1.基本概念
图是一种非常灵活的数据结构,由节点(顶点)和连接这些节点的边组成。图可以是有向的或无向的。有向图中的边有方向,而无向图中的边没有方向。
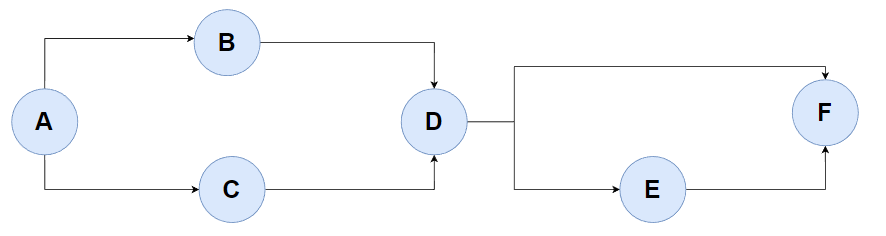
度是指与该顶点相邻的边的数量
在有向图中:
- 入度:指向某节点的边的数量。换句话说,入度表示有多少条边指向该节点。
- 出度:从某节点出发的边的数量。出度表示该节点指向其他节点的边的数量。
在带权图中,每条边都有一个与之关联的权值,这个权值可以表示距离、成本、时间等。
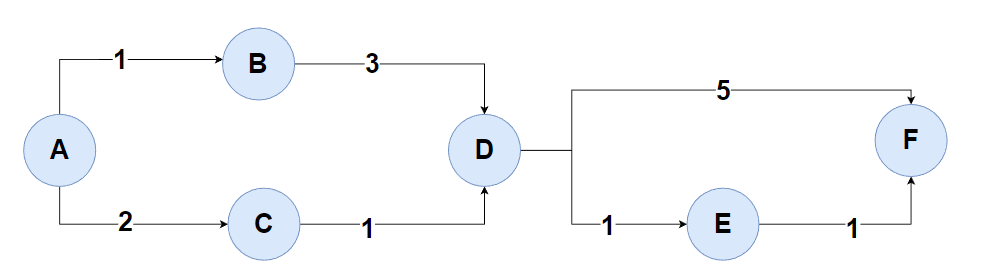
环:在有向图中,从一个顶点开始,可以通过若干条有向边返回到该顶点,那么就形成了一个环。
图的连通性:如果两个顶点之间存在路径,则这两个顶点是连通的,所有顶点都连通,则该图被称之为连通图,若子图连通,则称为连通分量。
2.遍历算法
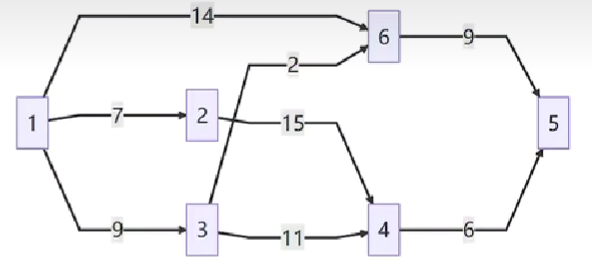
顶点类
package com.dreams.graph;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 顶点
*/
public class Vertex {
String name;
public List<Edge> edges;
public Vertex(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}边类
package com.dreams.graph;
/**
* 边
*/
public class Edge {
public Vertex linked;
public int weight;
public Edge(Vertex linked) {
this(linked, 1);
}
public Edge(Vertex linked, int weight) {
this.linked = linked;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
DFS
深度优先搜索(Depth-First Search),是一种用于遍历或搜索图形或树数据结构的算法。它从一个起始节点开始,尽可能深入地向下移动,直到无法进一步移动,然后回溯到前一个节点,继续探索其他路径。
在顶点类添加一个属性,表示该顶点是否被访问过
package com.dreams.graph;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 顶点
*/
public class Vertex {
String name;
public List<Edge> edges;
// 是否被访问过,用在 BFS 和 DFS
boolean visited;
public Vertex(boolean visited) {
this.visited = visited;
}
public Vertex(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}代码
package com.dreams.graph;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
/**
* 深度优先搜索 Depth-first search
*/
public class DFS {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vertex v1 = new Vertex("v1");
Vertex v2 = new Vertex("v2");
Vertex v3 = new Vertex("v3");
Vertex v4 = new Vertex("v4");
Vertex v5 = new Vertex("v5");
Vertex v6 = new Vertex("v6");
v1.edges = Arrays.asList(
new Edge(v3, 9),
new Edge(v2, 7),
new Edge(v6, 14)
);
v2.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v4,15));
v3.edges = Arrays.asList(
new Edge(v4, 11),
new Edge(v6, 2)
);
v4.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v5, 6));
v5.edges = Arrays.asList();
v6.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v5, 9));
dfs(v1);
}
private static void dfs(Vertex v) {
v.visited = true;
System.out.println(v.name);
for (Edge edge : v.edges) {
if (!edge.linked.visited) {
dfs(edge.linked);
}
}
}
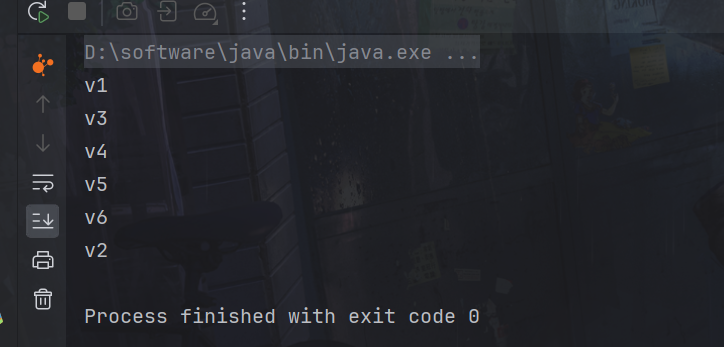
}
非递归实现
private static void dfs(Vertex v) {
LinkedList<Vertex> stack = new LinkedList<>();
stack.push(v);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Vertex pop = stack.pop();
pop.visited = true;
System.out.println(pop.name);
for (Edge edge : pop.edges) {
if (!edge.linked.visited) {
stack.push(edge.linked);
}
}
}
}
BFS
BFS,即广度优先搜索。
package com.dreams.graph;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 广度优先搜索 Breadth-first search
*/
public class BFS {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vertex v1 = new Vertex("v1");
Vertex v2 = new Vertex("v2");
Vertex v3 = new Vertex("v3");
Vertex v4 = new Vertex("v4");
Vertex v5 = new Vertex("v5");
Vertex v6 = new Vertex("v6");
v1.edges = Arrays.asList(
new Edge(v3, 9),
new Edge(v2, 7),
new Edge(v6, 14)
);
v2.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v4, 15));
v3.edges = Arrays.asList(
new Edge(v4, 11),
new Edge(v6, 2)
);
v4.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v5, 6));
v5.edges = Arrays.asList();
v6.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v5, 9));
bfs(v1);
}
private static void bfs(Vertex v) {
LinkedList<Vertex> queue = new LinkedList<>();
v.visited = true;
queue.offer(v);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Vertex poll = queue.poll();
System.out.println(poll.name);
for (Edge edge : poll.edges) {
if (!edge.linked.visited) {
edge.linked.visited = true;
queue.offer(edge.linked);
}
}
}
}
}
3.拓扑排序
拓扑排序是一种用于有向无环图(DAG)的排序算法,它将图中的顶点按照依赖关系进行排序,确保任何一个顶点都在其依赖的顶点之后。
步骤:
- 计算入度:遍历图中的每个顶点,统计每个顶点的入度。
- 选择入度为0的顶点:从入度为0的顶点中选择一个顶点,将其加入拓扑排序结果列表,并将其所有邻接顶点的入度减一。
- 更新入度:重复步骤3,直到所有顶点都被加入到拓扑排序结果中。
顶点类添加属性inDegree,表示入度数量。
package com.dreams.graph;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 顶点
*/
public class Vertex {
String name;
public List<Edge> edges;
// 是否被访问过,用在 BFS 和 DFS
boolean visited;
// 入度,用在拓扑排序
int inDegree;
public Vertex(boolean visited) {
this.visited = visited;
}
public Vertex(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}代码:
package com.dreams.graph;
import java.util.*;
/**
* <h3>拓扑排序 Kahn's algorithm</h3>
*/
public class TopologicalSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vertex v1 = new Vertex("网页基础");
Vertex v2 = new Vertex("Java基础");
Vertex v3 = new Vertex("JavaWeb");
Vertex v4 = new Vertex("Spring框架");
Vertex v5 = new Vertex("微服务框架");
Vertex v6 = new Vertex("数据库");
Vertex v7 = new Vertex("实战项目");
v1.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v3)); // +1
v2.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v3)); // +1
v3.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v4));
v6.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v4));
v4.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v5));
v5.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v7));
v7.edges = Arrays.asList();
List<Vertex> graph = Arrays.asList(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7);
// 1. 统计每个顶点的入度
for (Vertex v : graph) {
for (Edge edge : v.edges) {
edge.linked.inDegree++;
}
}
/*for (Vertex vertex : graph) {
System.out.println(vertex.name + " " + vertex.inDegree);
}*/
// 2. 将入度为0的顶点加入队列
LinkedList<Vertex> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (Vertex v : graph) {
if (v.inDegree == 0) {
queue.offer(v);
}
}
// 3. 队列中不断移除顶点,每移除一个顶点,把它相邻顶点入度减1,若减到0则入队
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Vertex poll = queue.poll();
// System.out.println(poll.name);
result.add(poll.name);
for (Edge edge : poll.edges) {
edge.linked.inDegree--;
if (edge.linked.inDegree == 0) {
queue.offer(edge.linked);
}
}
}
if (result.size() != graph.size()) {
System.out.println("出现环");
} else {
for (String key : result) {
System.out.println(key);
}
}
}
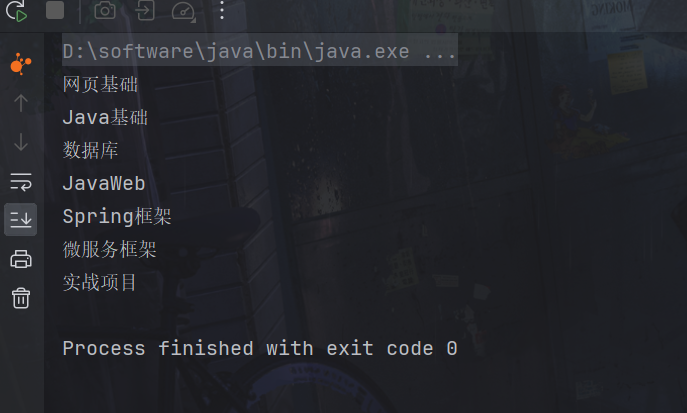
}
使用DFS方法,顶点类添加一个属性status,借用栈实现
package com.dreams.graph;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 顶点
*/
public class Vertex {
String name;
public List<Edge> edges;
// 是否被访问过,用在 BFS 和 DFS
boolean visited;
// 入度,用在拓扑排序
int inDegree;
// 状态 0-未访问 1-访问中 2-访问过,用在拓扑排序
int status;
public Vertex(boolean visited) {
this.visited = visited;
}
public Vertex(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}代码:
package com.dreams.graph;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 拓扑排序 DFS
*/
public class TopologicalSortDFS {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vertex v1 = new Vertex("网页基础");
Vertex v2 = new Vertex("Java基础");
Vertex v3 = new Vertex("JavaWeb");
Vertex v4 = new Vertex("Spring框架");
Vertex v5 = new Vertex("微服务框架");
Vertex v6 = new Vertex("数据库");
Vertex v7 = new Vertex("实战项目");
v1.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v3));
v2.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v3));
v3.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v4));
v6.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v4));
v4.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v5));
v5.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v7));
v7.edges = Arrays.asList();
List<Vertex> graph = Arrays.asList(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7);
LinkedList<String> stack = new LinkedList<>();
for (Vertex v : graph) {
dfs(v, stack);
}
System.out.println(stack);
}
private static void dfs(Vertex v, LinkedList<String> stack) {
if (v.status == 2) {
return;
}
if (v.status == 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("发现了环");
}
v.status = 1;
for (Edge edge : v.edges) {
dfs(edge.linked, stack);
}
v.status = 2;
stack.push(v.name);
}
}
4.迪克斯特拉算法
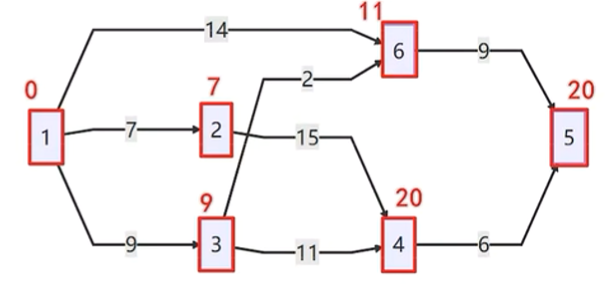
迪克斯特拉(Dijkstra)算法是一种用于解决单源最短路径问题的经典算法。
顶点类同样需要添加距离属性,默认无穷大
package com.dreams.graph;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* 顶点
*/
public class Vertex {
String name;
public List<Edge> edges;
boolean visited; // 是否被访问过,用在 BFS 和 DFS
int inDegree; // 入度,用在拓扑排序
int status; // 状态 0-未访问 1-访问中 2-访问过,用在拓扑排序
int dist = INF; // 距离
static final Integer INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
Vertex prev = null; // 记录从何而来
public Vertex(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
String n = name;
if (visited) {
n = "\u001B[31m" + name + "\u001B[0m";
}
return n + '(' + (dist == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "∞" : String.valueOf(dist)) + ") <- " + (prev == null ? "null" : prev.name);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Vertex vertex = (Vertex) o;
return Objects.equals(name, vertex.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0;
}
}
步骤:
- 1.将所有顶点标记为未访问。创建一个未访问顶点的集合。
- 2.为每个顶点分配一个临时距离值。对于我们的初始顶点,将其设置为零。对于所有其他顶点,将其设置为无穷大。
- 3.每次选择最小临时距离的未访问顶点,作为新的当前顶点
- 4.对于当前顶点,遍历其所有未访问的邻居,并更新它们的临时距离为更小。例如, 1->6 的距离是 14,而1->3->6的距离是11,这时将距离更新为11。否则,将保留上次距离值
- 5.当前顶点的邻居处理完成后,把它从未访问集合中删除
代码:
package com.dreams.graph;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/**
* <h3>迪克斯特拉 单源最短路径算法</h3>
*/
public class Dijkstra {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vertex v1 = new Vertex("v1");
Vertex v2 = new Vertex("v2");
Vertex v3 = new Vertex("v3");
Vertex v4 = new Vertex("v4");
Vertex v5 = new Vertex("v5");
Vertex v6 = new Vertex("v6");
v1.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v3, 9), new Edge(v2, 7), new Edge(v6, 14));
v2.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v4, 15));
v3.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v4, 11), new Edge(v6, 2));
v4.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v5, 6));
v5.edges = Arrays.asList();
v6.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v5, 9));
List<Vertex> graph = Arrays.asList(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6);
// Vertex v1 = new Vertex("v1");
// Vertex v2 = new Vertex("v2");
// Vertex v3 = new Vertex("v3");
// Vertex v4 = new Vertex("v4");
//
// v1.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v2, 2), new Edge(v3, 1));
// v2.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v3, -2));
// v3.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v4, 1));
// v4.edges = Arrays.asList();
//
// List<Vertex> graph = Arrays.asList(v1, v2, v3, v4);
dijkstra(graph, v1);
}
private static void dijkstra(List<Vertex> graph, Vertex source) {
ArrayList<Vertex> list = new ArrayList<>(graph);
source.dist = 0;
while (!list.isEmpty()) {
// 3. 选取当前顶点
Vertex curr = chooseMinDistVertex(list);
// 4. 更新当前顶点邻居距离
updateNeighboursDist(curr);
// 5. 移除当前顶点
list.remove(curr);
curr.visited = true;
}
for (Vertex v : graph) {
System.out.println(v);
}
}
private static void updateNeighboursDist(Vertex curr) {
for (Edge edge : curr.edges) {
Vertex n = edge.linked;
if (!n.visited) {
int dist = curr.dist + edge.weight;
if (dist < n.dist) {
n.dist = dist;
n.prev = curr;
}
}
}
}
private static Vertex chooseMinDistVertex(ArrayList<Vertex> list) {
Vertex min = list.get(0);
for (int i = 1; i < list.size(); i++) {
if (list.get(i).dist < min.dist) {
min = list.get(i);
}
}
return min;
}
}
使用优先级队列(小顶堆)优化:
注意更新距离时,直接将距离重新加入优先级队列,虽然队列存在相同顶点,但是依然可以选取距离最小值。
package com.dreams.graph;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
/**
* <h3>迪克斯特拉 单源最短路径算法</h3>
*/
public class DijkstraPriorityQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vertex v1 = new Vertex("v1");
Vertex v2 = new Vertex("v2");
Vertex v3 = new Vertex("v3");
Vertex v4 = new Vertex("v4");
Vertex v5 = new Vertex("v5");
Vertex v6 = new Vertex("v6");
v1.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v3, 9), new Edge(v2, 7), new Edge(v6, 14));
v2.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v4, 15));
v3.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v4, 11), new Edge(v6, 2));
v4.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v5, 6));
v5.edges = Arrays.asList();
v6.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v5, 9));
List<Vertex> graph = Arrays.asList(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6);
dijkstra(graph, v1);
}
private static void dijkstra(List<Vertex> graph, Vertex source) {
PriorityQueue<Vertex> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(v -> v.dist));
source.dist = 0;
for (Vertex v : graph) {
queue.offer(v);
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// System.out.println(queue);
// 3. 选取当前顶点
Vertex curr = queue.peek();
// 4. 更新当前顶点邻居距离
if(!curr.visited) {
updateNeighboursDist(curr, queue);
curr.visited = true;
}
// 5. 移除当前顶点
queue.poll();
}
for (Vertex v : graph) {
System.out.println(v);
}
}
private static void updateNeighboursDist(Vertex curr, PriorityQueue<Vertex> queue) {
for (Edge edge : curr.edges) {
Vertex n = edge.linked;
if (!n.visited) {
int dist = curr.dist + edge.weight;
if (dist < n.dist) {
n.dist = dist;
n.prev = curr;
queue.offer(n);
}
}
}
}
}
5.Bellman-Ford算法
贝尔曼-福特(Bellman-Ford)算法是一种用于解决单源最短路径问题的经典算法,它适用于含有负权边但不含负权环的图。
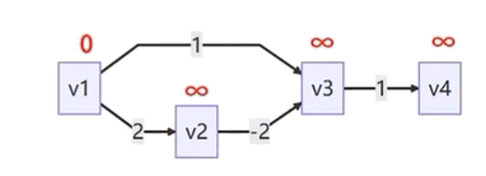
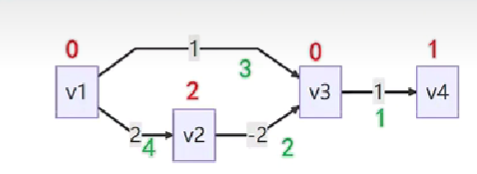
步骤:
初始化:
- 创建一个距离数组 dist[],用于记录源顶点到各个顶点的最短路径长度,初始化为无穷大(表示暂时未知最短路径)。
- 将源顶点的距离值设为0。
迭代更新:
- 进行 |V| – 1 次迭代,其中 |V| 是图中顶点的数量。
- 在每次迭代中,对图中的每条边 (u, v) 进行松弛操作,即尝试通过顶点 u 更新顶点 v 的最短路径长度,如果发现更短的路径,则更新 dist[v]。
检测负权环:
- 进行第 |V| 次迭代,检查是否存在负权环(环内权重相加等于负数)。
- 如果在这一轮迭代中仍然发生了距离的更新,则说明存在负权环。
最终结果:
如果不存在负权环,则 dist[] 数组中存储的就是源顶点到各个顶点的最短路径长度。
代码
package com.dreams.graph;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Bellman-Ford 算法,可以处理负边
*/
public class BellmanFord {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 正常情况
Vertex v1 = new Vertex("v1");
Vertex v2 = new Vertex("v2");
Vertex v3 = new Vertex("v3");
Vertex v4 = new Vertex("v4");
Vertex v5 = new Vertex("v5");
Vertex v6 = new Vertex("v6");
v1.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v3, 9), new Edge(v2, 7), new Edge(v6, 14));
v2.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v4, 15));
v3.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v4, 11), new Edge(v6, 2));
v4.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v5, 6));
v5.edges = Arrays.asList();
v6.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v5, 9));
List<Vertex> graph = Arrays.asList(v4, v5, v6, v1, v2, v3);
// 负边情况
/*Vertex v1 = new Vertex("v1");
Vertex v2 = new Vertex("v2");
Vertex v3 = new Vertex("v3");
Vertex v4 = new Vertex("v4");
v1.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v2, 2), new Edge(v3, 1));
v2.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v3, -2));
v3.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v4, 1));
v4.edges = Arrays.asList();
List<Vertex> graph = Arrays.asList(v1, v2, v3, v4);*/
// 负环情况
/* Vertex v1 = new Vertex("v1");
Vertex v2 = new Vertex("v2");
Vertex v3 = new Vertex("v3");
Vertex v4 = new Vertex("v4");
v1.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v2, 2));
v2.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v3, -4));
v3.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v4, 1), new Edge(v1, 1));
v4.edges = Arrays.asList();
List<Vertex> graph = Arrays.asList(v1, v2, v3, v4);*/
bellmanFord(graph, v1);
}
private static void bellmanFord(List<Vertex> graph, Vertex source) {
source.dist = 0;
int size = graph.size();
// 1. 进行 顶点个数 - 1 轮处理
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
// 2. 遍历所有的边
for (Vertex s : graph) {
for (Edge edge : s.edges) {
// 3. 处理每一条边
Vertex e = edge.linked;
if (s.dist != Integer.MAX_VALUE && s.dist + edge.weight < e.dist) {
e.dist = s.dist + edge.weight;
e.prev = s;
}
}
}
}
for (Vertex v : graph) {
System.out.println(v);
}
}
}
6.Floyd -Warshall多源最短路径算法
Floyd-Warshall 算法是一种经典的多源最短路径算法,用于计算图中所有顶点之间的最短路径。它适用于有向图或无向图,可以处理带负权边但不能处理带负环的图。
主要步骤:
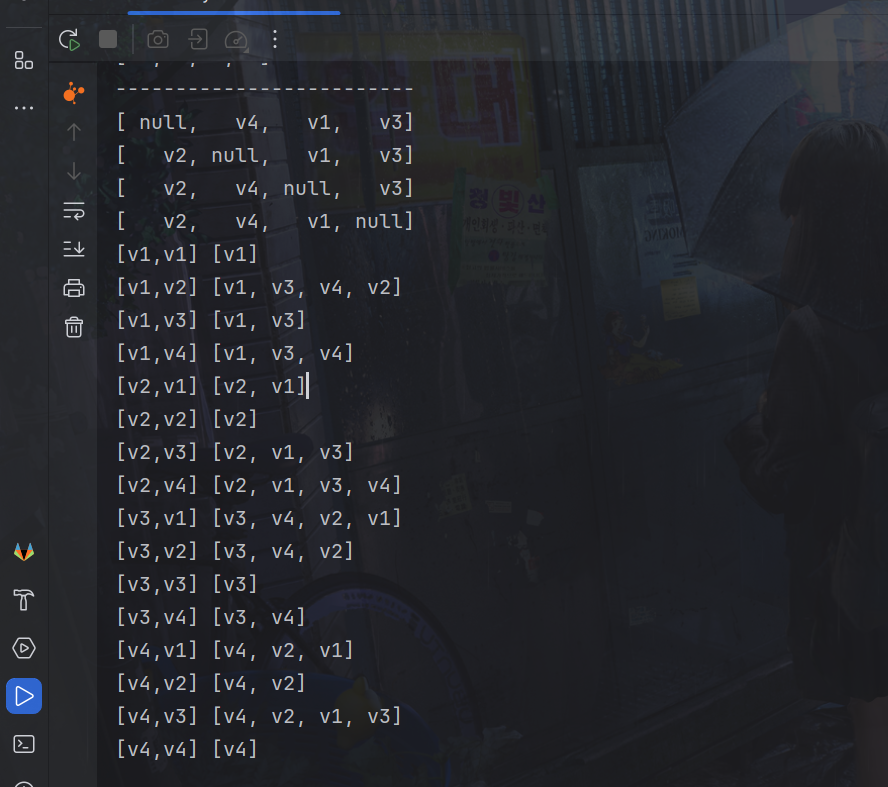
- 初始化距离矩阵: 创建一个 V × V 的矩阵 dist,其中 V 是图中顶点的数量。将 dist[i][j] 初始化为从顶点 i 到顶点 j 的直接距离,如果顶点之间没有直接连接,则将距离设置为一个足够大的值(比如正无穷)。
- 逐步更新距离矩阵: 对于每一对顶点 i 和 j,以及每一个顶点 k,尝试通过顶点 k 进行中转,检查是否存在一条路径比直接路径更短。如果存在更短的路径,则更新 dist[i][j] 为更短的路径长度。
- 输出最短路径结果: 最终得到的 dist 矩阵即为所有顶点对之间的最短路径长度。您可以根据需要将其输出或使用。
- 检查负环(可选): 如果图中存在负环,即从一个顶点出发,通过若干条边又回到该顶点,并且路径长度为负值,那么 Floyd-Warshall 算法将无法正确计算最短路径。可以通过检查 dist[i][i] 是否为负来判断是否存在负环。
代码:
package com.dreams.graph;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* Floyd - Warshall多源最短路径算法
*/
public class FloydWarshall {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 正常情况
Vertex v1 = new Vertex("v1");
Vertex v2 = new Vertex("v2");
Vertex v3 = new Vertex("v3");
Vertex v4 = new Vertex("v4");
v1.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v3, -2));
v2.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v1, 4), new Edge(v3, 3));
v3.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v4, 2));
v4.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v2, -1));
List<Vertex> graph = Arrays.asList(v1, v2, v3, v4);
// 负环情况
/*Vertex v1 = new Vertex("v1");
Vertex v2 = new Vertex("v2");
Vertex v3 = new Vertex("v3");
Vertex v4 = new Vertex("v4");
v1.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v2, 2));
v2.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v3, -4));
v3.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v4, 1), new Edge(v1, 1));
v4.edges = Arrays.asList();
List<Vertex> graph = Arrays.asList(v1, v2, v3, v4);*/
/*
直接连通
v1 v2 v3 v4
v1 0 ∞ -2 ∞
v2 4 0 3 ∞
v3 ∞ ∞ 0 2
v4 ∞ -1 ∞ 0
k=0 借助v1到达其它顶点
v1 v2 v3 v4
v1 0 ∞ -2 ∞
v2 4 0 2 ∞
v3 ∞ ∞ 0 2
v4 ∞ -1 ∞ 0
k=1 借助v2到达其它顶点
v1 v2 v3 v4
v1 0 ∞ -2 ∞
v2 4 0 2 ∞
v3 ∞ ∞ 0 2
v4 3 -1 1 0
k=2 借助v3到达其它顶点
v1 v2 v3 v4
v1 0 ∞ -2 0
v2 4 0 2 4
v3 ∞ ∞ 0 2
v4 3 -1 1 0
k=3 借助v4到达其它顶点
v1 v2 v3 v4
v1 0 -1 -2 0
v2 4 0 2 4
v3 5 1 0 2
v4 3 -1 1 0
*/
floydWarshall(graph);
}
static void floydWarshall(List<Vertex> graph) {
int size = graph.size();
int[][] dist = new int[size][size];
Vertex[][] prev = new Vertex[size][size];
// 1)初始化
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Vertex v = graph.get(i); // v1 (v3)
Map<Vertex, Integer> map = v.edges.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(e -> e.linked, e -> e.weight));
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) {
Vertex u = graph.get(j); // v3
if (v == u) {
dist[i][j] = 0;
} else {
dist[i][j] = map.getOrDefault(u, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
prev[i][j] = map.get(u) != null ? v : null;
}
}
}
print(prev);
// 2)看能否借路到达其它顶点
/*
v2->v1 v1->v?
dist[1][0] + dist[0][0]
dist[1][0] + dist[0][1]
dist[1][0] + dist[0][2]
dist[1][0] + dist[0][3]
*/
for (int k = 0; k < size; k++) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) {
// dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] // i行的顶点,借助k顶点,到达j列顶点
// dist[i][j] // i行顶点,直接到达j列顶点
if (dist[i][k] != Integer.MAX_VALUE &&
dist[k][j] != Integer.MAX_VALUE &&
dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] < dist[i][j]) {
dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j];
prev[i][j] = prev[k][j];
}
}
}
print(dist);
}
print(prev);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) {
path(prev, graph, i, j);
}
}
}
static void path(Vertex[][] prev, List<Vertex> graph, int i, int j) {
LinkedList<String> stack = new LinkedList<>();
System.out.print("[" + graph.get(i).name + "," + graph.get(j).name + "] ");
stack.push(graph.get(j).name);
while (i != j) {
Vertex p = prev[i][j];
stack.push(p.name);
j = graph.indexOf(p);
}
System.out.println(stack);
}
static void print(int[][] dist) {
System.out.println("-------------");
for (int[] row : dist) {
System.out.println(Arrays.stream(row).boxed()
.map(x -> x == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "∞" : String.valueOf(x))
.map(s -> String.format("%2s", s))
.collect(Collectors.joining(",", "[", "]")));
}
}
static void print(Vertex[][] prev) {
System.out.println("-------------------------");
for (Vertex[] row : prev) {
System.out.println(Arrays.stream(row).map(v -> v == null ? "null" : v.name)
.map(s -> String.format("%5s", s))
.collect(Collectors.joining(",", "[", "]")));
}
}
/*
v1 v2 v3 v4
v1 0 2 ∞ ∞
v2 ∞ 0 -4 ∞
v3 1 ∞ 0 1
v4 ∞ ∞ ∞ 0
k=0
v1 v2 v3 v4
v1 0 2 ∞ ∞
v2 ∞ 0 -4 ∞
v3 1 3 0 1
v4 ∞ ∞ ∞ 0
k=1
v1 v2 v3 v4
v1 0 2 -2 ∞
v2 ∞ 0 -4 ∞
v3 1 3 -1 1
v4 ∞ ∞ ∞ 0
*/
}
7.最小生成树- Prim 算法
Prim 算法是一种用于求解带权无向图的最小生成树的贪心算法。最小生成树是指一个无向图的生成树,其边的权值之和最小。
下面是 Prim 算法的基本步骤:
- 选择任意起始顶点作为生成树的根节点:从图中选择任意一个顶点作为起始顶点,并将其加入到最小生成树中。
- 将根节点相邻的边加入候选边集合:将根节点相邻的所有边加入到候选边集合中。
- 选择权值最小的边:从候选边集合中选择一条权值最小的边,并将其加入到最小生成树中。这条边连接的顶点被标记为已访问。
- 更新候选边集合:更新候选边集合,将所有与已访问顶点相连但未访问过的边加入到候选边集合中。
- 重复步骤 3 和步骤 4:重复执行步骤 3 和步骤 4,直到所有顶点都被访问过,或者直到最小生成树包含了图中的所有顶点。
- 输出最小生成树:最终得到的最小生成树即为算法的输出结果。
Prim 算法的时间复杂度取决于实现方式,通常情况下是 O(V^2) 或 O(ElogV),其中 V 是图中顶点的数量,E 是图中边的数量。
代码:
package com.dreams.graph;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 最小生成树 - Prim 算法
*/
public class Prim {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vertex v1 = new Vertex("v1");
Vertex v2 = new Vertex("v2");
Vertex v3 = new Vertex("v3");
Vertex v4 = new Vertex("v4");
Vertex v5 = new Vertex("v5");
Vertex v6 = new Vertex("v6");
Vertex v7 = new Vertex("v7");
v1.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v2, 2), new Edge(v3, 4), new Edge(v4, 1));
v2.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v1, 2), new Edge(v4, 3), new Edge(v5, 10));
v3.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v1, 4), new Edge(v4, 2), new Edge(v6, 5));
v4.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v1, 1), new Edge(v2, 3), new Edge(v3, 2),
new Edge(v5, 7), new Edge(v6, 8), new Edge(v7, 4));
v5.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v2, 10), new Edge(v4, 7), new Edge(v7, 6));
v6.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v3, 5), new Edge(v4, 8), new Edge(v7, 1));
v7.edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(v4, 4), new Edge(v5, 6), new Edge(v6, 1));
List<Vertex> graph = Arrays.asList(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7);
prim(graph, v1);
}
static void prim(List<Vertex> graph, Vertex source) {
ArrayList<Vertex> list = new ArrayList<>(graph);
source.dist = 0;
while (!list.isEmpty()) {
// 3. 选取当前顶点
Vertex curr = chooseMinDistVertex(list);
// 4. 更新当前顶点邻居距离
updateNeighboursDist(curr);
// 5. 移除当前顶点
list.remove(curr);
curr.visited = true;
}
for (Vertex v : graph) {
System.out.println(v);
}
}
private static void updateNeighboursDist(Vertex curr) {
for (Edge edge : curr.edges) {
Vertex n = edge.linked;
if (!n.visited) {
int dist = edge.weight;
if (dist < n.dist) {
n.dist = dist;
n.prev = curr;
}
}
}
}
private static Vertex chooseMinDistVertex(ArrayList<Vertex> list) {
Vertex min = list.get(0);
for (int i = 1; i < list.size(); i++) {
if (list.get(i).dist < min.dist) {
min = list.get(i);
}
}
return min;
}
}
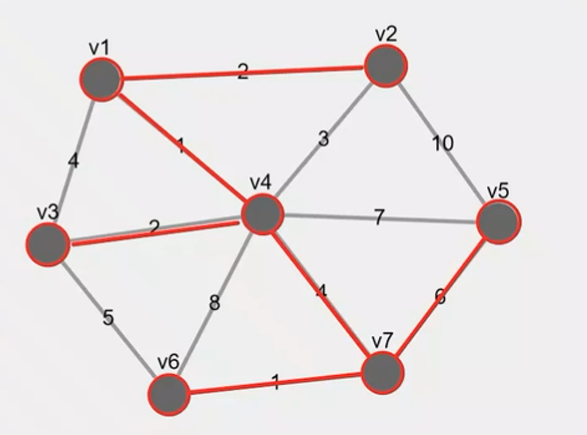
8.最小生成树-Kruskal算法
最小生成树-Kruskal(克鲁斯卡尔)算法
Kruskal 算法是一种用于求解带权无向图的最小生成树的贪心算法。与 Prim 算法不同的是,Kruskal 算法不需要选择起始顶点,而是通过按权重递增的顺序逐步选择边来构建最小生成树。
下面是 Kruskal 算法的基本步骤:
- 将图中的所有边按照权重从小到大进行排序:首先,将图中的所有边按照权重从小到大进行排序。
- 初始化一个空的最小生成树集合:开始时,最小生成树集合为空。
- 依次选择边并检查是否形成环路:从权重最小的边开始,依次选择边,并检查该边的两个顶点是否在最小生成树集合中已经连通。如果选择该边不会形成环路,则将其加入到最小生成树集合中。
- 重复步骤 3 直到最小生成树完成:重复执行步骤 3,直到最小生成树包含了图中的所有顶点,或者直到所有边都被考虑过。
- 输出最小生成树:最终得到的最小生成树即为算法的输出结果。
Kruskal 算法的时间复杂度通常为 O(ElogE),其中 E 是图中的边数。这是因为排序边的过程需要 O(ElogE) 的时间,而检查是否形成环路的过程通常可以通过并查集等数据结构在接近常量时间内完成。
代码:
package com.dreams.graph;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
/**
* 最小生成树 - Kruskal(克鲁斯卡尔) 算法
*/
public class Kruskal {
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
List<Vertex> vertices;
int start;
int end;
int weight;
public Edge(List<Vertex> vertices, int start, int end, int weight) {
this.vertices = vertices;
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
this.weight = weight;
}
public Edge(int start, int end, int weight) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge o) {
return Integer.compare(this.weight, o.weight);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return vertices.get(start).name + "<->" + vertices.get(end).name + "(" + weight + ")";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vertex v1 = new Vertex("v1");
Vertex v2 = new Vertex("v2");
Vertex v3 = new Vertex("v3");
Vertex v4 = new Vertex("v4");
Vertex v5 = new Vertex("v5");
Vertex v6 = new Vertex("v6");
Vertex v7 = new Vertex("v7");
List<Vertex> vertices = Arrays.asList(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7);
PriorityQueue<Edge> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(Arrays.asList(
new Edge(vertices, 0, 1, 2),
new Edge(vertices, 0, 2, 4),
new Edge(vertices, 0, 3, 1),
new Edge(vertices, 1, 3, 3),
new Edge(vertices, 1, 4, 10),
new Edge(vertices, 2, 3, 2),
new Edge(vertices, 2, 5, 5),
new Edge(vertices, 3, 4, 7),
new Edge(vertices, 3, 5, 8),
new Edge(vertices, 3, 6, 4),
new Edge(vertices, 4, 6, 6),
new Edge(vertices, 5, 6, 1)
));
kruskal(vertices.size(), queue);
}
static void kruskal(int size, PriorityQueue<Edge> queue) {
List<Edge> list = new ArrayList<>();
DisjointSet set = new DisjointSet(size);
while (list.size() < size - 1) {
Edge poll = queue.poll();
int i = set.find(poll.start);
int j = set.find(poll.end);
System.out.println(poll.start + "<->" +poll.end +set+ "["+i+" " +j+"]");
if (i != j) { // 未相交
list.add(poll);
set.union(i, j); // 相交
}
}
for (Edge edge : list) {
System.out.println(edge);
}
}
}上面使用的不相交集合。
package com.dreams.graph;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 不相交集合(并查集合)
*/
public class DisjointSet {
int[] s;
int[] size;
public DisjointSet(int size) {
s = new int[size];
this.size = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
s[i] = i;
this.size[i] = 1;
}
}
// find 是找到老大 - 优化:路径压缩
public int find(int x) { // x = 2
if (x == s[x]) {
return x;
}
return s[x] = find(s[x]); // 0 s[2]=0
}
// union 是让两个集合“相交”,即选出新老大,x、y 是原老大索引
public void union(int x, int y) {
if (size[x] < size[y]) {
int t = x;
x = y;
y = t;
}
s[y] = x;
size[x] = size[x] + size[y]; // 更新老大元素个数
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "内容:"+Arrays.toString(s) + "\n大小:" + Arrays.toString(size);
}
}
参考