytes(c, r.nextInt(10) + 1);
c++;
buf.writeBytes(bytes);
}
ctx.writeAndFlush(buf);
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 8080).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("client error", e);
} finally {
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
服务端
package com.dreams.buns;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.FixedLengthFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j
public class Server2 {
void start() {
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
// 调整系统的接收缓冲区(滑动窗口)
// serverBootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, 10);
// 调整 netty 的接收缓冲区(byteBuf)
serverBootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.RCVBUF_ALLOCATOR, new AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator(16, 16, 16));
serverBootstrap.group(boss, worker);
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(10));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8080).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("server error", e);
} finally {
boss.shutdownGracefully();
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Server2().start();
}
}使用 new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(10) 创建了一个定长解码器,它会将接收到的数据按照固定的长度进行切割,每个数据包的长度被设置为10个字节。这意味着,无论接收到的数据是多长,定长解码器都会将其切割成固定长度为10字节的数据包。
当接收到的数据达到这个固定长度时,FixedLengthFrameDecoder会将数据包传递给下一个Handler进行处理,从而保证每个数据包的长度是固定的,不会出现粘包和拆包问题。注意Handler的顺序。
服务端接收到定长
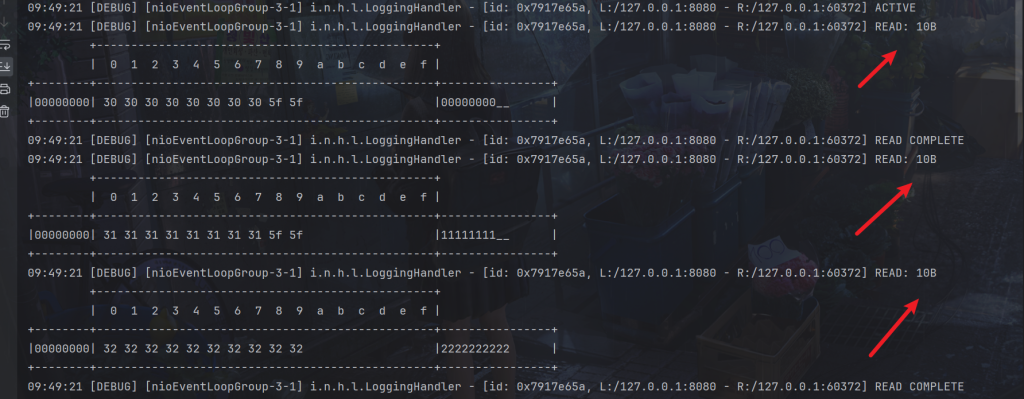
但是很明显会造成资源浪费
行解码器
服务端
package com.dreams.buns;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LineBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j
public class Server3 {
void start() {
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
// 调整系统的接收缓冲区(滑动窗口)
// serverBootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, 10);
// 调整 netty 的接收缓冲区(byteBuf)
serverBootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.RCVBUF_ALLOCATOR, new AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator(16, 16, 16));
serverBootstrap.group(boss, worker);
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8080).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("server error", e);
} finally {
boss.shutdownGracefully();
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Server3().start();
}
}使用 new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024) 创建了一个行解码器,它会将接收到的数据按照行分隔符(例如换行符 \n)进行切割,确保每个数据包都是以行为单位的,并且每行的最大长度被设置为1024个字节。
这意味着,无论接收到的数据是多长,行解码器都会将其按照行分隔符进行切割,以确保每个数据包都是完整的一行,并且每行的长度不会超过1024个字节。
客户端
package com.dreams.buns;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.util.Random;
public class Client3 {
static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Client1.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
send();
System.out.println("finish");
}
public static StringBuilder makeString(char c, int len) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(len + 2);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
sb.append(c);
}
sb.append("\n");
return sb;
}
private static void send() {
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(worker);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
// 会在连接 channel 建立成功后,会触发 active 事件
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ByteBuf buf = ctx.alloc().buffer();
char c = '0';
Random r = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
StringBuilder sb = makeString(c, r.nextInt(256) + 1);
c++;
buf.writeBytes(sb.toString().getBytes());
}
ctx.writeAndFlush(buf);
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 8080).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("client error", e);
} finally {
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}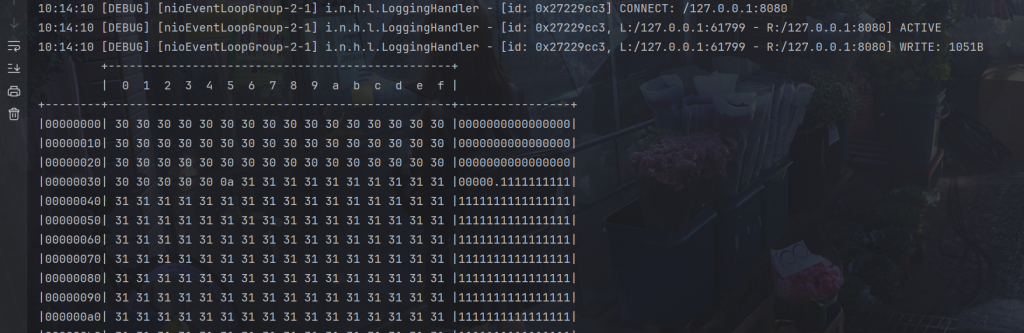
接收到的换行符
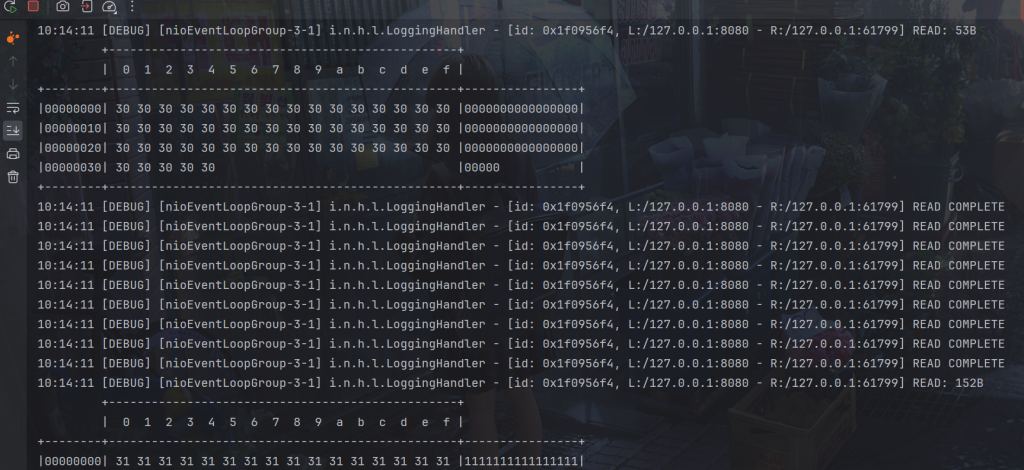
LTC解码器
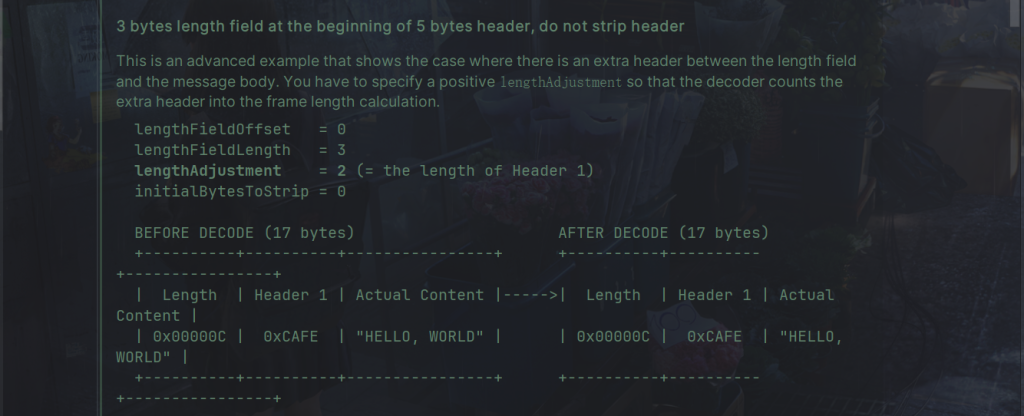
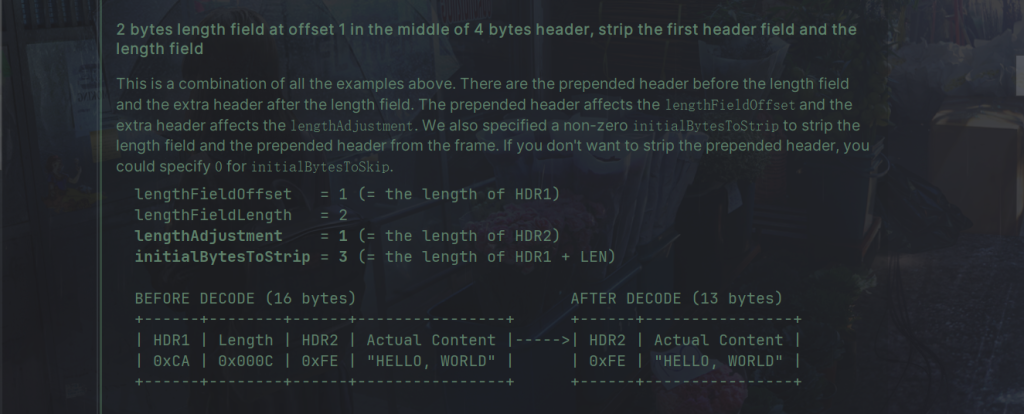
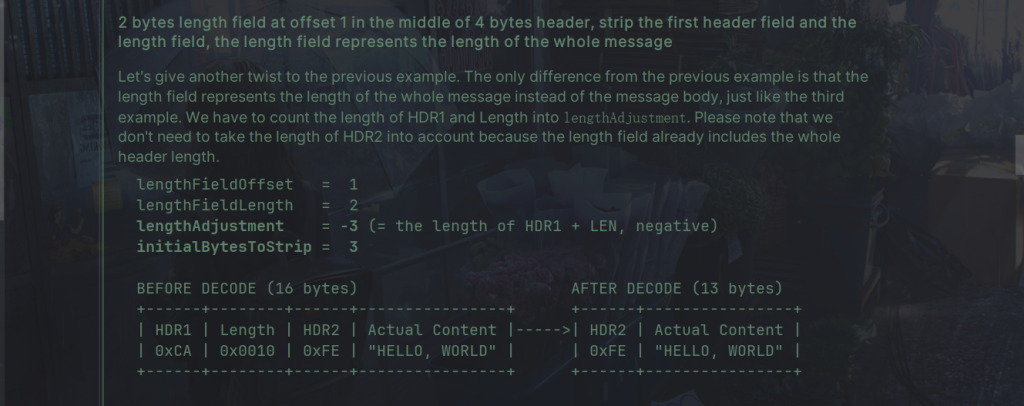
LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder 是一个用于根据消息中的长度字段动态切割接收到的 ByteBufs 的解码器。
LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder 的主要参数:
- lengthFieldOffset:指定长度字段在消息中的偏移量(以字节为单位),即长度字段相对于消息开头的位置。
- lengthFieldLength:指定长度字段的长度(以字节为单位),即长度字段本身占用的字节数。
- lengthAdjustment:指定长度字段的调整值,用于调整解析出的消息长度,常用于调整包含长度字段的消息总长度。如果消息长度包括了长度字段本身的长度,则设置为0;否则根据实际情况设置。
- initialBytesToStrip:指定要从解析出的消息中去除的字节数,即去除消息头部的字节数。通常设置为长度字段的长度,表示去除长度字段本身的字节数。
下面是源码的例子:
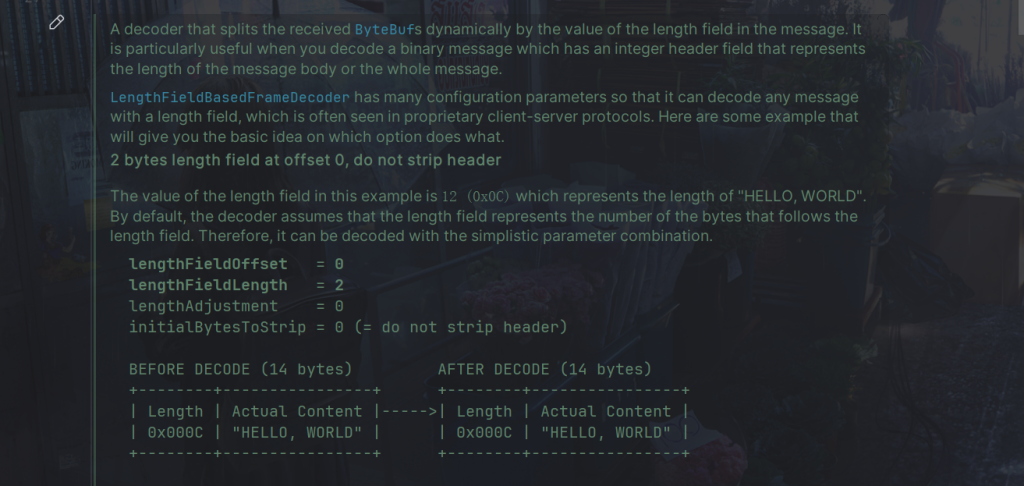
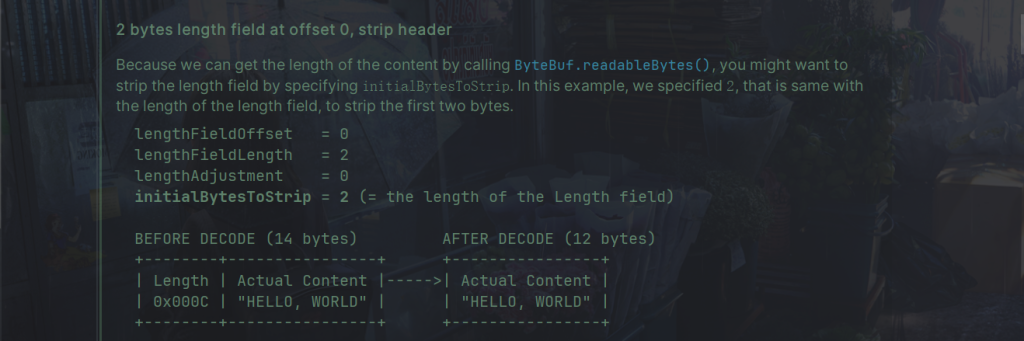
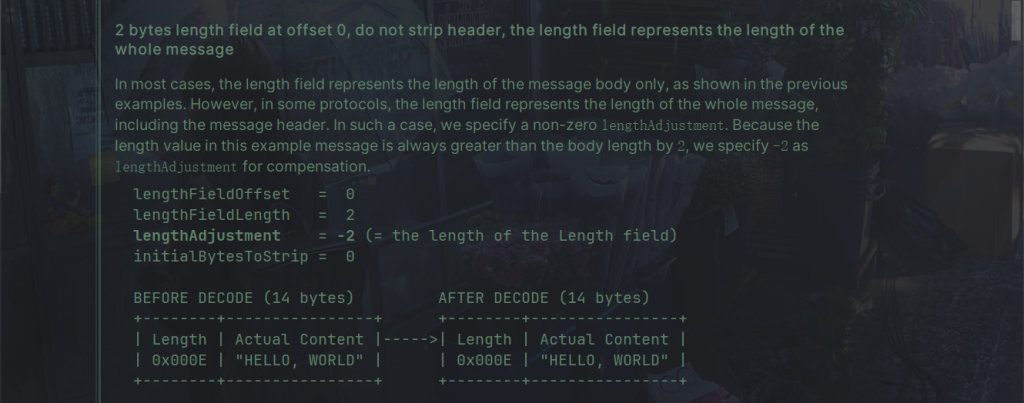
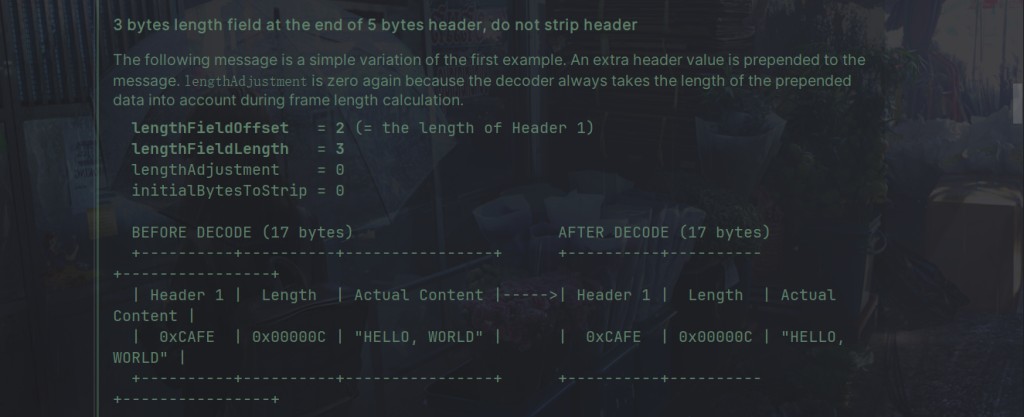
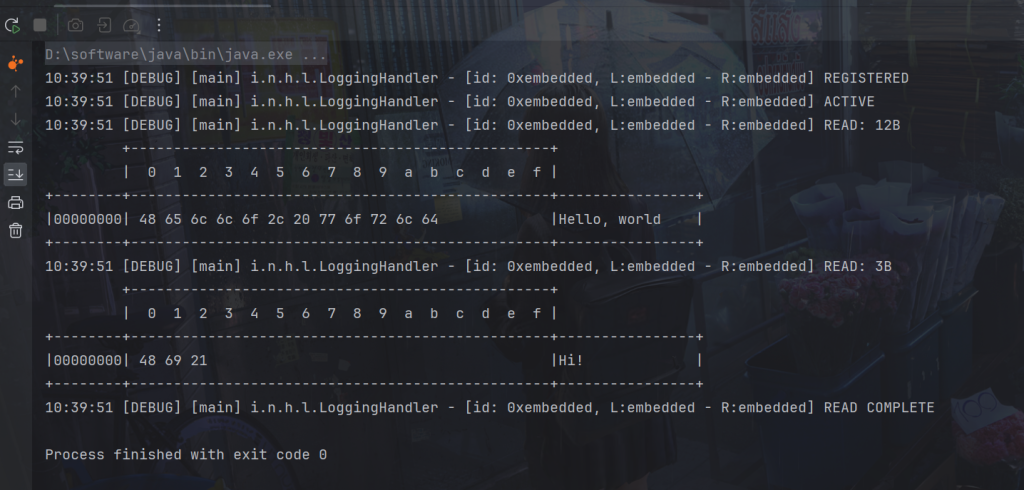
代码:
package com.dreams.buns;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBufAllocator;
import io.netty.channel.embedded.EmbeddedChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
public class TestLengthFieldDecoder {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel(
new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(
1024, 0, 4, 1,5),
new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG)
);
// 4 个字节的内容长度, 实际内容
ByteBuf buffer = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer();
send(buffer, "Hello, world");
send(buffer, "Hi!");
channel.writeInbound(buffer);
}
private static void send(ByteBuf buffer, String content) {
byte[] bytes = content.getBytes(); // 实际内容
int length = bytes.length; // 实际内容长度
//写入长度
buffer.writeInt(length);
//写入版本号
buffer.writeByte(1);
//写入内容
buffer.writeBytes(bytes);
}
}
该handle是线程不安全的,
LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder 不是线程安全的主要原因是它内部维护了一些状态信息,这些状态信息在多个线程之间共享可能会导致不一致或意外的行为。
具体来说,LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder 是一个解码器,用于从字节流中解析出帧(frames)。它依赖于一些参数,如长度字段的偏移量、长度字段的长度等来确定如何从字节流中解析出帧。
如果LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder 被提取出来共用。
可以理解为如果一个工人处理时接收到一个半包,就会等待获取完毕再发送,但是在还是半包时被另一个工人处理,就会和另一个工人合成完整的包发送。
所以因此,为了确保解码器的正确性,通常建议每个线程使用自己独立的 LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder 实例,而不是共享同一个实例。
Netty给线程安全的类加上了@Sharable
@Sharable注解用于标记一个ChannelHandler可以被多个Channel安全地共享,以简化处理程序的使用。当一个ChannelHandler被标记为@Sharable时,Netty会确保它的实例可以被多个Channel共享而不会导致线程安全问题。
不安全的
安全的,比如日志处理
2.协议设计与解析
redis协议
Redis 客户端发送的请求格式如下:
*<number of arguments>\r\n $<length of argument>\r\n <argument>\r\n ...
参数解释:
- <number of arguments>:表示请求中的参数个数,以 * 开头,后面跟着参数个数的数字。
- <length of argument>:表示参数的长度,以 $ 开头,后面跟着参数长度的数字。
- <argument>:表示具体的参数内容,以 \r\n 结尾。
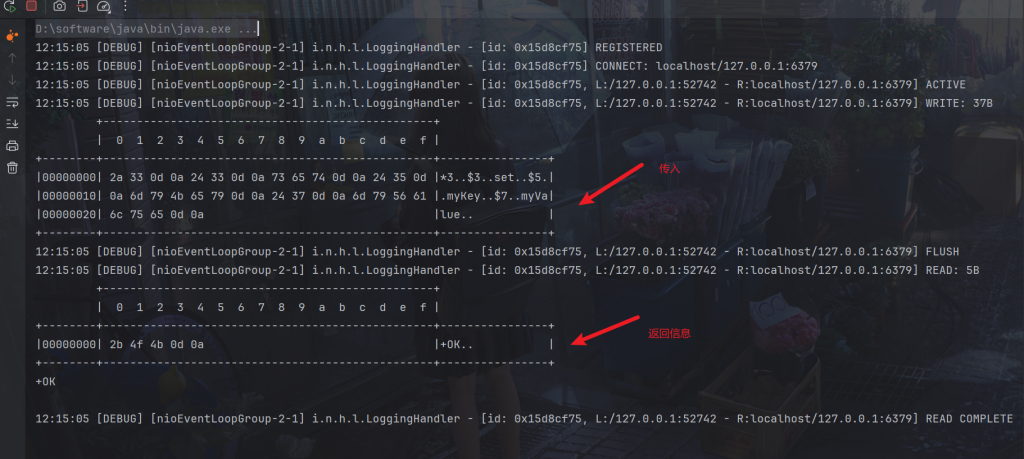
比如redis命令
set myKey myValue
格式就是这样:
*3\r\n $3\r\n SET\r\n $5\r\n myKey\r\n $7\r\n myValue\r\n
代码举例:
package com.dreams.netty;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
@Slf4j
public class RedisDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//回车,换行
byte[] LINE = {13, 10};
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(worker);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
// 会在连接 channel 建立成功后,会触发 active 事件
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
set(ctx);
}
private void set(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ByteBuf buf = ctx.alloc().buffer();
buf.writeBytes("*3".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
buf.writeBytes("$3".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
buf.writeBytes("set".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
buf.writeBytes("$5".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
buf.writeBytes("myKey".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
buf.writeBytes("$7".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
buf.writeBytes("myValue".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
ctx.writeAndFlush(buf);
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
//获取接收到的结果
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println(buf.toString(Charset.defaultCharset()));
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 6379).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("client error", e);
} finally {
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}可以看到正常发送和接收结果
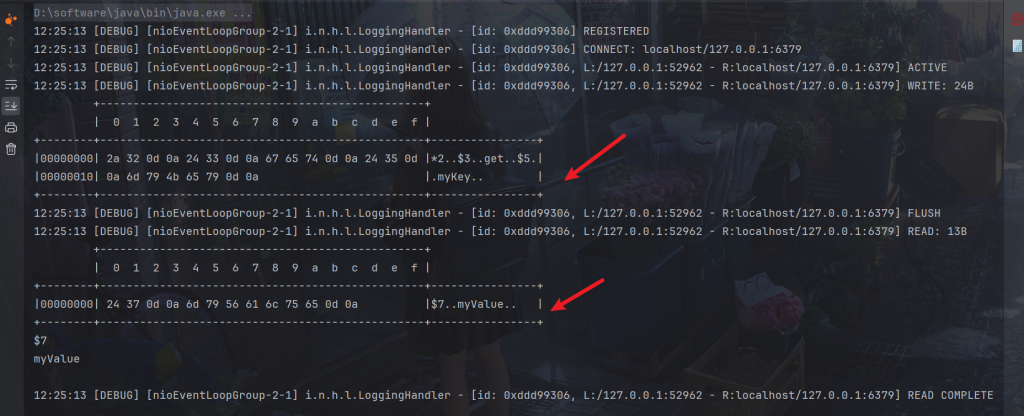
替换为get请求
private void get(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ByteBuf buf = ctx.alloc().buffer();
buf.writeBytes("*2".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
buf.writeBytes("$3".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
buf.writeBytes("get".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
buf.writeBytes("$5".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
buf.writeBytes("myKey".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
ctx.writeAndFlush(buf);
}
http协议编解码
HttpServerCodec 实际上是两个编解码器的组合:HttpRequestDecoder 和 HttpResponseEncoder。其中:
- HttpRequestDecoder 负责将字节流解码为 HttpRequest 对象,即解析客户端发送的 HTTP 请求;
- HttpResponseEncoder 负责将 HttpResponse 对象编码为字节流,即将服务器端的 HTTP 响应转换为字节流以发送给客户端。
代码:
package com.dreams.netty;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.*;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.List;
@Slf4j
public class HttpDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
serverBootstrap.group(boss, worker);
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
log.debug("{}",msg.getClass());
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8080).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("server error", e);
} finally {
boss.shutdownGracefully();
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
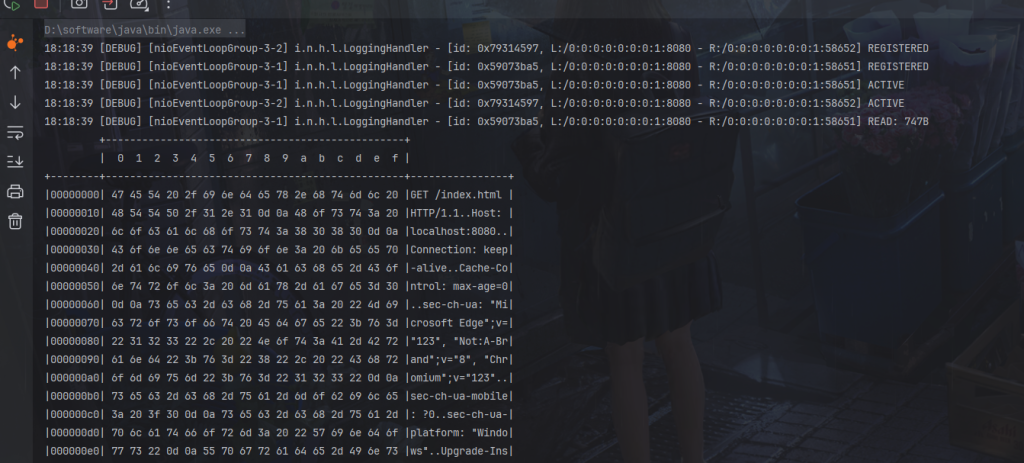
}在浏览器随便请求一下
可以看到接收到了
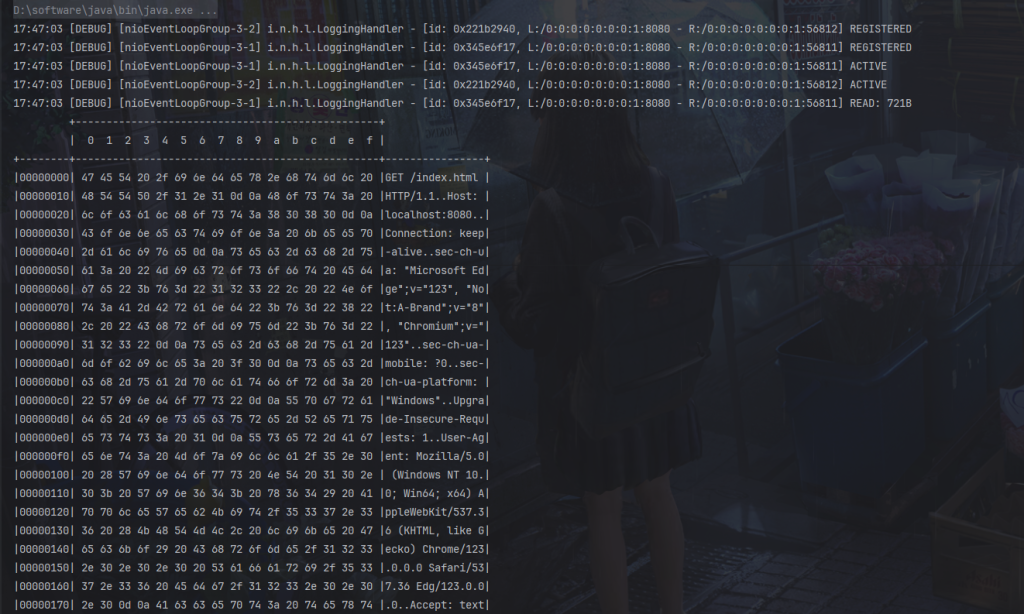
最后输出的两个类是我们使用getclass得来的结果
可以看到返回了两次,解析成了两部分。
io.netty.handler.codec.http.DefaultHttpRequest 类型的对象表示 HTTP 请求的对象,只包含请求行和请求头等。
io.netty.handler.codec.http.LastHttpContent 类型的对象。LastHttpContent 表示 HTTP 报文的最后一个部分,也就是请求体。
当然get请求不会有请求体,那也会返回LastHttpContent 对象,为空而已。
如果想对其处理,可以判断其类型。
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
log.debug("{}", msg.getClass());
if (msg instanceof HttpRequest) { // 请求行,请求头
//逻辑
} else if (msg instanceof HttpContent) { //请求体
//逻辑
}
}也可以使用SimpleChannelInboundHandler。
SimpleChannelInboundHandler 是一个泛型类,你需要指定它的类型参数为要处理的消息的类型。当有入站消息进入时,Netty 会根据指定的泛型类型来判断是否可以处理该消息,并将其传递给相应的 channelRead0() 方法进行处理。
如下代码就只处理DefaultHttpRequest
ch.pipeline().addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<DefaultHttpRequest>() {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, DefaultHttpRequest msg) throws Exception {
//逻辑
}
});比如:
ch.pipeline().addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<HttpRequest>() {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpRequest msg) throws Exception {
// 获取请求
log.debug(msg.uri());
// 返回响应
DefaultFullHttpResponse response =
new DefaultFullHttpResponse(msg.protocolVersion(), HttpResponseStatus.OK);
byte[] bytes = "<h1>Hello, world!</h1>".getBytes();
response.headers().setInt(CONTENT_LENGTH, bytes.length);
response.content().writeBytes(bytes);
// 写回响应
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
});
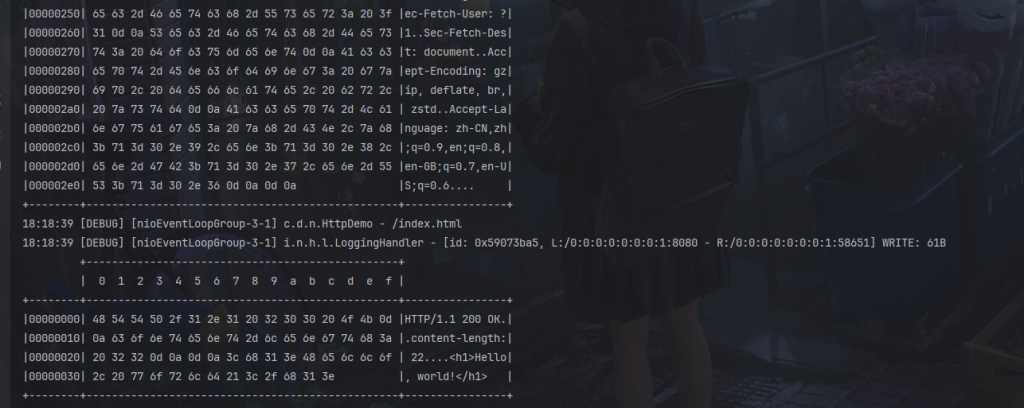
代码创建了一个 HTTP 响应对象 DefaultFullHttpResponse,并设置了响应状态码为 OK(200)。将 “Hello, world!” 字符串转换为字节数组,并将其作为响应内容设置到 DefaultFullHttpResponse 对象中。然后我们要设置响应头部的 Content-Length 字段为响应内容的字节数,否则浏览器不知道大小会一直转圈等待。
最后,通过 ctx.writeAndFlush(response) 将构造好的响应对象发送回客户端,并刷新到通道中。
前面我们设置了ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerCodec()),它既是入站处理器也是出站处理器,所以我们,所以我们将构造好的响应对象写回时,同样会触发HttpServerCodec()
然后浏览器会自动请求一个图标/favicon.ico,也是返回正常。
自定义协议
自定义协议要素
- 魔数:用来在第一时间判定是否是无效数据包(4个字节)
- 版本号:可以支持协议的升级(1个字节)
- 序列化算法:消息正文到底采用哪种序列化反序列化方式,可以由此扩展,例如: json, protobuf、hessian, jdk(1个字节)
- 指令类型:是登录、注册、单聊、群聊…..跟业务相关(1个字节)
- 请求序号:为了双工通信,提供异步能力(1个字节)
- 正文长度(4个字节)
- 消息正文(正文长度个字节)
代码
定义消息父类
定义包message包下创建Message类,注意实现了序列化功能,所以子类继承后也有序列化功能。
package com.dreams.message;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Data
public abstract class Message implements Serializable {
public static Class<?> getMessageClass(int messageType) {
return messageClasses.get(messageType);
}
private int sequenceId;
private int messageType;
public abstract int getMessageType();
//登录相关指令类型(请求,响应)
public static final int LoginRequestMessage = 0;
public static final int LoginResponseMessage = 1;
//聊天相关指令类型
public static final int ChatRequestMessage = 2;
public static final int ChatResponseMessage = 3;
//创建聊天室相关指令类型
public static final int GroupCreateRequestMessage = 4;
public static final int GroupCreateResponseMessage = 5;
//加入聊天室相关指令类型
public static final int GroupJoinRequestMessage = 6;
public static final int GroupJoinResponseMessage = 7;
//退出聊天室相关指令类型
public static final int GroupQuitRequestMessage = 8;
public static final int GroupQuitResponseMessage = 9;
//相关指令类型
public static final int GroupChatRequestMessage = 10;
public static final int GroupChatResponseMessage = 11;
//相关指令类型
public static final int GroupMembersRequestMessage = 12;
public static final int GroupMembersResponseMessage = 13;
private static final Map<Integer, Class<?>> messageClasses = new HashMap<>();
static {
messageClasses.put(LoginRequestMessage, LoginRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(LoginResponseMessage, LoginResponseMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(ChatRequestMessage, ChatRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(ChatResponseMessage, ChatResponseMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupCreateRequestMessage, GroupCreateRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupCreateResponseMessage, GroupCreateResponseMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupJoinRequestMessage, GroupJoinRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupJoinResponseMessage, GroupJoinResponseMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupQuitRequestMessage, GroupQuitRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupQuitResponseMessage, GroupQuitResponseMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupChatRequestMessage, GroupChatRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupChatResponseMessage, GroupChatResponseMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupMembersRequestMessage, GroupMembersRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupMembersResponseMessage, GroupMembersResponseMessage.class);
}
}这将作为所有消息父类
举例登录请求类如下
package com.dreams.message;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.ToString;
@Data
@ToString(callSuper = true)
public class LoginRequestMessage extends Message {
private String username;
private String password;
private String nickname;
public LoginRequestMessage() {
}
public LoginRequestMessage(String username, String password, String nickname) {
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.nickname = nickname;
}
@Override
public int getMessageType() {
return LoginRequestMessage;
}
}编解码器逻辑放在protocol包下
新建protocol包,模仿HttpServerCodec,我们取名为MessageCodec
ByteToMessageCodec 是 Netty 中用于编解码器实现的抽象类,它既可以将字节数据解码成消息对象,也可以将消息对象编码成字节数据。我们继承 ByteToMessageCodec 并实现其中的 decode() 和 encode() 方法来完成解码和编码的逻辑。
ByteToMessageCodec 方法解释:
- decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out):解码器方法,用于将输入的字节流解码成消息对象。你需要在这个方法中实现解析字节流的逻辑,并将解析出的消息对象添加到输出列表 out 中。如果没有足够的字节用于解码一个完整的消息,则 decode() 方法应该返回 null,以表示需要更多的输入字节。当解码成功时,应该调用 out.add() 将解析出的消息对象添加到输出列表中。
- encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, I msg, ByteBuf out):编码器方法,用于将消息对象编码成字节流。你需要在这个方法中实现将消息对象转换成字节流的逻辑,并写入到 ByteBuf 中。当你完成了消息的编码时,Netty 会自动将 ByteBuf 中的数据发送到网络。需要注意的是,ByteBuf 是 Netty 中用于处理字节数据的缓冲区。
package com.dreams.protocol;
import com.dreams.message.Message;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.ByteToMessageCodec;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.util.List;
@Slf4j
//@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class MessageCodec extends ByteToMessageCodec<Message> {
@Override
public void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Message msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
//......编码,出站前编码
}
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
//......解码,入站解码
}
}
然后按照需要的要素发送编码和解码
package com.dreams.protocol;
import com.dreams.message.Message;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.ByteToMessageCodec;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.util.List;
@Slf4j
//@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class MessageCodec extends ByteToMessageCodec<Message> {
@Override
public void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Message msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
// 1. 4 字节的魔数
out.writeBytes(new byte[]{1, 2, 3, 4});
// 2. 1 字节的版本,
out.writeByte(1);
// 3. 1 字节的序列化方式 jdk 0 , json 1
out.writeByte(0);
// 4. 1 字节的指令类型
out.writeByte(msg.getMessageType());
// 5. 4 个字节
out.writeInt(msg.getSequenceId());
// 无意义,对齐填充,满2的整数倍
out.writeByte(0xff);
// 6. 获取内容的字节数组
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(msg);
byte[] bytes = bos.toByteArray();
// 7. 长度
out.writeInt(bytes.length);
// 8. 写入内容
out.writeBytes(bytes);
}
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
int magicNum = in.readInt();
byte version = in.readByte();
byte serializerType = in.readByte();
byte messageType = in.readByte();
int sequenceId = in.readInt();
in.readByte();
int length = in.readInt();
byte[] bytes = new byte[length];
in.readBytes(bytes, 0, length);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes));
Message message = (Message) ois.readObject();
log.debug("{}, {}, {}, {}, {}, {}", magicNum, version, serializerType, messageType, sequenceId, length);
log.debug("{}", message);
out.add(message);
}
}其中
字节的指令类型获取
out.writeByte(msg.getMessageType());
由子类实现父类Message类的抽象方法获取
public abstract int getMessageType();
比如登录请求实现返回代表自己常量的类型
@Override
public int getMessageType() {
return LoginRequestMessage;
}请求序号也同理
out.writeInt(msg.getSequenceId());
父类也有
private int sequenceId
消息子类继承父类就自带这个属性
解码按照定义的要素读取即可
测试:
为了解决黏包半包问题,我们使用LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder
package com.dreams;
import com.dreams.message.LoginRequestMessage;
import com.dreams.protocol.MessageCodec;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBufAllocator;
import io.netty.channel.embedded.EmbeddedChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
public class MessageCodecDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel(
new LoggingHandler(),
//解决黏包半包问题
new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(
1024, 12, 4, 0, 0),
new MessageCodec()
);
// 测试encode
LoginRequestMessage message = new LoginRequestMessage("dreams", "123456", "dreams");
// channel.writeOutbound(message);
// 测试decode
ByteBuf buf = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer();
// 手动调用encode方法,仅为测试。
new MessageCodec().encode(null, message, buf);
channel.writeInbound(buf);
}
}出站正常
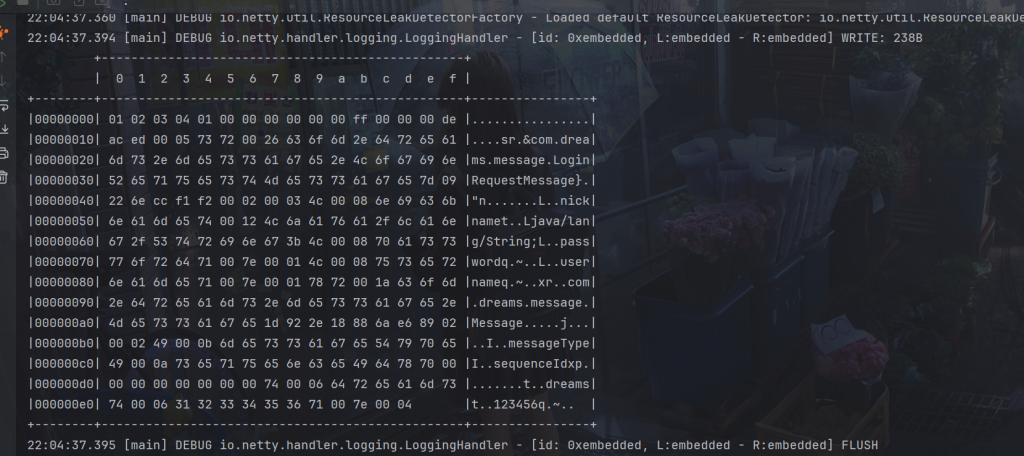
入站正常
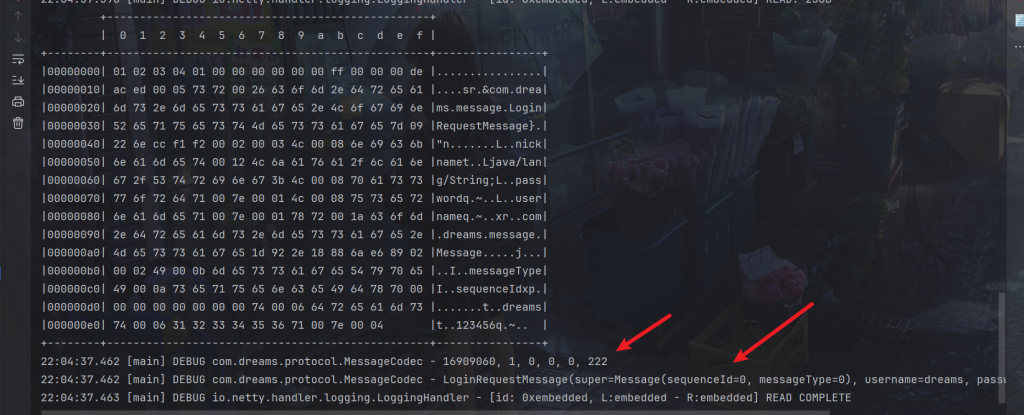
线程安全配置注解
注意:ByteToMessageCodec不允许子类有@Sharable注解
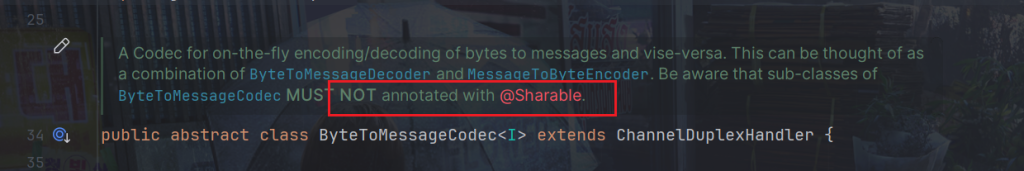
构造方法
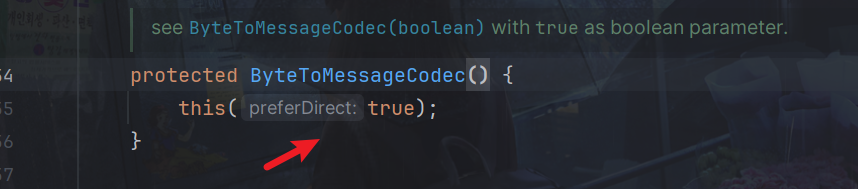
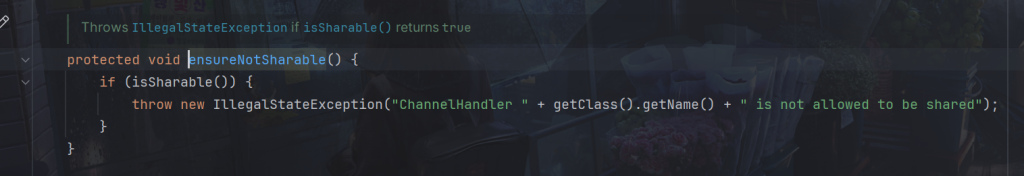
逻辑在该方法ensureNotSharable();
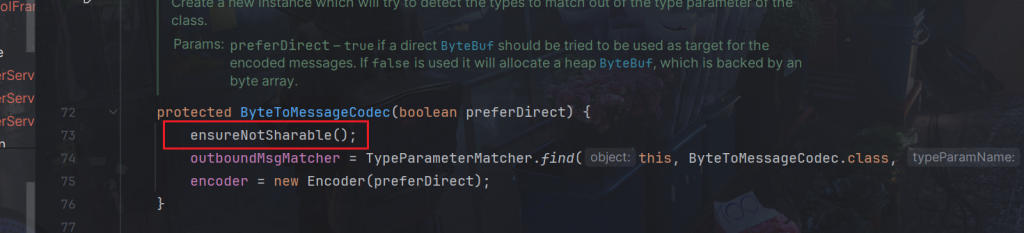
会抛出异常IllegalStateException
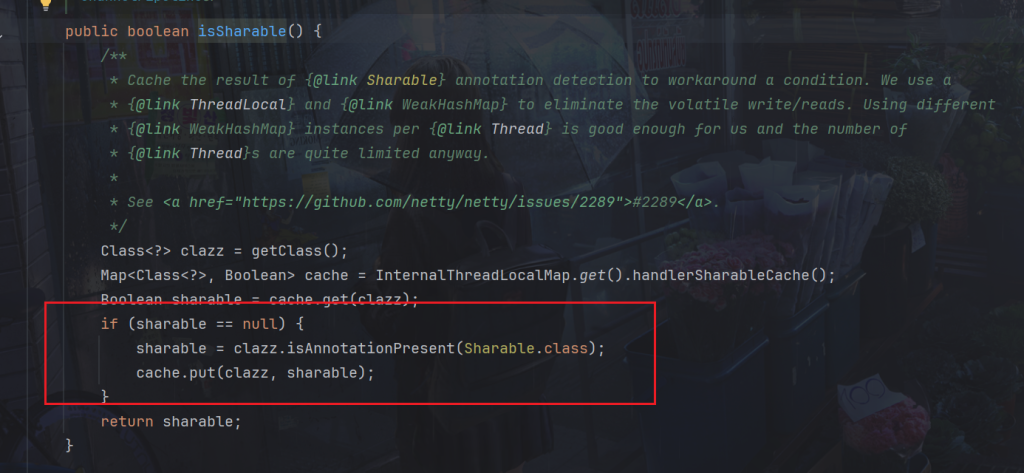
判断逻辑在这里
所以我们可以让它继承MessageToMessageCodec
MessageToMessageCodec是Netty中的一个抽象类,用于将一种消息类型解码成另一种消息类型,或将一种消息类型编码成另一种消息类型。它同时实现了ChannelInboundHandler和ChannelOutboundHandler接口,因此可以同时用作入站(inbound)和出站(outbound)处理器。
除了在encode方法中需要通过ctx.alloc().buffer()获取buffer
其余与上面代码encode方法和decode方法一样,所以直接复制就行,就不贴出代码了
package com.dreams.protocol;
import com.dreams.message.Message;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.MessageToMessageCodec;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.util.List;
@Slf4j
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
/**
* 必须和 LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder 一起使用,确保接到的 ByteBuf 消息是完整的
*/
public class MessageCodecSharable extends MessageToMessageCodec<ByteBuf, Message> {
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Message msg, List<Object> outList) throws Exception {
ByteBuf out = ctx.alloc().buffer();
//......
}
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
//......
}
}
3.聊天业务
客户端
package com.dreams.client;
import com.dreams.message.*;
import com.dreams.protocol.MessageCodecSharable;
import com.dreams.protocol.ProcotolFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.IdleState;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.IdleStateEvent;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.IdleStateHandler;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@Slf4j
public class ChatClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
LoggingHandler LOGGING_HANDLER = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
MessageCodecSharable MESSAGE_CODEC = new MessageCodecSharable();
CountDownLatch WAIT_FOR_LOGIN = new CountDownLatch(1);
AtomicBoolean LOGIN = new AtomicBoolean(false);
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(group);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
//在连接建立后触发 active 事件
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProcotolFrameDecoder());
// ch.pipeline().addLast(LOGGING_HANDLER);
ch.pipeline().addLast(MESSAGE_CODEC);
//用来判断是不是 读空闲时间过长,或 写空闲时间过长
//3s 内如果没有向服务器写数据,会触发一个 IdleState#WRITER_IDLEI事件
ch.pipeline().addLast(new IdleStateHandler(0,3,0));
//ChannelDuplexHandler 可以同时作为入站和出站处理器
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelDuplexHandler(){
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {
if (evt instanceof IdleStateEvent) {
IdleStateEvent state = (IdleStateEvent) evt;
if (state.state() == IdleState.WRITER_IDLE) {
// log.info("3s 没有发送到数据,发送心跳包");
ctx.writeAndFlush(new PingMessage());
}
}
}
});
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
//接收响应消息
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
log.info("msg:{}", msg);
if (msg instanceof LoginResponseMessage) {
LoginResponseMessage response = (LoginResponseMessage) msg;
if (response.isSuccess()){
LOGIN.set(true);
}
//唤醒system in线程
WAIT_FOR_LOGIN.countDown();
}
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
new Thread(() -> {
//负责接收用户在控制台的输入,负责向服务器发送各种消息
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("username:");
String username = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.print("password:");
String password = scanner.nextLine();
// 构造消息对象
LoginRequestMessage request = new LoginRequestMessage(username, password);
// 发送消息
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(request);
//阻塞
try {
WAIT_FOR_LOGIN.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
//如果登录成功
if (LOGIN.get()) {
while (true) {
System.out.println("==================================");
System.out.println("send [username] [content]");
System.out.println("gsend [group name] [content]");
System.out.println("gcreate [group name] [m1,m2,m3...]");
System.out.println("gmembers [group name]");
System.out.println("gjoin [group name]");
System.out.println("gquit [group name]");
System.out.println("quit");
System.out.println("==================================");
String command = scanner.nextLine();
if (command != null && command.length() > 0) {
String[] commandList = command.split(" ");
switch (commandList[0]) {
case "send":
ChatRequestMessage message = new ChatRequestMessage(username, commandList[1], commandList[2]);
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(message);
break;
case "gsend":
GroupChatRequestMessage groupMessage = new GroupChatRequestMessage(username, commandList[1], commandList[2]);
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(groupMessage);
break;
case "gcreate":
String members = commandList[2];
if (members != null && members.length() > 0) {
String[] memberList = members.split(",");
Set<String> memberSet = Arrays.stream(memberList).collect(Collectors.toSet());
GroupCreateRequestMessage groupCreateRequestMessage = new GroupCreateRequestMessage(commandList[1], memberSet);
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(groupCreateRequestMessage);
}
break;
case "gmembers":
GroupMembersRequestMessage groupMembersRequestMessage = new GroupMembersRequestMessage(commandList[1]);
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(groupMembersRequestMessage);
break;
case "gjoin":
GroupJoinRequestMessage groupJoinRequestMessage = new GroupJoinRequestMessage(username, commandList[1]);
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(groupJoinRequestMessage);
break;
case "gquit":
GroupQuitRequestMessage groupQuitRequestMessage = new GroupQuitRequestMessage(username, commandList[1]);
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(groupQuitRequestMessage);
break;
case "quit":
ctx.channel().close();
return;
}
}
}
} else {
ctx.channel().close();
}
},"system in").start();
}
});
}
});
Channel channel = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 8080).sync().channel();
channel.closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("client error", e);
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
服务端
在初始化Channel时,添加了一些处理器,包括:
- ProcotolFrameDecoder:用于解码协议帧。
- MessageCodecSharable:用于编解码消息对象。
- IdleStateHandler:用于进行心跳检测。
- ChannelDuplexHandler:同时作为入站和出站处理器,用于处理空闲状态事件。
- LoginRequestMessageHandler:处理登录请求消息。
- ChatRequestMessageHandler:处理聊天请求消息。
- GroupChatRequestMessageHandler:处理群聊请求消息。
- GroupJoinRequestMessageHandler:处理加入群组请求消息。
- GroupCreateRequestMessageHandler:处理创建群组请求消息。
- GroupMembersRequestMessageHandler:处理获取群成员列表请求消息。
- GroupQuitRequestMessageHandler:处理退出群组请求消息。
代码:
package com.dreams.server;
import com.dreams.message.GroupChatRequestMessage;
import com.dreams.protocol.MessageCodecSharable;
import com.dreams.protocol.ProcotolFrameDecoder;
import com.dreams.server.handler.*;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelDuplexHandler;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.IdleState;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.IdleStateEvent;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.IdleStateHandler;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j
public class ChatServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
LoggingHandler LOGGING_HANDLER = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
MessageCodecSharable MESSAGE_CODEC = new MessageCodecSharable();
LoginRequestMessageHandler LOGIN_HANDLER = new LoginRequestMessageHandler();
ChatRequestMessageHandler CHAT_HANDLER = new ChatRequestMessageHandler();
GroupCreateRequestMessageHandler GROUP_CREATE_HANDLER = new GroupCreateRequestMessageHandler();
GroupJoinRequestMessageHandler GROUP_JOIN_HANDLER = new GroupJoinRequestMessageHandler();
GroupMembersRequestMessageHandler GROUP_MEMBERS_HANDLER = new GroupMembersRequestMessageHandler();
GroupQuitRequestMessageHandler GROUP_QUIT_HANDLER = new GroupQuitRequestMessageHandler();
GroupChatRequestMessageHandler GROUP_CHAT_HANDLER = new GroupChatRequestMessageHandler();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
serverBootstrap.group(boss, worker);
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProcotolFrameDecoder());
// ch.pipeline().addLast(LOGGING_HANDLER);
ch.pipeline().addLast(MESSAGE_CODEC);
//用来判断是不是 读空闲时间过长,或 写空闲时间过长
ch.pipeline().addLast(new IdleStateHandler(5,0,0));
//ChannelDuplexHandler 可以同时作为入站和出站处理器
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelDuplexHandler(){
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {
if (evt instanceof IdleStateEvent) {
IdleStateEvent state = (IdleStateEvent) evt;
if (state.state() == IdleState.READER_IDLE) {
// log.info("IdleState.READER_IDLE 5s 没有接收到数据");
ctx.channel().close();
}
}
}
});
ch.pipeline().addLast(LOGIN_HANDLER);
ch.pipeline().addLast(CHAT_HANDLER);
ch.pipeline().addLast(GROUP_CHAT_HANDLER);
ch.pipeline().addLast(GROUP_JOIN_HANDLER);
ch.pipeline().addLast(GROUP_CREATE_HANDLER);
ch.pipeline().addLast(GROUP_MEMBERS_HANDLER);
ch.pipeline().addLast(GROUP_QUIT_HANDLER);
}
});
Channel channel = serverBootstrap.bind(8080).sync().channel();
channel.closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("server error", e);
} finally {
boss.shutdownGracefully();
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}Netty框架中的IdleStateHandler类创建一个处理器,用于检测连接的空闲状态。在上述代码中,IdleStateHandler的构造函数参数为(5, 0, 0),具体含义如下:
- 第一个参数:读空闲时间,即在指定时间内没有接收到读事件(包括数据读取、心跳等),则会触发读空闲事件。
- 第二个参数:写空闲时间,即在指定时间内没有发生写操作,则会触发写空闲事件。
- 第三个参数:所有类型的空闲时间,即在指定时间内既没有读操作也没有写操作,则会触发所有类型的空闲事件。
userEventTriggered方法是Netty中的一种回调方法,用于处理自定义的用户事件。当ChannelPipeline中的事件触发时,会调用该方法进行处理。在上述代码中,ChannelDuplexHandler类重写了userEventTriggered方法,用于处理空闲状态事
Netty中可以使用两个处理器来实现心跳机制。
- 首先,使用IdleStateHandler创建了一个处理器,构造函数参数为(0, 3, 0),表示写空闲时间为3秒。当连接在3秒内没有发生写操作时,会触发写空闲事件。
- 然后,在ChannelDuplexHandler的userEventTriggered方法中,通过判断事件类型是否为IdleStateEvent来处理空闲事件。如果是写空闲事件(WRITER_IDLE),则发送心跳包(PingMessage)来保持连接的活跃状态。
- 整体的逻辑是,当连接在3秒内没有发生写操作时,会触发写空闲事件,进而触发ChannelDuplexHandler中的userEventTriggered方法,从而发送心跳包。这样可以确保连接在长时间无数据传输时不会被断开。
JDK序列化
前面自定义协议时,我们使用了java自带的序列化操作,现在我们可以扩展为支持多种序列化操作。
在protocol包下定义Serializer接口
package com.dreams.protocol;
public interface Serializer {
// 反序列化方法
<T> T deserialize(Class<T> clazz, byte[] bytes);
// 序列化方法
<T> byte[] serialize(T object);
}我们需要传入Class<T> clazz参数,虽然JDK自带的序列化方法不需要知道类型信息,但其他需要,比如JSON。
可以直接使用枚举实现该接口。
package com.dreams.protocol;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public enum SerializerAlgorithm implements Serializer {
// Java 实现
Java {
@Override
public <T> T deserialize(Class<T> clazz, byte[] bytes) {
try {
ObjectInputStream in =
new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes));
Object object = in.readObject();
return (T) object;
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("SerializerAlgorithm.Java 反序列化错误", e);
}
}
@Override
public <T> byte[] serialize(T object) {
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
new ObjectOutputStream(out).writeObject(object);
return out.toByteArray();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("SerializerAlgorithm.Java 序列化错误", e);
}
}
}
}添加配置类读取配置文件,提供获取序列化算法的方法:getSerializerAlgorithm方法从加载的配置文件中获取serializer.algorithm属性的值,如果该属性不存在,则返回默认的序列化算法SerializerAlgorithm.Java
package com.dreams.config;
import com.dreams.protocol.SerializerAlgorithm;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
public abstract class Config {
static Properties properties;
static {
try (InputStream in = Config.class.getResourceAsStream("/application.properties")) {
properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(e);
}
}
public static int getServerPort() {
String value = properties.getProperty("server.port");
if(value == null) {
return 8080;
} else {
return Integer.parseInt(value);
}
}
public static SerializerAlgorithm getSerializerAlgorithm() {
String value = properties.getProperty("serializer.algorithm");
if(value == null) {
return SerializerAlgorithm.Java;
} else {
return SerializerAlgorithm.valueOf(value);
}
}
}在resources下创建配置application.properties
serializer.algorithm=Java
- ordinal()是枚举类型中的一个方法,它返回枚举常量的序号,从0开始。在这里,Config.getSerializerAlgorithm().ordinal()会返回当前配置中所使用的序列化算法的枚举值的序号,即0或1。
- 当serializerAlgorithm的值为0时,表示使用JDK序列化算法,当值为1时,表示使用JSON序列化算法。通过SerializerAlgorithm.values()[serializerAlgorithm]可以根据序号获取对应的序列化算法枚举类型,以便后续使用该算法进行序列化或反序列化操作。
package com.dreams.protocol;
import com.dreams.config.Config;
import com.dreams.message.Message;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.MessageToMessageCodec;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 必须和 LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder 一起使用,确保接到的 ByteBuf 消息是完整的
*/
public class MessageCodecSharable extends MessageToMessageCodec<ByteBuf, Message> {
@Override
public void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Message msg, List<Object> outList) throws Exception {
ByteBuf out = ctx.alloc().buffer();
// 1. 4 字节的魔数
out.writeBytes(new byte[]{1, 2, 3, 4});
// 2. 1 字节的版本,
out.writeByte(1);
// 3. 1 字节的序列化方式 jdk 0 , json 1
out.writeByte(Config.getSerializerAlgorithm().ordinal());
// 4. 1 字节的指令类型
out.writeByte(msg.getMessageType());
// 5. 4 个字节
out.writeInt(msg.getSequenceId());
// 无意义,对齐填充
out.writeByte(0xff);
// 6. 获取内容的字节数组
byte[] bytes = Config.getSerializerAlgorithm().serialize(msg);
// 7. 长度
out.writeInt(bytes.length);
// 8. 写入内容
out.writeBytes(bytes);
outList.add(out);
}
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
int magicNum = in.readInt();
byte version = in.readByte();
byte serializerAlgorithm = in.readByte(); // 0 或 1
byte messageType = in.readByte(); // 0,1,2...
int sequenceId = in.readInt();
in.readByte();
int length = in.readInt();
byte[] bytes = new byte[length];
in.readBytes(bytes, 0, length);
// 找到反序列化算法
SerializerAlgorithm algorithm = SerializerAlgorithm.values()[serializerAlgorithm];
// 确定具体消息类型
Class<?> messageClass = Message.getMessageClass(messageType);
Object message = algorithm.deserialize(messageClass, bytes);
// log.debug("{}, {}, {}, {}, {}, {}", magicNum, version, serializerType, messageType, sequenceId, length);
// log.debug("{}", message);
out.add(message);
}
}JSON序列化
导入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.code.gson</groupId>
<artifactId>gson</artifactId>
<version>2.8.5</version>
</dependency>同样在枚举类下SerializerAlgorithm 下java枚举同级加入JSON枚举
// Json 实现(引入了 Gson 依赖)
Json {
@Override
public <T> T deserialize(Class<T> clazz, byte[] bytes) {
//字节数组转为字符串,
String json = new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
//再转为java对象
return new Gson().fromJson(json, clazz);
}
@Override
public <T> byte[] serialize(T object) {
//java对象转为JSON字符串
String json = new Gson().toJson(object);
//再转为字节数组,确保客户端和服务器编码一致
return json.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
}
};简单测试:
import com.dreams.message.LoginRequestMessage;
import com.dreams.protocol.MessageCodecSharable;
import io.netty.channel.embedded.EmbeddedChannel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
/**
* @author PoemsAndDreams
* @date 2024-04-08 20:47
* @description //TODO
*/
public class SerializerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MessageCodecSharable CODEC = new MessageCodecSharable();
LoggingHandler LOGGING = new LoggingHandler();
EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel(LOGGING, CODEC, LOGGING);
LoginRequestMessage message = new LoginRequestMessage("dreams", "123");
channel.writeOutbound(message);
}
}换成Json
serializer.algorithm=Json
如下
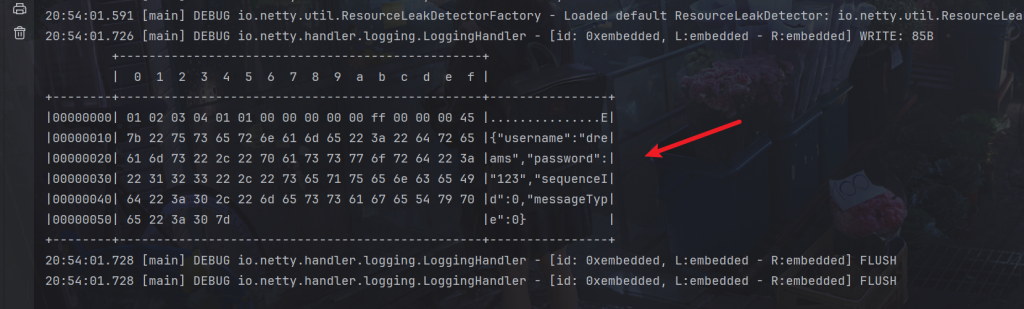
换成Java
serializer.algorithm=Java
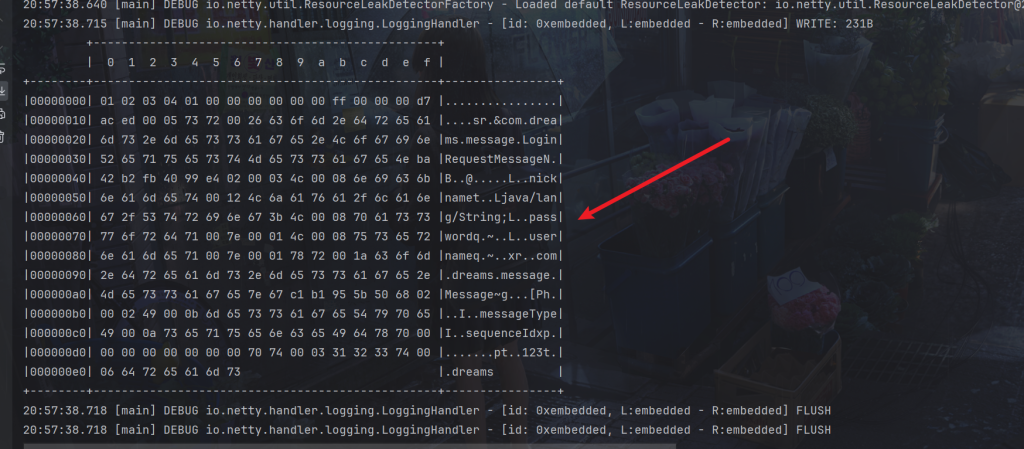
RPC调用
package com.dreams.message;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Data
public abstract class Message implements Serializable {
public static Class<?> getMessageClass(int messageType) {
return messageClasses.get(messageType);
}
......
public static final int RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_REQUEST = 101;
public static final int RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_RESPONSE = 102;
private static final Map<Integer, Class<?>> messageClasses = new HashMap<>();
static {
......
messageClasses.put(RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_REQUEST, RpcRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_RESPONSE, RpcResponseMessage.class);
}
}- Sequence ID (序列ID): 序列ID用于标识消息的顺序或唯一性。在一个消息队列或通信系统中,不同消息可能需要按照一定的顺序执行,或者需要唯一标识以便进行跟踪和管理。
- Interface Name (接口名称): 接口名称指定了远程服务中要调用的具体接口。在RPC系统中,客户端需要指定要调用的远程接口,以便服务器知道要执行哪些操作。
- Method Name (方法名称): 方法名称表示要调用的远程接口中的具体方法。通过指定方法名称,客户端可以告诉服务器应该执行哪个方法。
- Return Type (返回类型): 返回类型表示调用远程方法后期望得到的返回值类型。这可以帮助服务器执行方法并将结果正确地返回给客户端。
- Parameter Types (参数类型): 参数类型数组包含了方法调用时传递给远程方法的参数的类型。这是为了确保在远程调用时能够正确地匹配参数类型。
- Parameter Values (参数值): 参数值数组包含了方法调用时传递给远程方法的具体参数值。这些值将与参数类型数组中的类型一一对应,确保在远程调用时传递正确的参数。
package com.dreams.message;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.ToString;
@Getter
@ToString(callSuper = true)
public class RpcRequestMessage extends Message {
/**
* 调用的接口全限定名,服务端根据它找到实现
*/
private String interfaceName;
/**
* 调用接口中的方法名
*/
private String methodName;
/**
* 方法返回类型
*/
private Class<?> returnType;
/**
* 方法参数类型数组
*/
private Class[] parameterTypes;
/**
* 方法参数值数组
*/
private Object[] parameterValue;
public RpcRequestMessage(int sequenceId, String interfaceName, String methodName, Class<?> returnType, Class[] parameterTypes, Object[] parameterValue) {
super.setSequenceId(sequenceId);
this.interfaceName = interfaceName;
this.methodName = methodName;
this.returnType = returnType;
this.parameterTypes = parameterTypes;
this.parameterValue = parameterValue;
}
@Override
public int getMessageType() {
return RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_REQUEST;
}
}RPC响应
package com.dreams.message;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.ToString;
@Data
@ToString(callSuper = true)
public class RpcResponseMessage extends Message {
/**
* 返回值
*/
private Object returnValue;
/**
* 异常值
*/
private Exception exceptionValue;
@Override
public int getMessageType() {
return RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_RESPONSE;
}
}服务端代码:
package com.dreams.server;
import com.dreams.protocol.MessageCodecSharable;
import com.dreams.protocol.ProcotolFrameDecoder;
import com.dreams.server.handler.RpcRequestMessageHandler;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j
public class RpcServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
LoggingHandler LOGGING_HANDLER = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
MessageCodecSharable MESSAGE_CODEC = new MessageCodecSharable();
RpcRequestMessageHandler RPC_HANDLER = new RpcRequestMessageHandler();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
serverBootstrap.group(boss, worker);
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProcotolFrameDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(LOGGING_HANDLER);
ch.pipeline().addLast(MESSAGE_CODEC);
ch.pipeline().addLast(RPC_HANDLER);
}
});
Channel channel = serverBootstrap.bind(8080).sync().channel();
channel.closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("server error", e);
} finally {
boss.shutdownGracefully();
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}简单的服务端代码没什么好说的,重点逻辑在在RpcRequestMessageHandler
在写RpcRequestMessageHandler代码前,需要准备一些接口和实现类来测试
比如我们需要远程调用这个接口
package com.dreams.server.service;
public interface HelloService {
String sayHello(String name);
}再来一个实现类
package com.dreams.server.service;
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
@Override
public String sayHello(String msg) {
return "你好, " + msg;
}
}
因为这里没有使用spring或springboot,所以需要一个工厂来处理它们的关系
package com.dreams.server.service;
import com.dreams.config.Config;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class ServicesFactory {
static Properties properties;
static Map<Class<?>, Object> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
static {
try (InputStream in = Config.class.getResourceAsStream("/application.properties")) {
properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
Set<String> names = properties.stringPropertyNames();
for (String name : names) {
if (name.endsWith("Service")) {
Class<?> interfaceClass = Class.forName(name);
Class<?> instanceClass = Class.forName(properties.getProperty(name));
map.put(interfaceClass, instanceClass.newInstance());
}
}
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException | InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(e);
}
}
public static <T> T getService(Class<T> interfaceClass) {
return (T) map.get(interfaceClass);
}
}读取的配置文件application.properties:
com.dreams.server.service.HelloService=com.dreams.server.service.HelloServiceImpl
使用反射实现:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
RpcRequestMessage message = new RpcRequestMessage(
1,
"com.dreams.server.service.HelloService",
"sayHello",
String.class,
new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]{"梦想"}
);
HelloService service = (HelloService)
ServicesFactory.getService(Class.forName(message.getInterfaceName()));
Method method = service.getClass().getMethod(message.getMethodName(), message.getParameterTypes());
Object invoke = method.invoke(service, message.getParameterValue());
System.out.println(invoke);
}
RpcRequestMessageHandler代码
package com.dreams.server.handler;
import com.dreams.message.RpcRequestMessage;
import com.dreams.message.RpcResponseMessage;
import com.dreams.server.service.HelloService;
import com.dreams.server.service.ServicesFactory;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Slf4j
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class RpcRequestMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcRequestMessage> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcRequestMessage message) {
RpcResponseMessage response = new RpcResponseMessage();
response.setSequenceId(message.getSequenceId());
try {
HelloService service = (HelloService)
ServicesFactory.getService(Class.forName(message.getInterfaceName()));
Method method = service.getClass().getMethod(message.getMethodName(), message.getParameterTypes());
Object invoke = method.invoke(service, message.getParameterValue());
response.setReturnValue(invoke);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
String msg = e.getCause().getMessage();
response.setExceptionValue(new Exception("远程调用出错:" + msg));
}
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
}客户端代码
package com.dreams.client;
import com.dreams.client.handler.RpcResponseMessageHandler;
import com.dreams.message.RpcRequestMessage;
import com.dreams.protocol.MessageCodecSharable;
import com.dreams.protocol.ProcotolFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j
public class RpcClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
LoggingHandler LOGGING_HANDLER = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
MessageCodecSharable MESSAGE_CODEC = new MessageCodecSharable();
RpcResponseMessageHandler RPC_HANDLER = new RpcResponseMessageHandler();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(group);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProcotolFrameDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(LOGGING_HANDLER);
ch.pipeline().addLast(MESSAGE_CODEC);
ch.pipeline().addLast(RPC_HANDLER);
}
});
Channel channel = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 8080).sync().channel();
ChannelFuture future = channel.writeAndFlush(new RpcRequestMessage(
1,
"com.dreams.server.service.HelloService",
"sayHello",
String.class,
new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]{"梦想"}
)).addListener(promise -> {
if (!promise.isSuccess()) {
Throwable cause = promise.cause();
log.error("error", cause);
}
});
channel.closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("client error", e);
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
可能会报这个错误
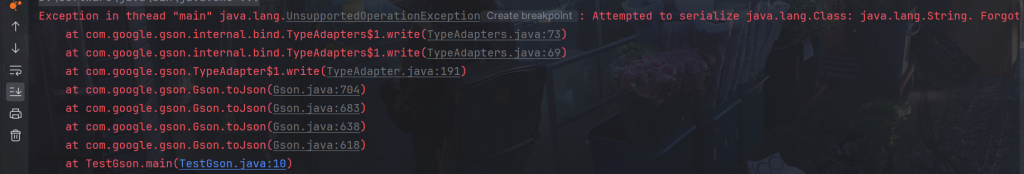
模拟一下这个异常
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class TestGson {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new Gson().toJson(String.class));
}
}输出如下

java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException 异常,这是因为 Gson 无法序列化 java.lang.Class 对象。这通常发生在尝试将一个不支持的类型直接传递给 Gson 的 toJson 方法时。
解决方法就是
import com.google.gson.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
class ClassCodec implements JsonSerializer<Class<?>>, JsonDeserializer<Class<?>> {
@Override
public Class<?> deserialize(JsonElement json, Type typeOfT, JsonDeserializationContext context) throws JsonParseException {
try {
String str = json.getAsString();
return Class.forName(str);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new JsonParseException(e);
}
}
@Override // String.class
public JsonElement serialize(Class<?> src, Type typeOfSrc, JsonSerializationContext context) {
// class -> json
return new JsonPrimitive(src.getName());
}
}
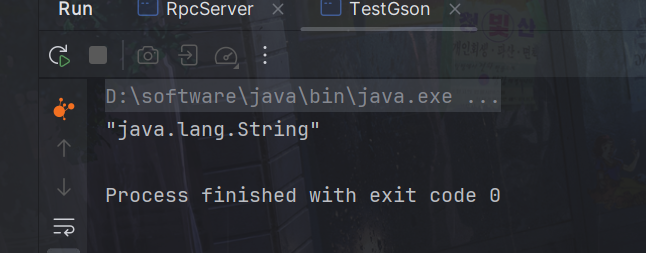
调用即可
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.GsonBuilder;
public class TestGson {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Gson gson = new GsonBuilder().registerTypeAdapter(Class.class, new ClassCodec()).create();
System.out.println(gson.toJson(String.class));
}
}成功
JSON序列化改造,当然如果没有报java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException异常可以不用更改。
// Json 实现(引入了 Gson 依赖)
Json {
@Override
public <T> T deserialize(Class<T> clazz, byte[] bytes) {
Gson gson = new GsonBuilder().registerTypeAdapter(Class.class, new ClassCodec()).create();
//字节数组转为字符串,
String json = new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
//再转为java对象
return gson.fromJson(json, clazz);
}
@Override
public <T> byte[] serialize(T object) {
Gson gson = new GsonBuilder().registerTypeAdapter(Class.class, new ClassCodec()).create();
//java对象转为JSON字符串
String json = gson.toJson(object);
//再转为字节数组,确保客户端和服务器编码一致
return json.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
}
};package com.dreams.client;
import com.dreams.client.handler.RpcResponseMessageHandler;
import com.dreams.message.RpcRequestMessage;
import com.dreams.protocol.MessageCodecSharable;
import com.dreams.protocol.ProcotolFrameDecoder;
import com.dreams.server.service.HelloService;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
import io.netty.util.concurrent.DefaultPromise;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.Random;
@Slf4j
public class RpcClientManager {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HelloService service = getProxyService(HelloService.class);
System.out.println(service.sayHello("梦想"));
}
// 创建代理类
public static <T> T getProxyService(Class<T> serviceClass) {
ClassLoader loader = serviceClass.getClassLoader();
Class<?>[] interfaces = new Class[]{serviceClass};
// sayHello "张三"
Object o = Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, interfaces, (proxy, method, args) -> {
// 创建Random对象
Random random = new Random();
// 1. 将方法调用转换为 消息对象
int sequenceId = random.nextInt(50) ;
RpcRequestMessage msg = new RpcRequestMessage(
sequenceId,
serviceClass.getName(),
method.getName(),
method.getReturnType(),
method.getParameterTypes(),
args
);
// 2. 将消息对象发送出去
getChannel().writeAndFlush(msg);
// 3. 准备一个空 Promise 对象,来接收结果 指定 promise 对象异步接收结果线程
DefaultPromise<Object> promise = new DefaultPromise<>(getChannel().eventLoop());
RpcResponseMessageHandler.PROMISES.put(sequenceId, promise);
// promise.addListener(future -> {
// // 线程
// });
// 4. 等待 promise 结果
promise.await();
if(promise.isSuccess()) {
// 调用正常
return promise.getNow();
} else {
// 调用失败
throw new RuntimeException(promise.cause());
}
});
return (T) o;
}
private static Channel channel = null;
private static final Object LOCK = new Object();
// 获取唯一的 channel 对象
public static Channel getChannel() {
if (channel != null) {
return channel;
}
synchronized (LOCK) { // t2
if (channel != null) { // t1
return channel;
}
initChannel();
return channel;
}
}
// 初始化 channel 方法
private static void initChannel() {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
LoggingHandler LOGGING_HANDLER = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
MessageCodecSharable MESSAGE_CODEC = new MessageCodecSharable();
RpcResponseMessageHandler RPC_HANDLER = new RpcResponseMessageHandler();
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(group);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProcotolFrameDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(LOGGING_HANDLER);
ch.pipeline().addLast(MESSAGE_CODEC);
ch.pipeline().addLast(RPC_HANDLER);
}
});
try {
channel = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 8080).sync().channel();
channel.closeFuture().addListener(future -> {
group.shutdownGracefully();
});
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("client error", e);
}
}
}DefaultPromise<Object> promise = new DefaultPromise<>(getChannel().eventLoop());:创建了一个DefaultPromise对象,用于接收RPC调用结果。这里的promise对象指定了异步接收结果的线程。
RpcResponseMessageHandler.PROMISES.put(sequenceId, promise);:将生成的序列号与promise对象关联,以便在接收到响应时能够找到对应的promise对象。
promise.await();:等待promise对象完成,即等待RPC调用结果返回。
if(promise.isSuccess()) { … }:如果RPC调用成功,则返回promise对象中的结果;否则抛出一个RuntimeException。
处理服务器响应消息的 RpcResponseMessageHandler 类
package com.dreams.client.handler;
import com.dreams.message.RpcResponseMessage;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.util.concurrent.Promise;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
@Slf4j
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class RpcResponseMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcResponseMessage> {
// 序号 用来接收结果的 promise 对象
public static final Map<Integer, Promise<Object>> PROMISES = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
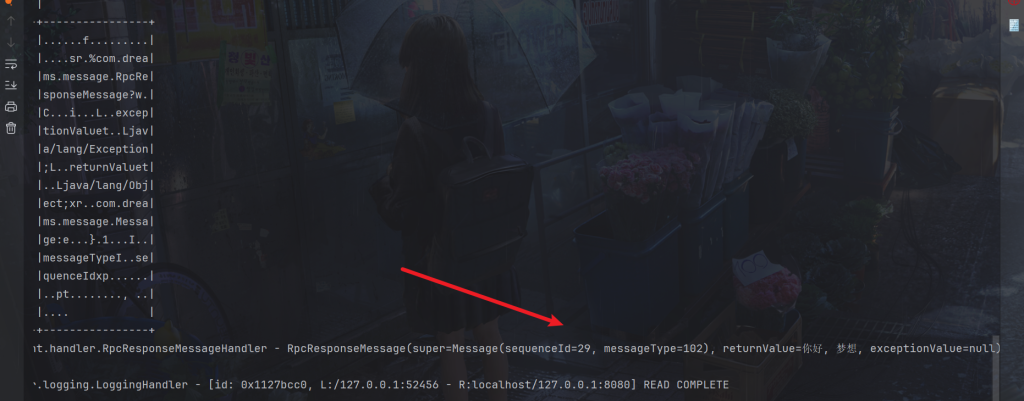
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcResponseMessage msg) throws Exception {
log.debug("{}", msg);
// 拿到空的 promise
Promise<Object> promise = PROMISES.remove(msg.getSequenceId());
if (promise != null) {
Object returnValue = msg.getReturnValue();
Exception exceptionValue = msg.getExceptionValue();
if(exceptionValue != null) {
promise.setFailure(exceptionValue);
} else {
promise.setSuccess(returnValue);
}
}
}
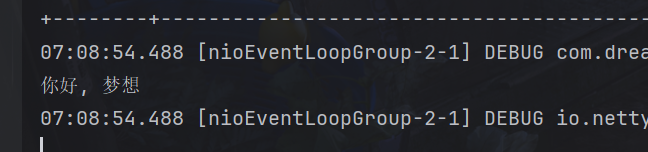
}
4.常用参数
CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS是Netty中用于设置连接超时的参数,表示连接超时的毫秒数。
用在客户端建立连接时,如果在指定毫秒内无法连接,会抛出 timeout 异常
比如通过option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 5000)来设置连接超时时间为5秒。
服务端使用
new ServerBootstrap().option() // 是给 ServerSocketChannel 配置参数 new ServerBootstrap().childOption() // 给 5ocketChannel 配置参数
客户端使用举例
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j
public class TestConnectionTimeout {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap()
.group(group)
.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 300)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new LoggingHandler());
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 8080);
future.sync().channel().closeFuture().sync(); // 断点1
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.debug("timeout");
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}不启动服务器,自然会连接超时
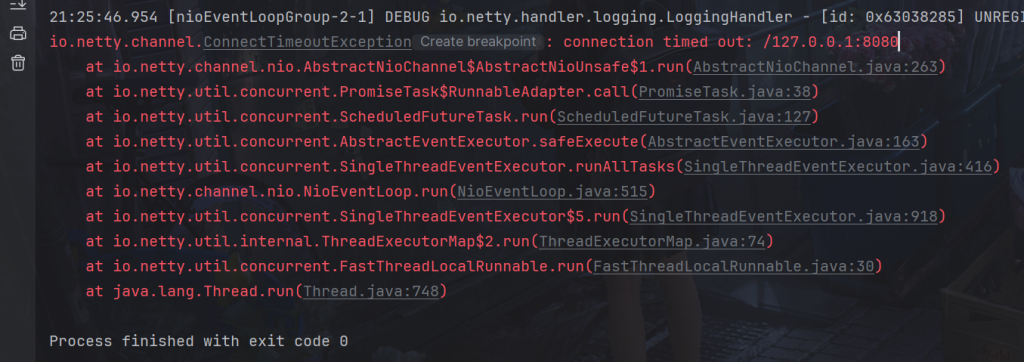
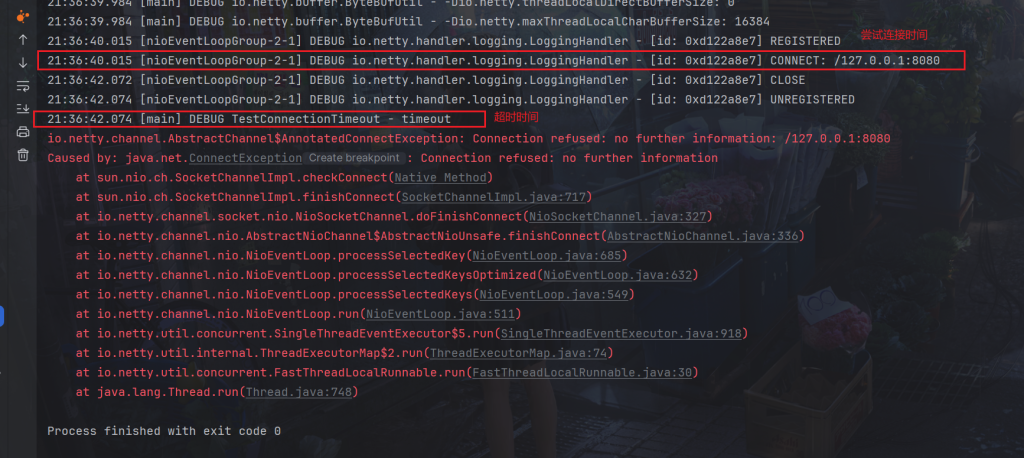
当然如果不启动服务器,而CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS时间又比较长,Netty会自动检测出来,而没必要等待CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS时间到达
比如5秒
.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 5000)
实际2秒就检测出来了
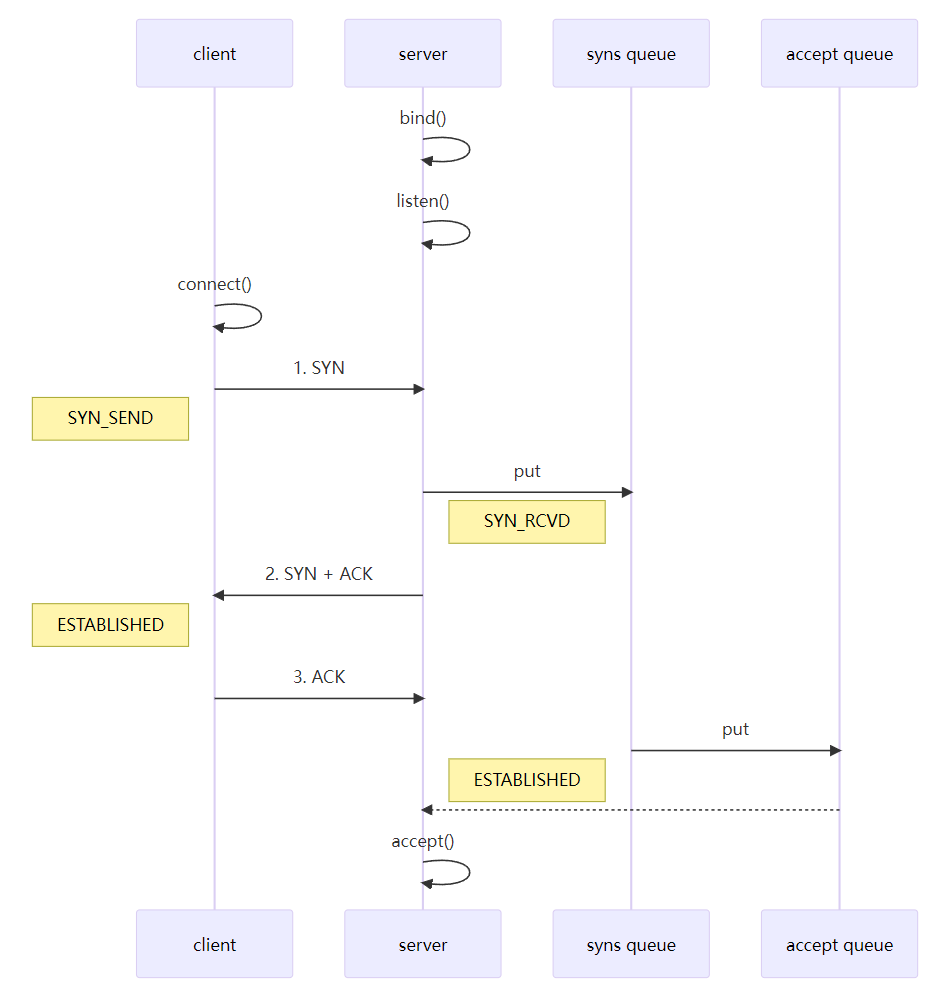
第二次握手,server 回复 SYN + ACK 给 client,client 收到,状态改变为 ESTABLISHED,并发送 ACK 给 server
sync queue – 半连接队列
大小通过 /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_max_syn_backlog 指定,在syncookies 启用的情况下,逻辑上没有最大值限制,这个设置便被忽略
accept queue – 全连接队列
其大小通过 /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn 指定,在使用 listen 函数时,内核会根据传入的 backlog 参数与系统参数,取二者的较小值,比如nio的bind(8080,backlog)也设置了,就取二者的较小值。
SO_BACKLOG就是用于配置ServerSocketChannel的选项之一。它表示ServerSocket的接受队列的最大长度。
当一个客户端尝试连接到服务器时,服务器会将该连接放入一个未完成连接的队列中,直到服务器接受该连接或者超过了队列的最大长度。SO_BACKLOG参数就是用来设置这个队列的最大长度。
同样在.option配置
package com.dreams.netty;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
public class TestBacklogServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ServerBootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 2)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler());
}
}).bind(8080);
}
}
ulimit -n
属于操作系统参数
ulimit -n 是用于设置或显示当前用户进程打开文件描述符(File Descriptor)数量的命令。在Linux系统中,每个进程都有一个限制,用于控制它可以同时打开的文件数量。文件描述符是操作系统为了访问文件而分配的一个整数。除了文件之外,套接字、管道等资源也会消耗文件描述符。
- 如果使用 ulimit -n 命令而不带参数,则会显示当前用户进程的文件描述符限制数量。
- 如果使用 ulimit -n <number> 命令,可以将当前用户进程的文件描述符限制数量设置为 <number>。需要注意的是,这个设置只会对当前的 shell 会话有效,当关闭该会话后,设置会被重置为默认值。
可以通过编辑 /etc/security/limits.conf 文件来永久性地设置文件描述符的限制,以便在系统重新启动后依然有效。
TCP_NODELAY
属于 SocketChannal 参数,
TCP_NODELAY是一个TCP套接字选项,用于禁用Nagle算法。
Nagle算法是一种用于减少小分组传输的方法。它通过将小的数据块组合成更大的数据块,从而减少网络传输中的数据包数量。尤其是对于延迟敏感的应用程序,Nagle算法可以显著提高性能。
然而,在某些情况下,Nagle算法可能导致延迟增加,尤其是对于需要实时数据传输的应用程序,比如在线游戏或实时通信应用程序。在这种情况下,禁用Nagle算法可以提高传输的实时性和响应性。
TCP_NODELAY选项用于控制是否启用Nagle算法。当设置TCP_NODELAY选项为true时,表示禁用Nagle算法;当设置为false时,表示启用Nagle算法。
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true) // 设置TCP_NODELAY选项为true,禁用Nagle算法
.childHandler(new MyServerInitializer());
SO_SNDBUF
SO_SNDBUF 属于 SocketChannal 参数
在网络编程中,SO_SNDBUF是一个Socket选项,用于设置发送缓冲区的大小。发送缓冲区是用于存储待发送数据的内存区域,发送端将数据放入缓冲区中,然后由操作系统负责将缓冲区中的数据发送到网络上。
SO_SNDBUF选项允许开发者设置发送缓冲区的大小,从而影响数据发送的性能和效率。增大发送缓冲区的大小可以提高发送数据的吞吐量,尤其是在高带宽、高延迟的网络环境下。但是需要注意的是,设置过大的发送缓冲区可能会占用过多的系统内存资源,并可能导致内存压力增大。
在Java中,可以使用Socket类或ServerSocket类的setSendBufferSize()方法来设置发送缓冲区的大小。
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", 8080);
socket.setSendBufferSize(1024 * 1024); // 设置发送缓冲区大小为1MB在Netty中,可以使用ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF选项来设置发送缓冲区的大小。
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, 1024 * 1024) // 设置发送缓冲区大小为1MB
.childHandler(new MyServerInitializer());
SO_RCVBUF
SO_RCVBUF 既可用于 SocketChannal 参数,也可以用于 ServerSocketChannal 参数(建议设置到 ServerSocketChannal 上)
SO_RCVBUF用于设置接收缓冲区的大小。接收缓冲区是用于存储接收到的数据的内存区域,接收端将数据从网络中读取并放入接收缓冲区中,然后应用程序可以从缓冲区中读取数据进行处理。
SO_RCVBUF选项允许开发者设置接收缓冲区的大小,从而影响数据接收的性能和效率。增大接收缓冲区的大小可以提高接收数据的吞吐量,尤其是在高带宽、高延迟的网络环境下。但是需要注意的是,设置过大的接收缓冲区可能会占用过多的系统内存资源,并可能导致内存压力增大。
在Java中,可以使用Socket类或ServerSocket类的setReceiveBufferSize()方法来设置接收缓冲区的大小。
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", 8080);
socket.setSendBufferSize(1024 * 1024); // 设置发送缓冲区大小为1MB在Netty中,可以使用ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF选项来设置发送缓冲区的大小。
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, 1024 * 1024) // 设置发送缓冲区大小为1MB
.childHandler(new MyServerInitializer());
属于 SocketChannal 参数
用来分配 ByteBuf, ctx.alloc()
ALLOCATOR是用于分配ByteBuf对象的工厂,通常通过ctx.alloc()方法获取。ALLOCATOR决定了出站数据的分配方式,即发送数据时所使用的内存分配方式。
Netty的ByteBuf分配器默认采用基于池化的方式,以减少内存的频繁分配和释放。这种方式能够提高性能并降低内存碎片化的风险。ALLOCATOR还可以通过ChannelConfig的allocator方法进行配置,以适应不同的内存管理需求。
基本使用方式:
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = ctx.alloc().buffer();
log.debug("alloc buf {}", buf);
}
});
RCVBUF_ALLOCATOR
属于 SocketChannal 参数
控制 netty 接收缓冲区大小
RCVBUF_ALLOCATOR是用于控制Netty接收缓冲区大小的参数。它负责入站数据的分配,并决定了入站缓冲区的大小。同时,它还能根据网络流量的情况动态调整缓冲区的大小。
对于RCVBUF_ALLOCATOR,Netty采用了默认的DirectChannelConfig实现,该实现使用了直接内存(direct memory)来进行数据接收和处理。具体的缓冲区是否采用池化方式,以及具体的分配策略,则是由ALLOCATOR参数决定的。
如果想要定制RCVBUF_ALLOCATOR,可以通过以下步骤:
- 获取ChannelPipeline对象:
在Netty中,可以通过ChannelHandlerContext获取到ChannelPipeline对象。 - 获取ChannelConfig对象:
通过ChannelPipeline对象的channel().config()方法获取到ChannelConfig对象。 - 设置RCVBUF_ALLOCATOR:
通过ChannelConfig对象的setRecvByteBufAllocator()方法设置RCVBUF_ALLOCATOR。可以使用Netty提供的预定义的分配器,如FixedRecvByteBufAllocator、AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator等,也可以自定义实现。
代码演示:
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ctx.pipeline(); ChannelConfig config = pipeline.channel().config(); config.setRecvByteBufAllocator(new FixedRecvByteBufAllocator(1024)); // 使用固定大小的接收缓冲区分配器